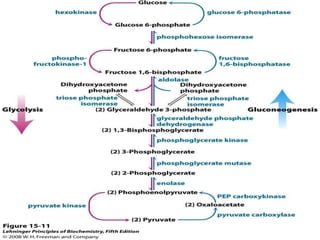
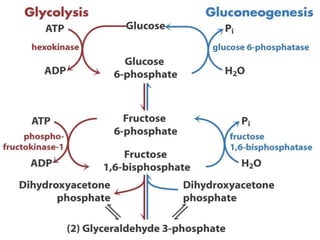
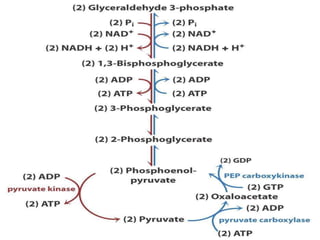
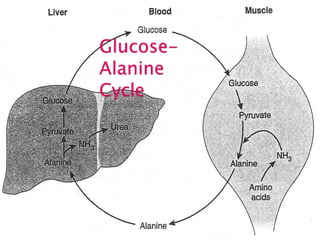
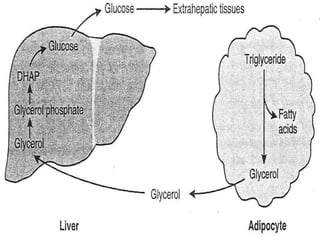
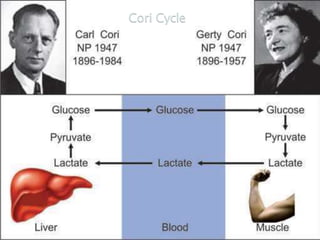
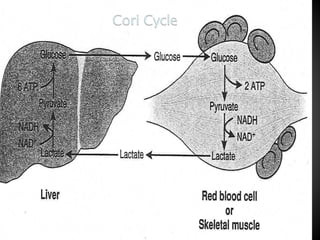
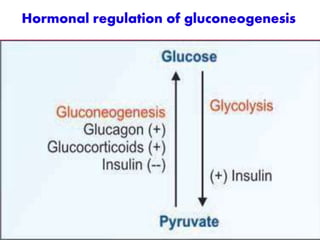
Gluconeogenesis is the process by which glucose is synthesized from non-carbohydrate precursors like lactate, pyruvate, glycerol, and glucogenic amino acids. It mainly occurs in the liver and kidney cytosol. The pathway closely resembles glycolysis but bypasses three irreversible steps through alternate enzymes. Regulation involves hormonal control and allosteric effectors that favor either gluconeogenesis or glycolysis.