Embed presentation


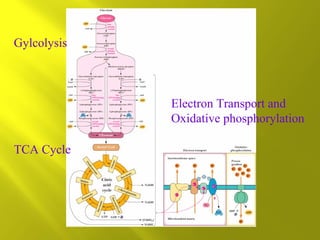
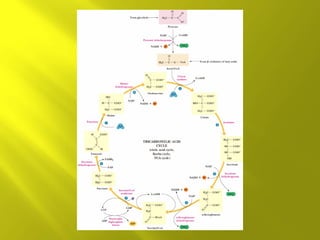
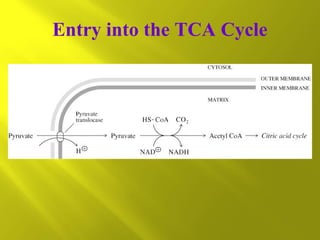
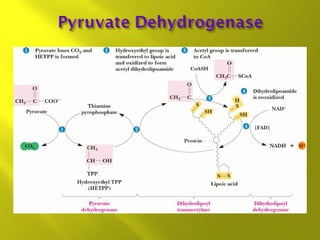
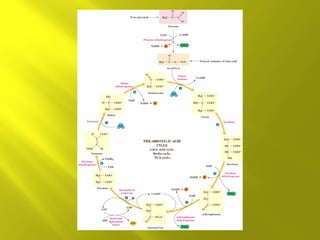
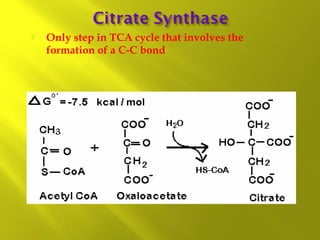
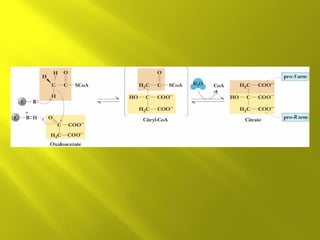
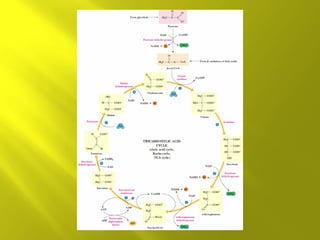
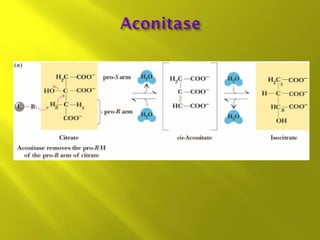
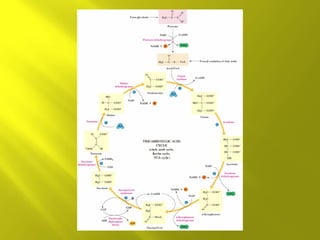
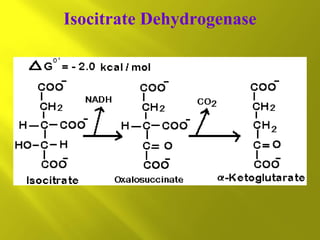
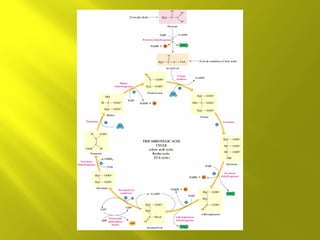
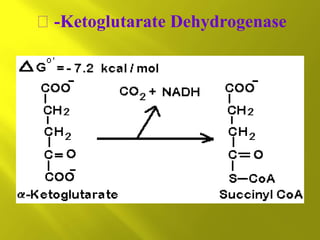
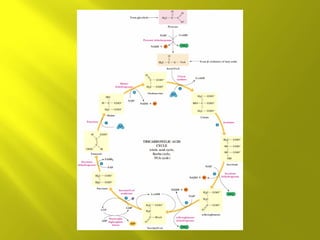
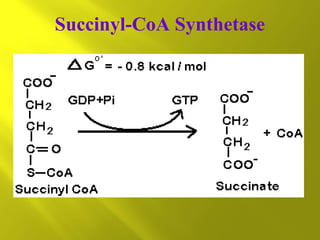
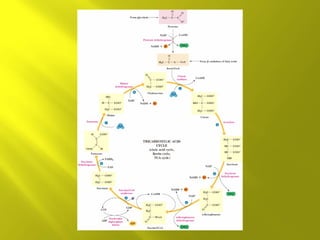
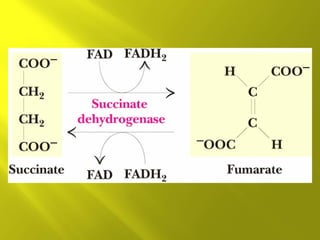
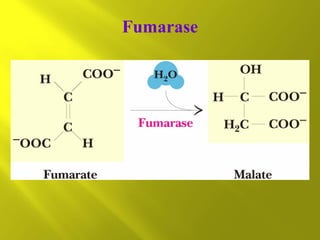
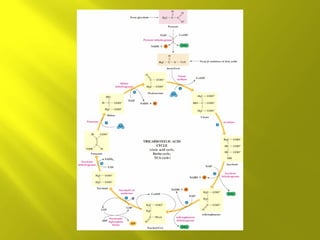
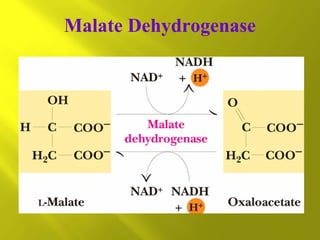
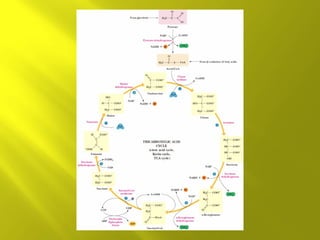

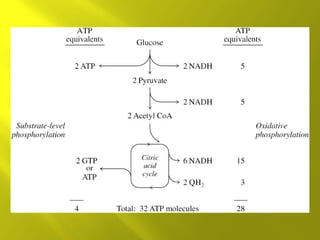
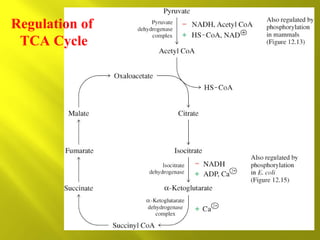
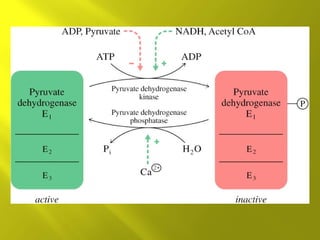
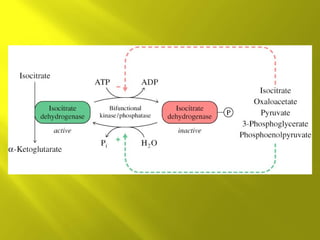
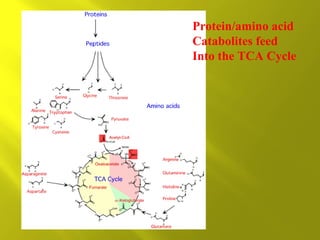
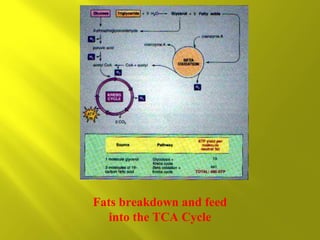
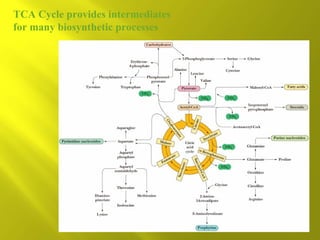

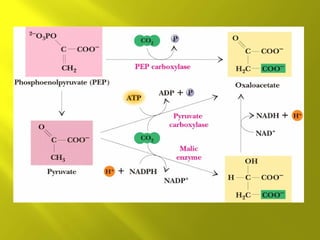
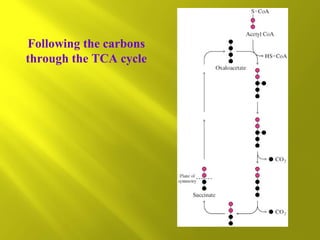
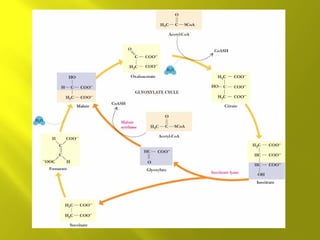
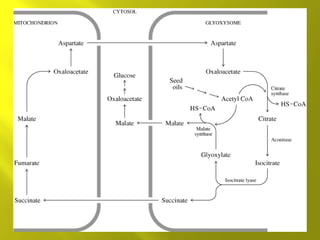

This document summarizes the citric acid cycle, also known as the Krebs cycle or TCA cycle. It outlines the key steps in the cycle, including the enzymes involved in each reaction. These steps ultimately generate ATP through oxidative phosphorylation as acetyl-CoA is oxidized, yielding carbon dioxide and hydrogen ions. In total, the oxidation of one acetyl-CoA molecule in the TCA cycle produces 10 ATP molecules. The TCA cycle is also regulated and provides intermediates for other biosynthetic processes.



































