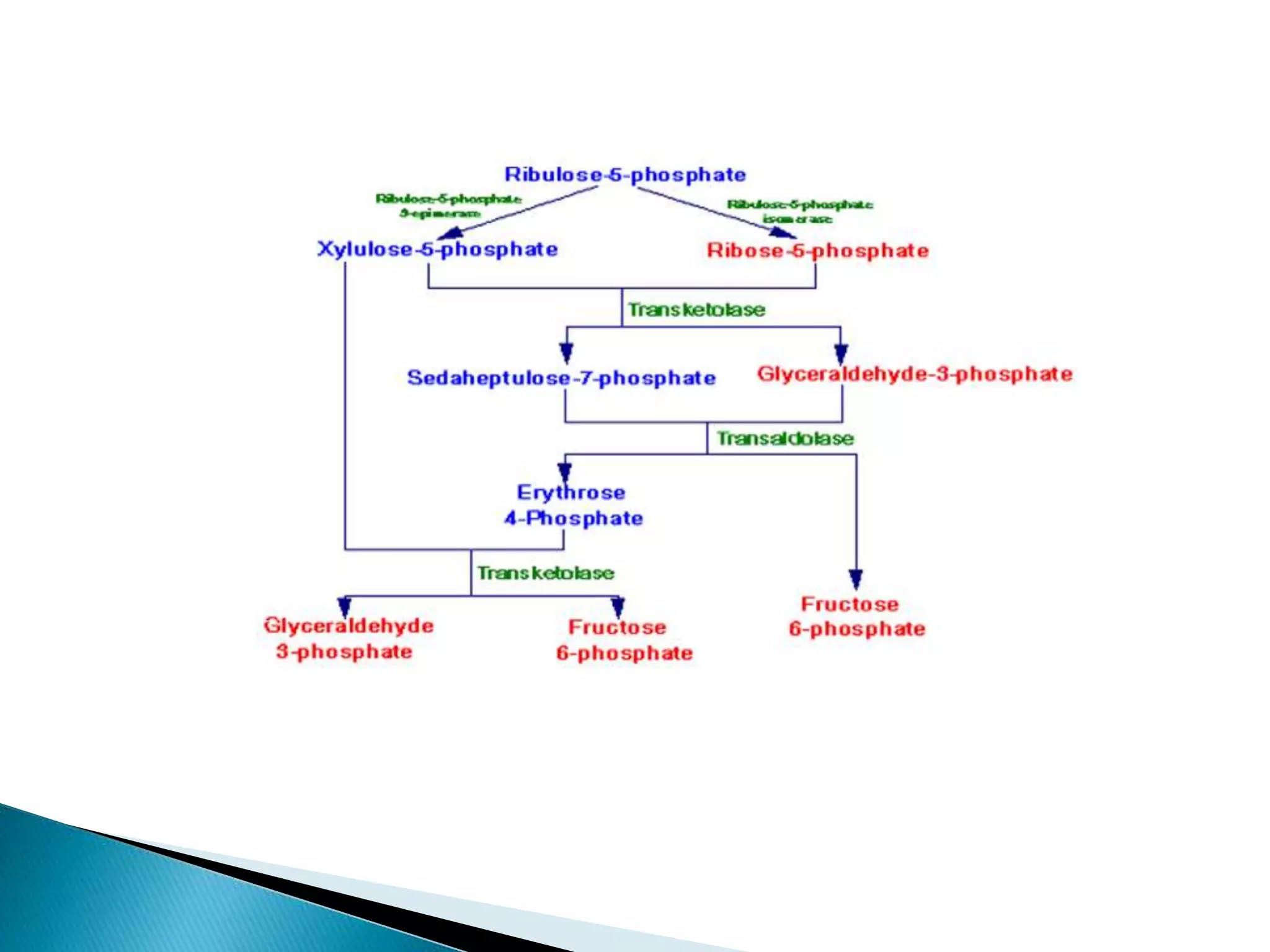
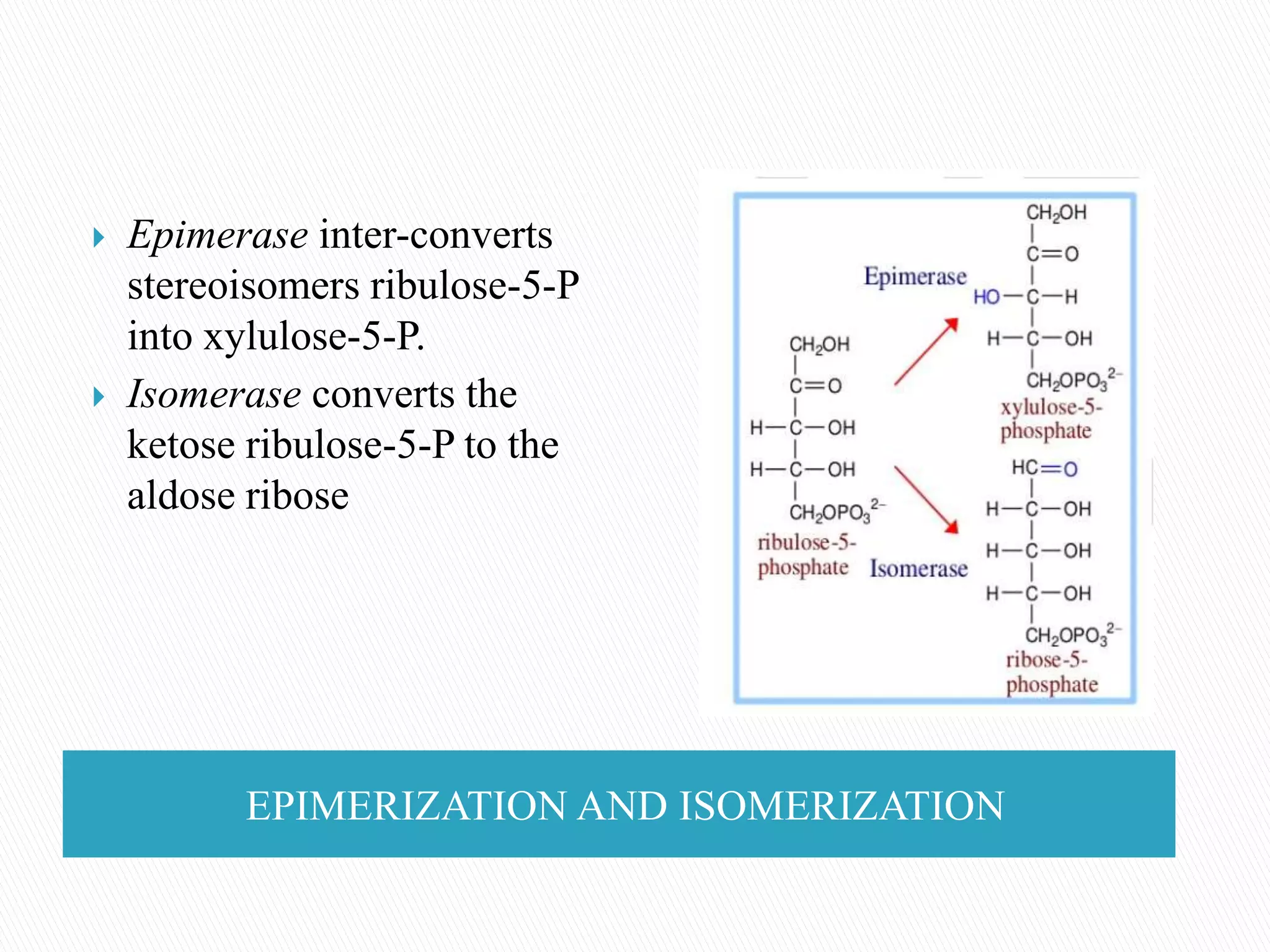
The document outlines the two major phases of the pentose phosphate pathway: oxidative and non-oxidative. The oxidative phase generates NADPH vital for various biosynthetic processes, while the non-oxidative phase produces 5-carbon sugars for nucleotide and amino acid synthesis. Overall, the pentose phosphate pathway serves as an alternative to glycolysis and plays a crucial role in cellular metabolism, particularly in tissues like the liver and adipose tissue.