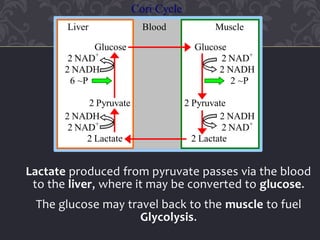
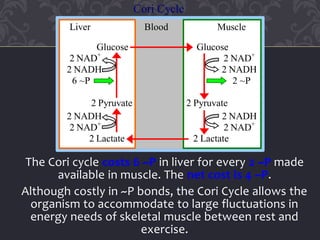
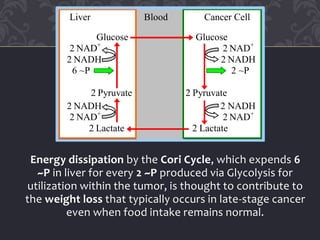
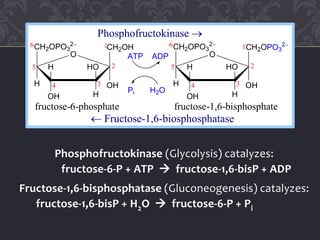
Gluconeogenesis and glycolysis share many of the same enzymes but operate in opposite directions. Three irreversible steps in glycolysis - those catalyzed by hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase - must be bypassed in gluconeogenesis. This is accomplished through different enzymes that catalyze reversible reactions, such as glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Regulation ensures that glycolysis and gluconeogenesis do not operate simultaneously, which would waste energy. Key control points include allosteric regulation by adenine nucleotides and hormonal stimulation of cAMP and protein phosphorylation.







![When gluconeogenesis is active in liver, oxaloacetate is
diverted to form glucose. Oxaloacetate depletion hinders
acetyl CoA entry into Krebs Cycle. The increase in [acetyl
CoA] activates Pyruvate Carboxylase to make oxaloacetate.
Pyruvate
Carboxylase
(pyruvate
oxaloactate)
is allosterically
activated by
acetyl CoA.
[Oxaloacetate]
tends to be
limiting for
Krebs cycle.
Glucose-6-phosphatase
glucose-6-P glucose
Gluconeogenesis Glycolysis
pyruvate
fatty acids
acetyl CoA ketone bodies
oxaloacetate citrate
Krebs Cycle](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-200421155217/85/Gluconeogenesis-12-320.jpg)






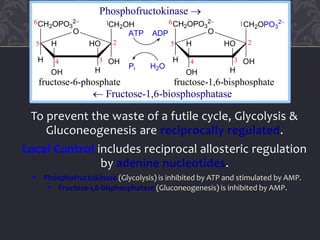




![Recall that Phosphofructokinase, the rate-limiting
step of Glycolysis, is allosterically inhibited by ATP.
At high concentration, ATP binds at a low-affinity
regulatory site, promoting the tense conformation.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
[Fructose-6-phosphate] mM
PFKActivity
high [ATP]
low [ATP]
Sigmoidal
dependence of
reaction rate on
[fructose-6-
phosphate] is
observed at
high [ATP].](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-200421155217/85/Gluconeogenesis-25-320.jpg)
![Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate promotes the relaxed state,
activating Phosphofructokinase even at high [ATP].
Thus activation by fructose-2,6-bisphosphate, whose
concentration fluctuates in response to external
hormonal signals, supersedes local control by [ATP].
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0 0.5 1 1.5 2
[Fructose-6-phosphate] mM
PFKActivity
high [ATP]
low [ATP]
PFK activity in
the presence of the
globally controlled
allosteric regulator
fructose-2,6-
bisphosphate is
similar to that at
low ATP.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-200421155217/85/Gluconeogenesis-26-320.jpg)


![cAMP-dependent phosphorylation of the bi-functional
enzyme activates FBPase2 and inhibits PFK2.
[Fructose-2,6-bisphosphate] thus decreases in liver cells
in response to a cAMP signal cascade, activated by
glucagon when blood glucose is low.
(active as Phosphofructokinase-2)
Enz-OH
ATP ADP
fructose-6-P fructose-2,6-bisP
Pi
Enz-O-PO3
2
(active as Fructose-Bisphosphatase-2)
View an
animation.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/gluconeogenesis-200421155217/85/Gluconeogenesis-29-320.jpg)