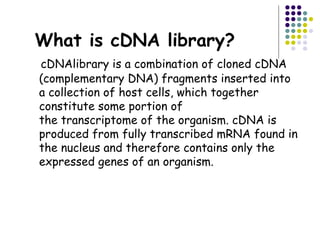
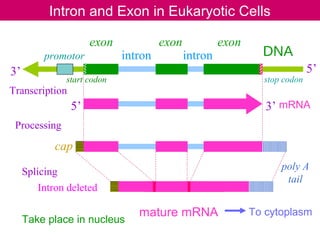
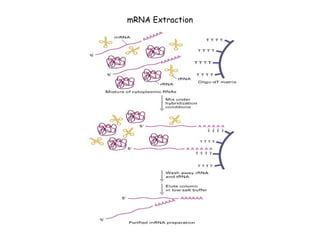
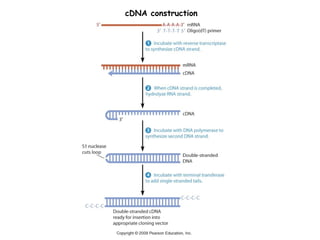
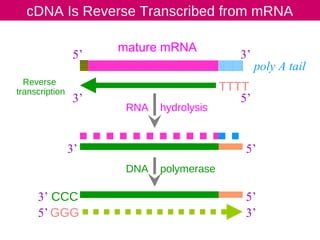
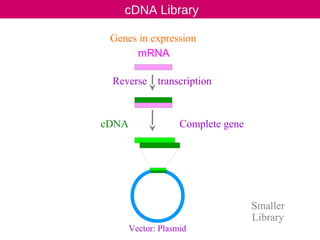
cDNA is produced from mRNA found in the nucleus and contains only the expressed genes of an organism. To create a cDNA library, mRNA is first extracted and purified from a cell, then reverse transcribed into cDNA using an oligo-dT primer that binds to the poly-A tail. The resulting single-stranded cDNA is converted into double-stranded DNA and cloned into plasmids in bacteria. cDNA libraries are useful for reproducing eukaryotic genomes without introns, expressing eukaryotic genes in prokaryotes, discovering novel genes, and studying alternative splicing in different cells.