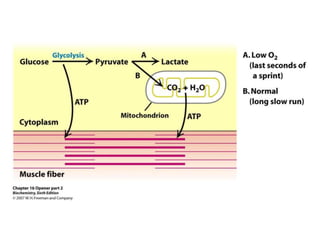
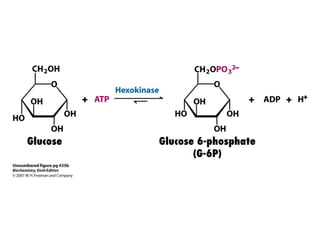
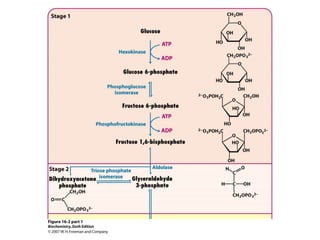
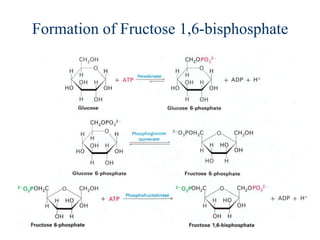
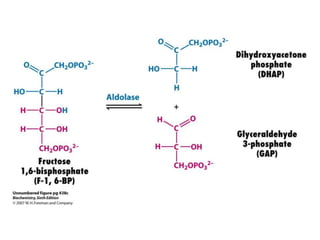
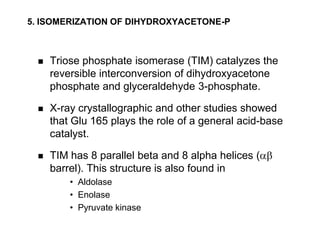
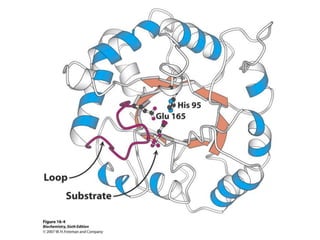
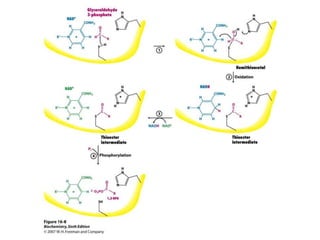
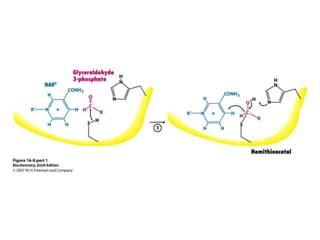
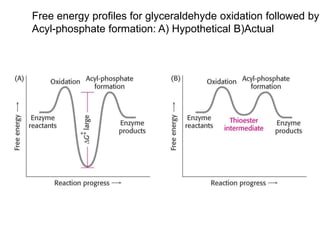
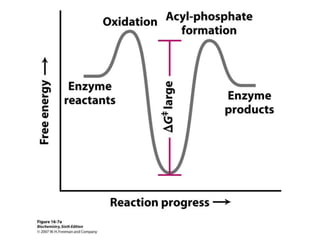
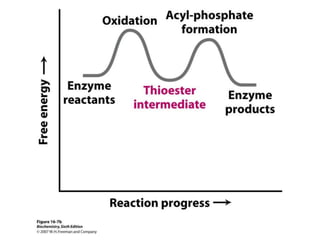
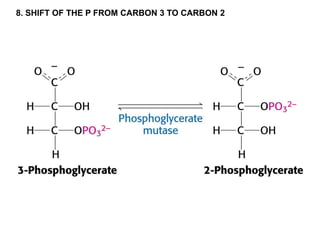
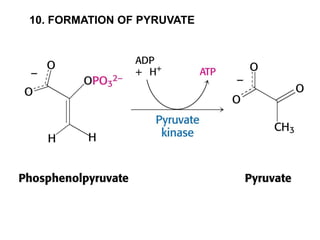
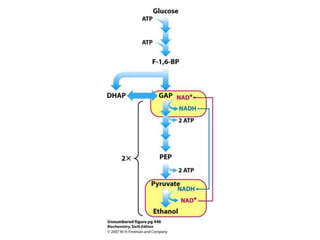
This document provides an overview of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. It discusses the key reactions and enzymes involved in glycolysis, which converts glucose to pyruvate, producing a small amount of ATP. Three reactions of glycolysis are irreversible. Under anaerobic conditions, pyruvate can be reduced to lactate. Glycolysis occurs in the cytosol of almost every living cell and was the first metabolic pathway to be studied in detail. Phosphorylation of intermediates traps molecules in the cell and provides energy for chemical reactions. The document also compares the enzymes hexokinase and glucokinase, and examines regulatory points in glycolysis.