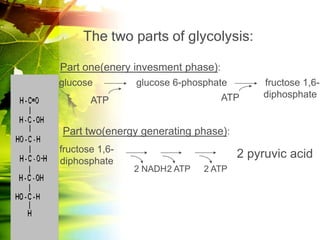
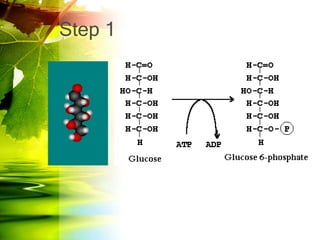
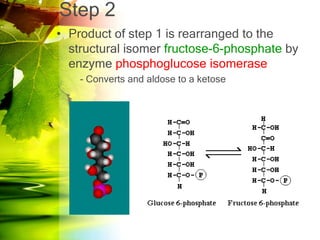
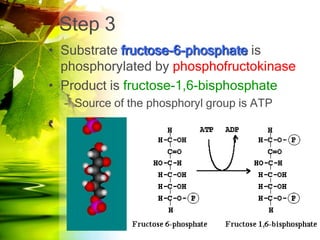
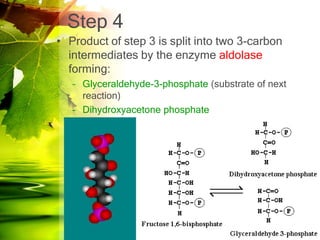
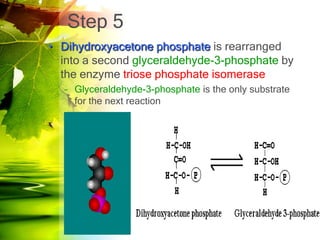
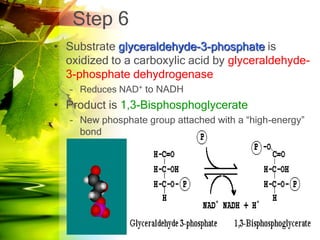
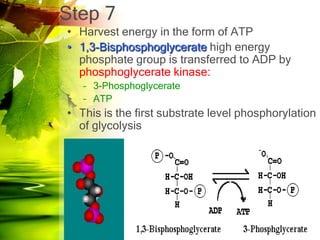
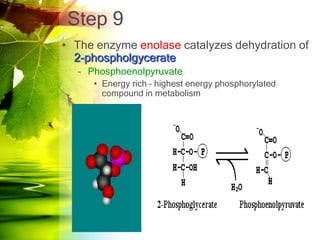
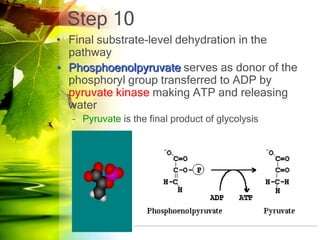
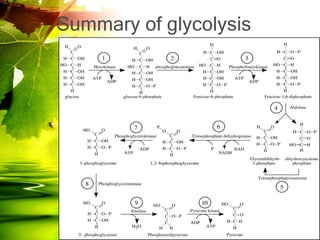
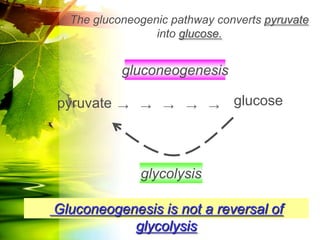
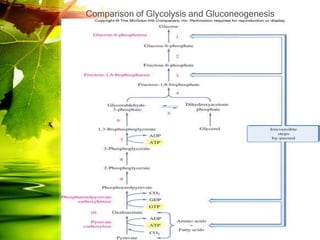
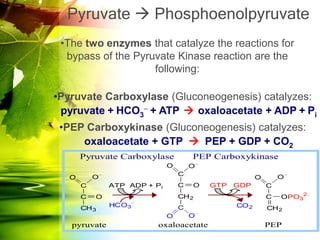
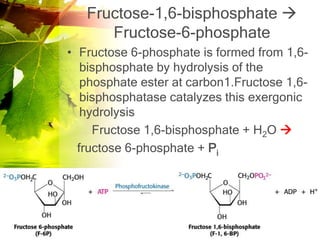
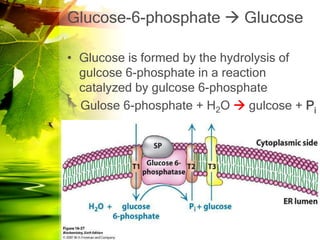
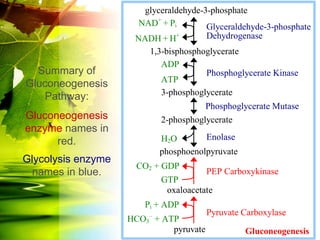
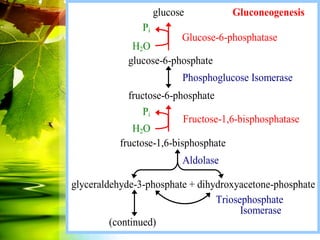
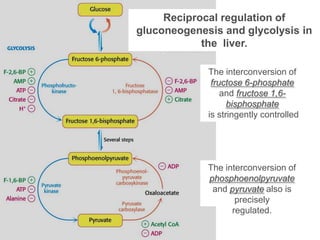
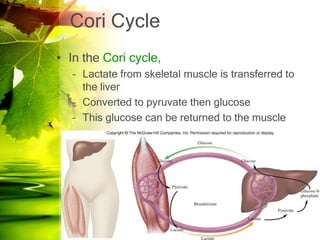
The document discusses glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, detailing the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate and the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate sources, respectively. It outlines the steps in glycolysis, including energy investment and generation phases, and highlights the regulatory mechanisms governing these metabolic pathways. Additionally, the document explains the Cori cycle, which involves the conversion of lactate from muscles to glucose in the liver.