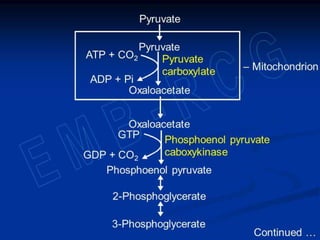
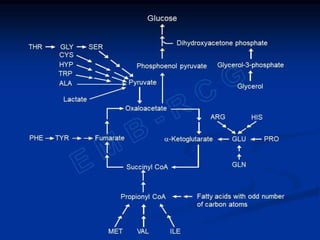
Gluconeogenesis is the synthesis of glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates like lactate, glycerol and certain amino acids. It occurs in the liver and kidneys when carbohydrate availability is low, such as during fasting or diabetes. While fatty acids can provide energy, glucose is still required by certain tissues and as a precursor for lactose production. Gluconeogenesis bypasses the irreversible steps of glycolysis using different enzymes and pathways that convert substrates like pyruvate and the Cori cycle transfers lactate from muscles to the liver for glucose synthesis. Gluconeogenesis is regulated both long-term through induction of enzymes by glucocorticoids and repression by insulin, and short-term through the