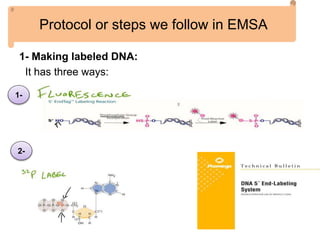
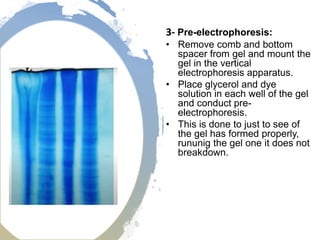
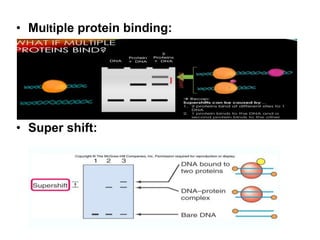
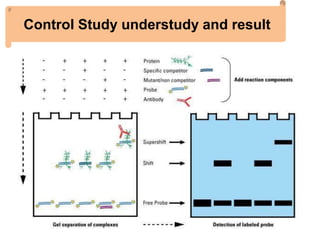
The electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) is a sensitive and rapid technique used to detect specific-binding interactions between nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) and proteins. The assay separates protein-nucleic acid complexes from unbound nucleic acids through non-denaturing gel electrophoresis, allowing for the visualization of binding events. EMSA is widely utilized for analyzing protein-DNA interactions, but has limitations such as influencing factors on mobility and the inability to measure protein weights directly.