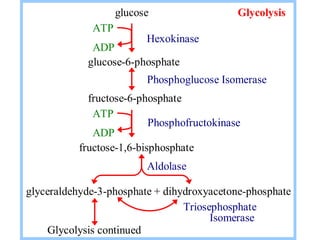
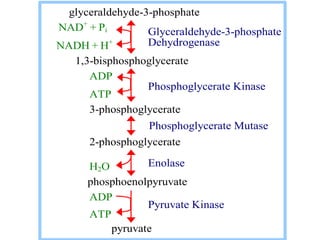
1. Glycolysis is a metabolic pathway that converts glucose into pyruvate, producing ATP. It takes place in the cytosol of cells and is the first step in extracting energy from glucose under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions.
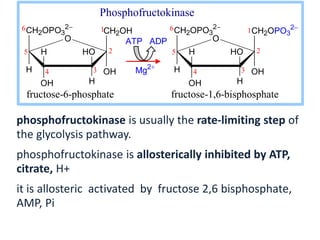
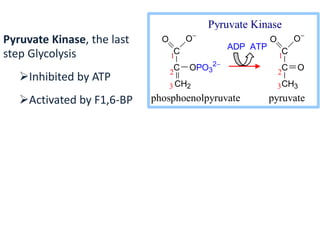
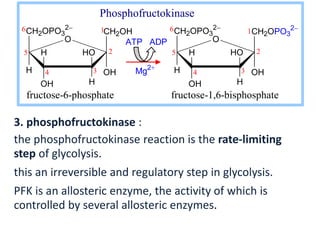
2. Glycolysis is regulated by three key enzymes - hexokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Phosphofructokinase is usually the rate-limiting step and is regulated by various allosteric effectors.
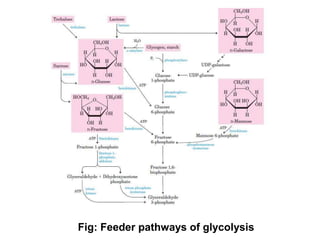
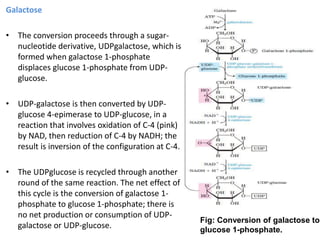
3. Glycolysis connects to many feeder pathways allowing other sugars like fructose, galactose, and glycogen to enter at various points and ultimately be broken down into py







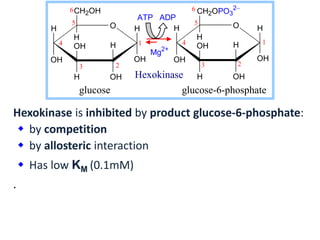
![ Glucokinase has a high KM (10mM) for glucose.
It is active only at high [glucose].
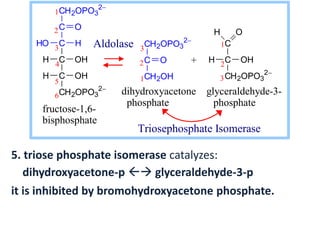
H O
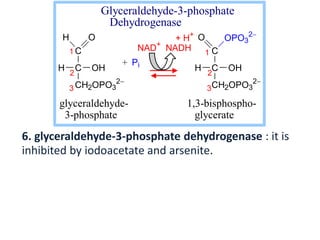
OH
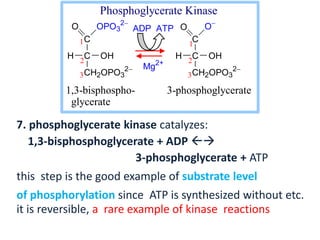
H
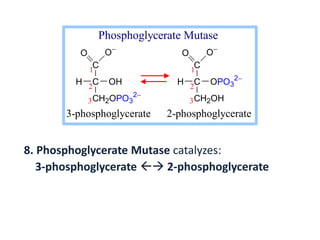
OHH
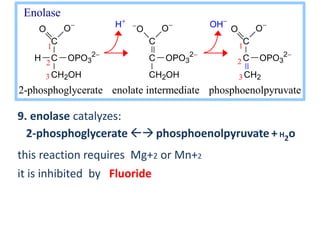
OH
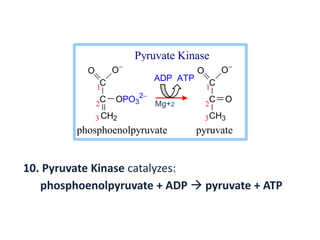
CH2OH
H
OH
H H O
OH
H
OHH
OH
CH2OPO3
2
H
OH
H
23
4
5
6
1 1
6
5
4
3 2
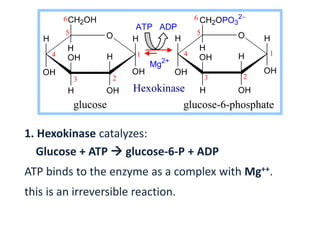
ATP ADP
Mg2+
glucose glucose-6-phosphate
Hexokinase
Glucokinase (
a variant of
Hexokinase) is
found in liver.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/glycolysis-200424132157/85/Glycolysis-22-320.jpg)