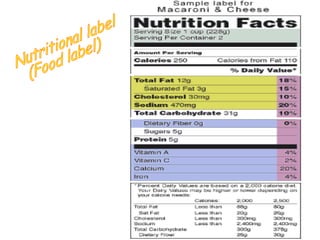
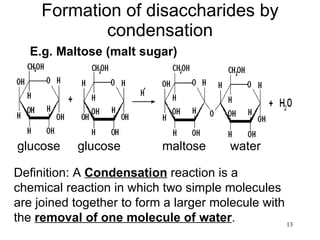
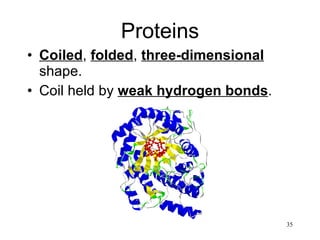
The document discusses the key nutrients needed by the human body - carbohydrates, fats, proteins, and water. It defines each nutrient, describes their chemical composition and basic units, functions in the body, sources, and common tests used for their identification.