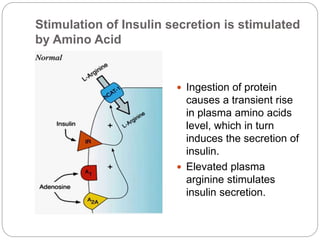
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by beta cells in the pancreas that regulates fuel metabolism. It has important anabolic effects, promoting the storage and synthesis of glycogen, triglycerides, and proteins. Insulin secretion is stimulated by increases in blood glucose, amino acids, and gastrointestinal hormones after eating. It works to promote glucose uptake and storage in liver, muscle and fat tissues, while inhibiting glucose production and release. Insulin also increases lipid synthesis and inhibits lipid breakdown to regulate lipid metabolism.