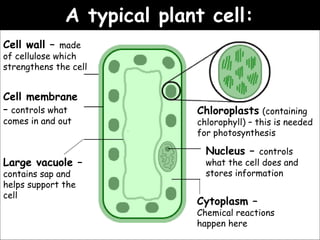
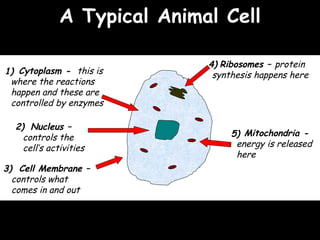
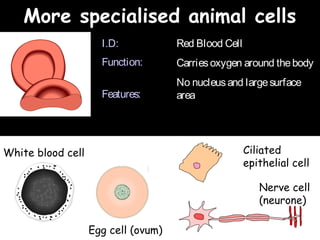
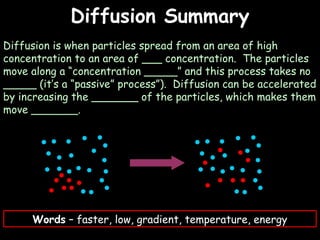
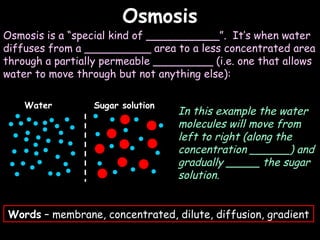
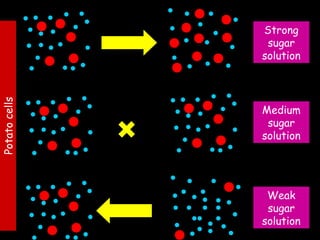
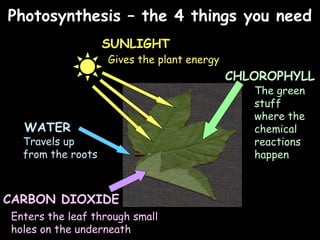
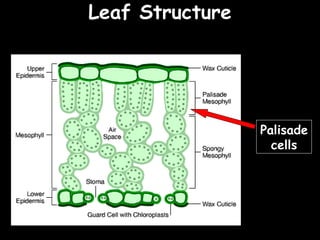
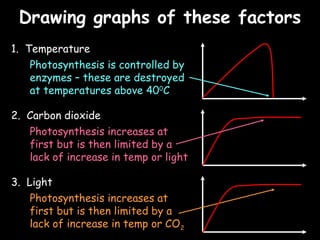
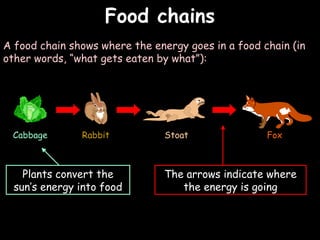
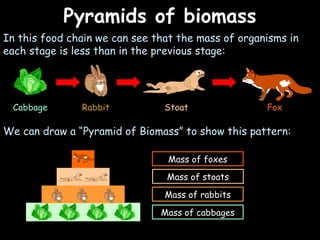
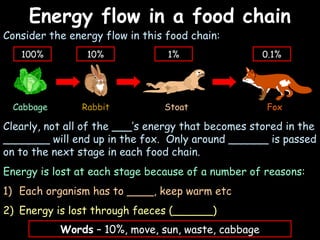
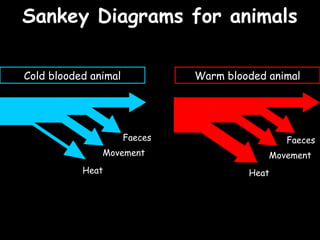
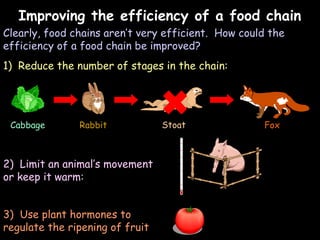
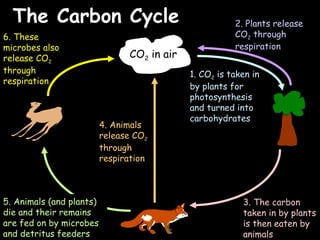
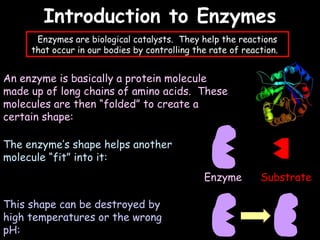
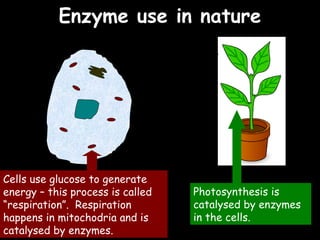
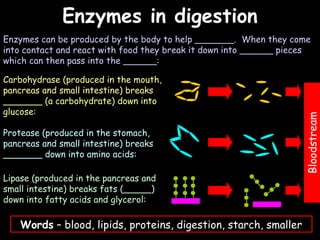
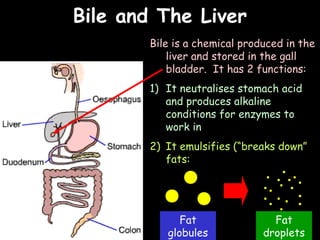
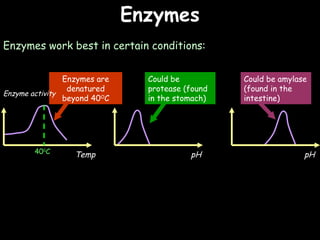
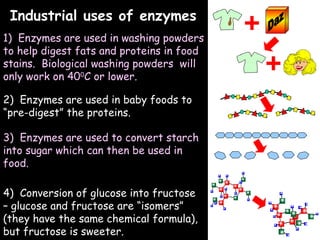
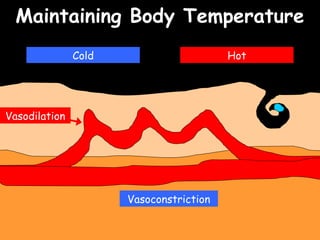
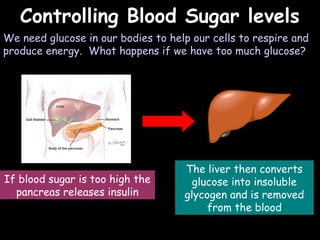
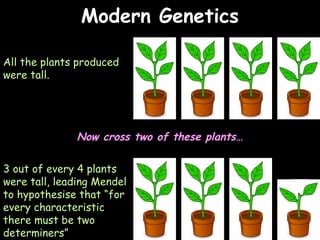
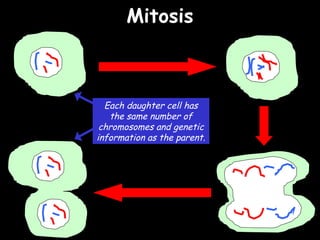
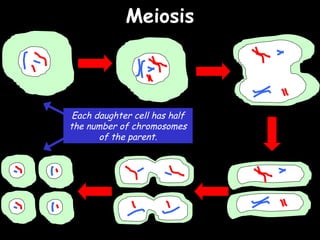
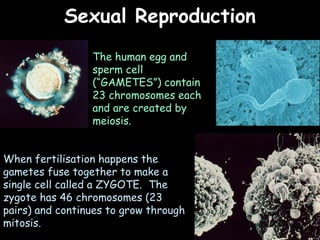
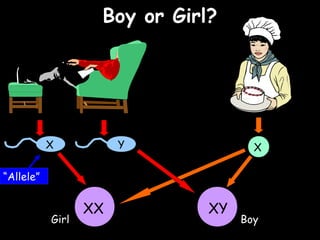
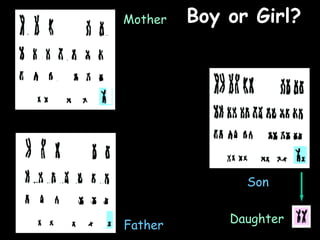
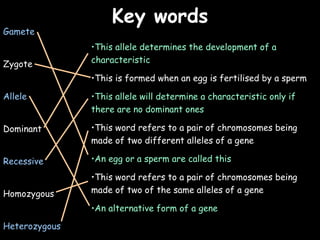
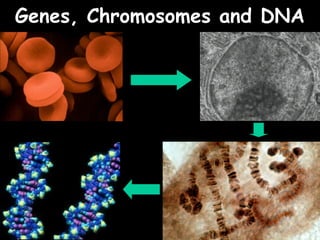
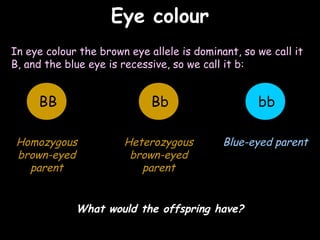
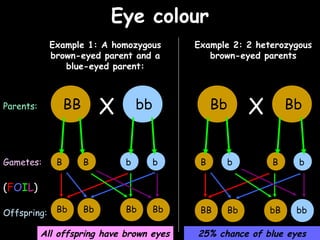
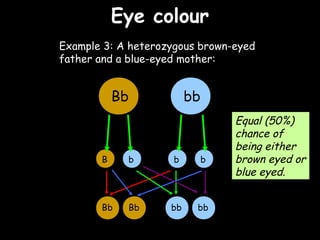
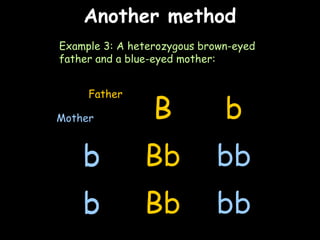
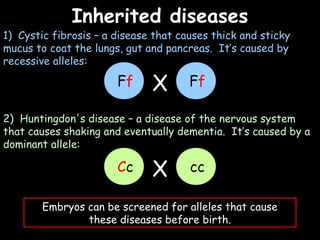
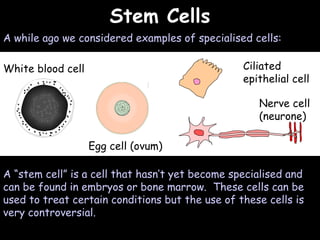
The document provides information about biology topics including plant and animal cell structure, diffusion and osmosis, photosynthesis, respiration, enzymes, genetics, and homeostasis. A typical plant cell contains a cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole, cytoplasm, and chloroplasts. A typical animal cell contains a nucleus, mitochondria, cell membrane, and cytoplasm. Diffusion is the passive movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration, while osmosis is the diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane. Photosynthesis requires carbon dioxide, water, chlorophyll, and sunlight to produce glucose and oxygen. Respiration uses glucose and oxygen to produce energy, water, and carbon dioxide. Enzymes are