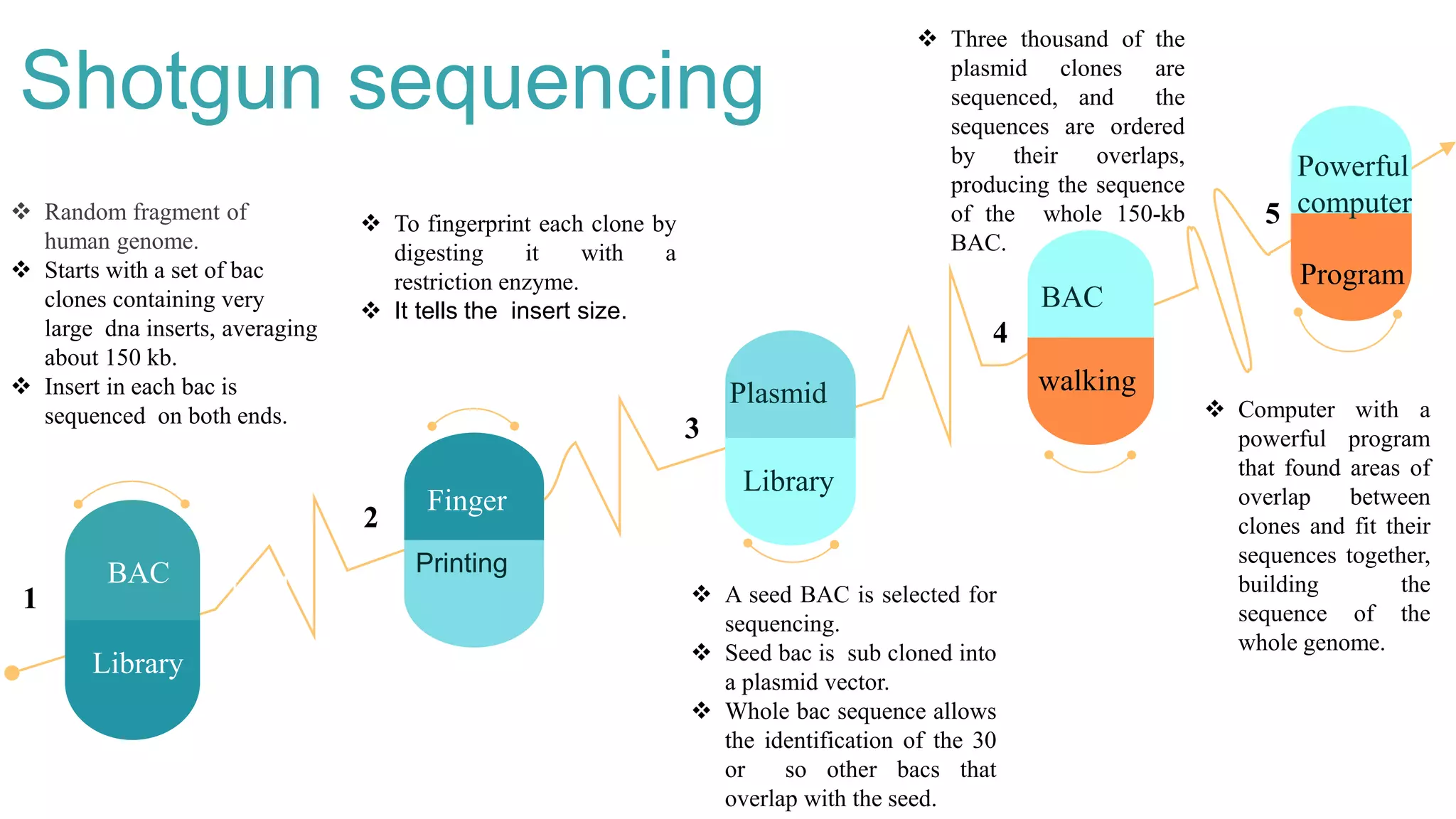
This document provides an overview of whole genome sequencing. It discusses the history and development of genome sequencing technologies. Several methods of whole genome sequencing are described, including shotgun sequencing which involves randomly breaking DNA into fragments, sequencing the fragments, and reassembling them using overlapping regions. Applications of whole genome sequencing include disease diagnosis, drug development, forensics, and agriculture. Both advantages and limitations of different sequencing technologies are presented. The document concludes that genome sequencing can help isolate genetic markers in a cost-effective manner.