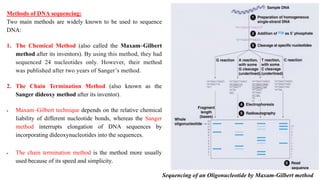
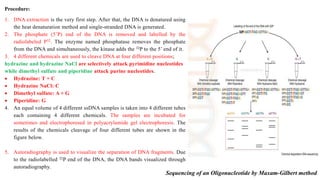
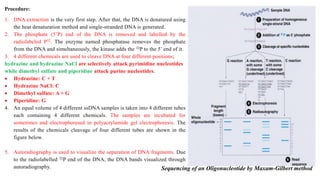
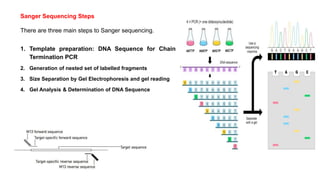
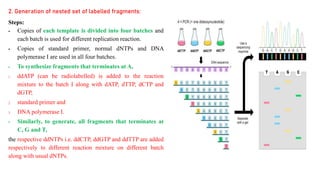
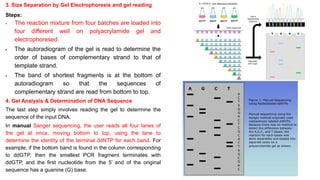
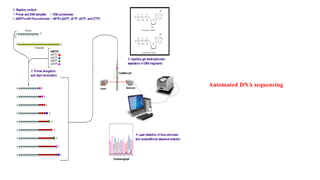
DNA sequencing refers to determining the order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule. The first DNA sequence was obtained in the 1970s using chromatography. Modern methods use dye-based sequencing and automation. The two main historical methods are the Maxam-Gilbert chemical degradation method and the Sanger dideoxy chain termination method. Next generation sequencing now allows millions of DNA molecules to be sequenced in parallel through massively parallel sequencing technologies.