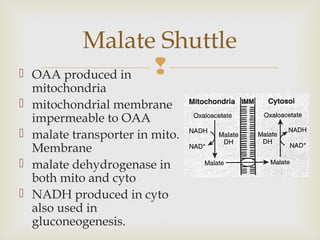
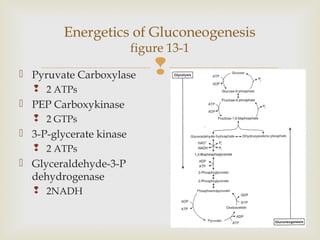
Gluconeogenesis is the de novo synthesis of glucose that occurs primarily in the liver and kidneys. It plays an important role in preventing hypoglycemia by producing glucose from non-carbohydrate precursors during periods of fasting. The process uses similar enzymes as glycolysis but in the reverse direction and requires energy in the form of ATP and GTP at certain steps. Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis are coordinately regulated by hormones and metabolites to prevent wasteful cycling between the two pathways.