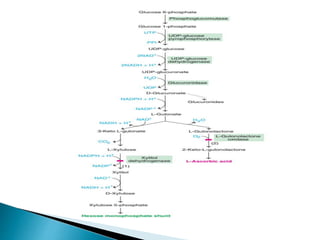
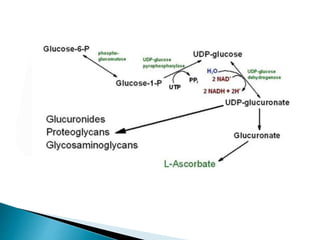
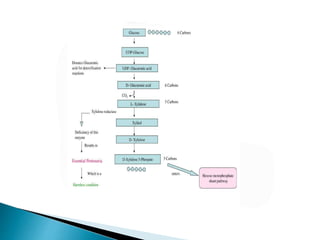
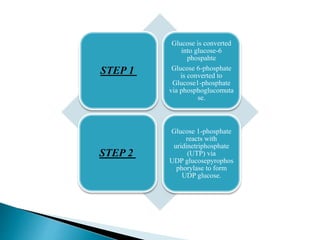
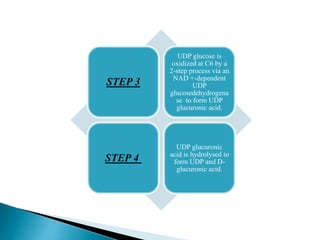
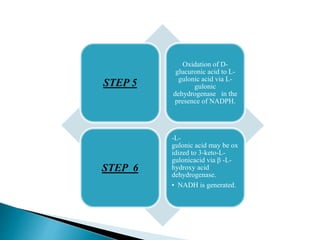
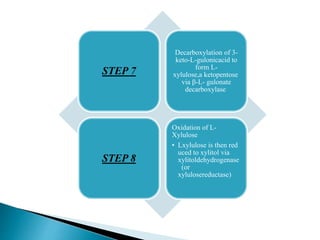
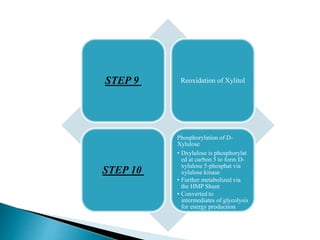
The glucuronic acid pathway is a minor glucose metabolism route that facilitates the synthesis of glucuronic acid, pentoses, and vitamin C (in animals capable of synthesis). This pathway involves converting glucose to UDP-glucuronate, which is crucial for detoxifying foreign substances and forming mucopolysaccharides. In humans and certain primates, vitamin C cannot be synthesized due to enzyme deficiencies, necessitating dietary intake.