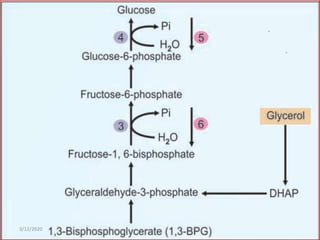
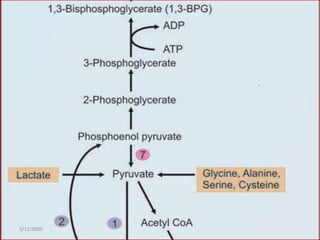
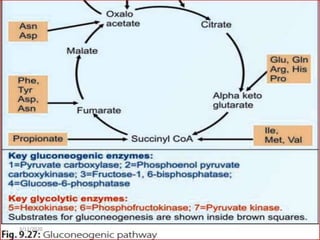
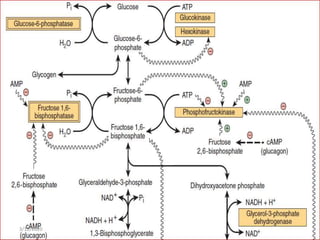
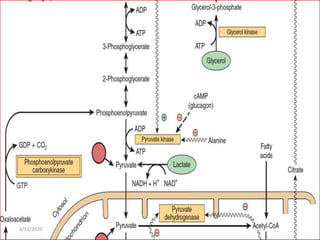
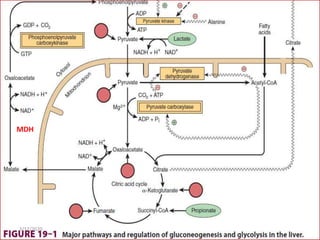
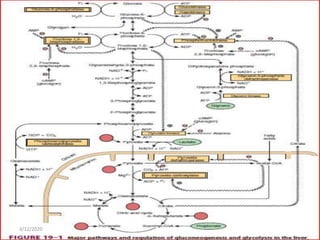
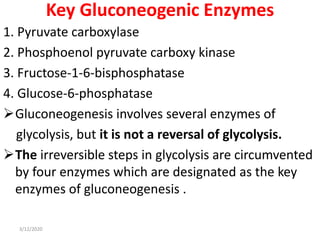
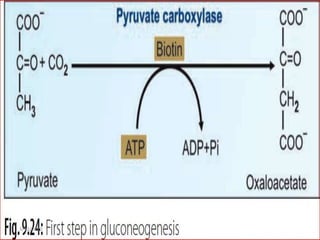
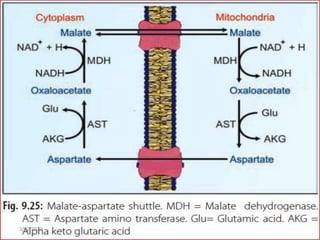
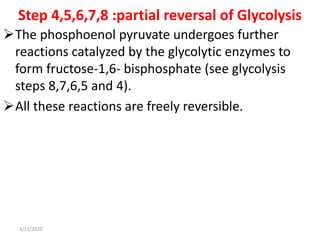
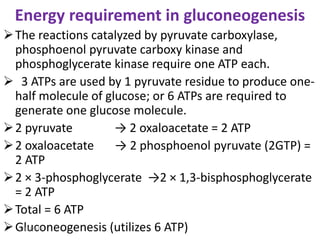
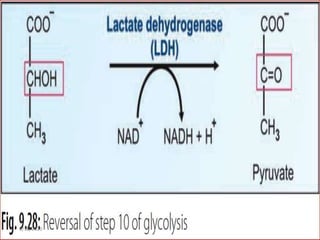
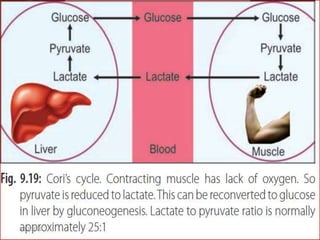
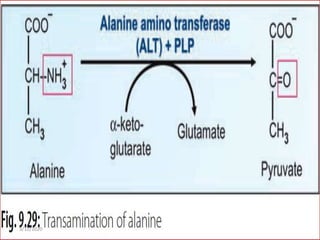
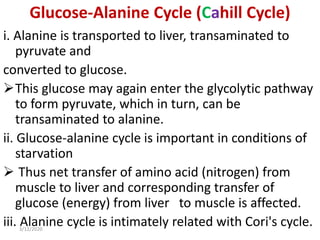
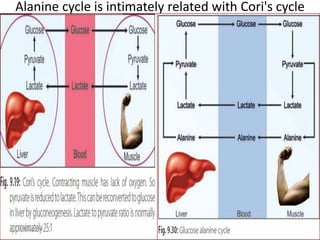
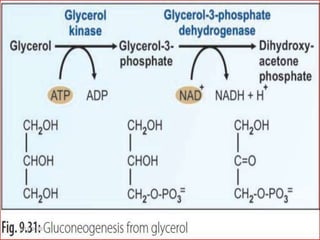
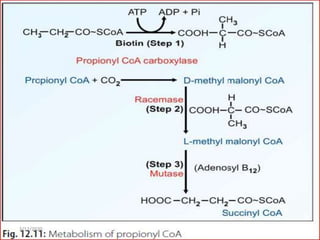
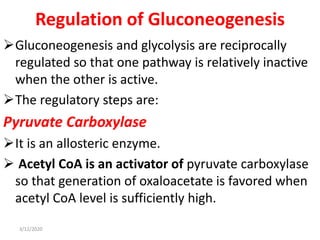
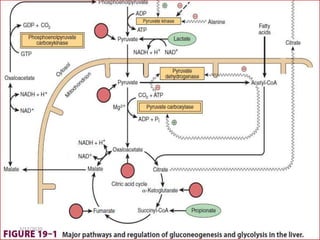
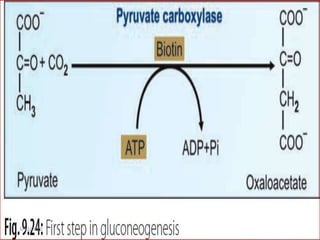
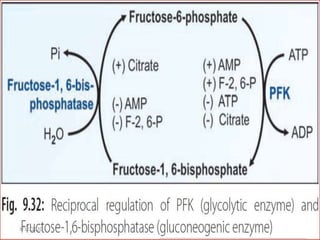
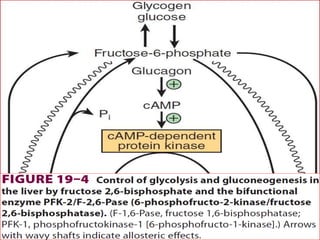
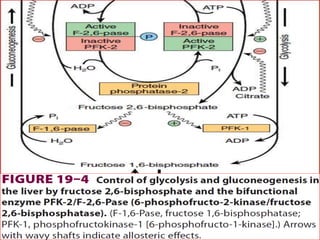
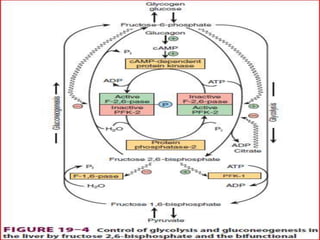
Gluconeogenesis is the process by which glucose is produced from non-carbohydrate precursors in the liver and kidneys. It involves converting substrates like lactate, amino acids, and glycerol into glucose through a series of enzymatic reactions. Key enzymes in gluconeogenesis bypass irreversible steps in glycolysis. Gluconeogenesis is regulated by enzymes like pyruvate carboxylase and fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase to produce glucose when blood sugar levels fall, such as during periods of fasting.