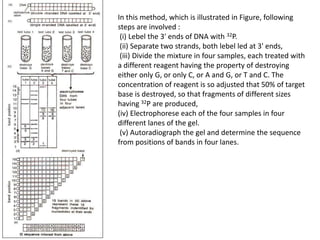
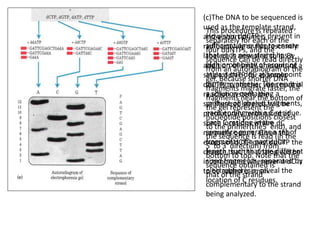
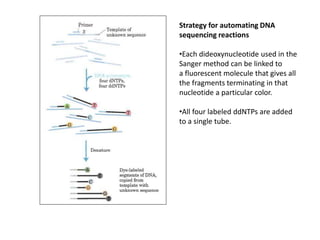
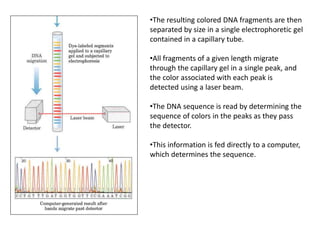
The document discusses techniques for DNA sequencing, including early methods developed in the 1970s by Maxam and Gilbert as well as Sanger. It provides details on how both methods work, such as using specific chemical or enzymatic reactions to generate labeled DNA fragments of different lengths corresponding to nucleotide positions in the sequence. The document also describes how these methods were later automated, using fluorescent tags on dideoxynucleotides and capillary electrophoresis to simultaneously sequence multiple samples in a single gel. This allowed rapid determination of thousands of nucleotides and enabled large genome sequencing projects such as the Human Genome Project.