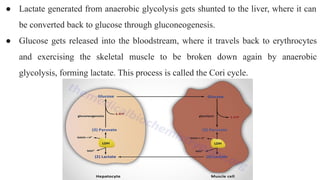
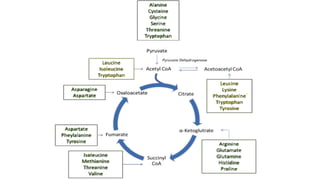
Gluconeogenesis is a metabolic pathway that generates glucose from non-carbohydrate substrates like lactate, glycerol, and certain amino acids. It occurs mainly in the liver and kidneys through a series of 11 enzyme-catalyzed reactions that largely run in reverse of glycolysis. Key regulated enzymes in gluconeogenesis bypass the three irreversible steps in glycolysis to allow for glucose synthesis. The pathway is regulated to prevent futile cycling between glucose breakdown and synthesis.