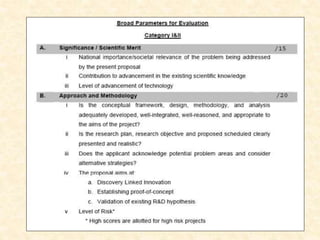
This document provides guidelines for writing a research proposal. It begins by outlining the key components of a proposal, including an original idea, preliminary work, objectives, budget, and timelines. It then goes into more detail on specific sections. The title should be short and explanatory. The novelty, inventive step, national importance, and market potential should be clearly described. Preliminary work and background information should provide scientific basis. Objectives must be specific and quantifiable. The budget and milestones must be realistic and achievable. Technical details should include significance, methodology, and potential problems. The proposal aims to establish proof of concept with anticipated deliverables.