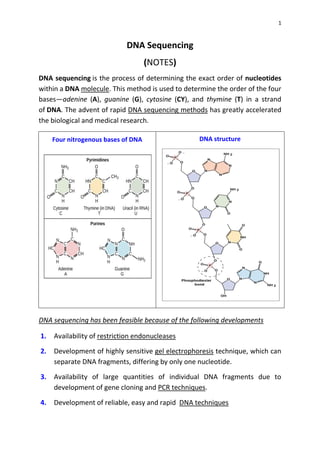
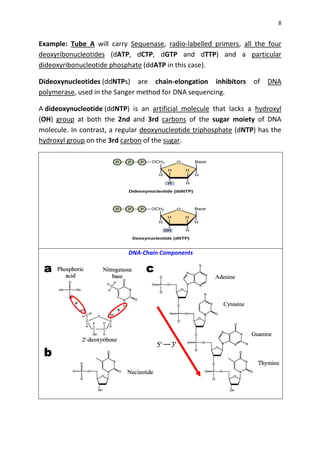
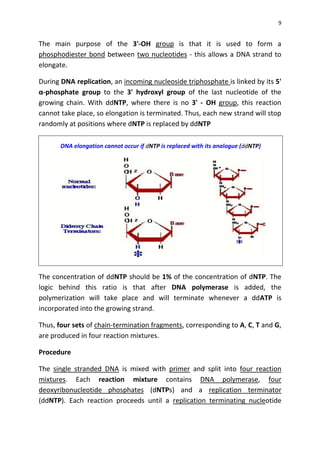
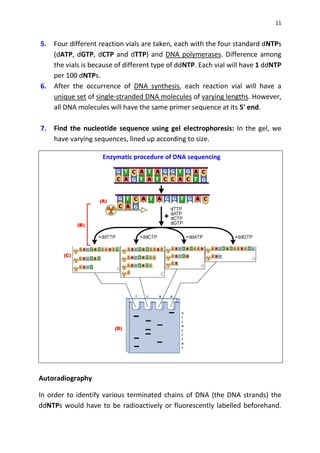
DNA sequencing determines the precise order of nucleotides in a DNA molecule, primarily using two techniques: Maxam-Gilbert (chemical) sequencing and Sanger (enzymatic) sequencing. The Maxam-Gilbert method involves chemical modifications and cleavage of DNA, while the Sanger method utilizes chain-terminating dideoxynucleotides to generate fragments for size-based analysis. Advances in sequencing techniques have made DNA sequencing quicker and more accessible, paving the way for significant research breakthroughs such as the Human Genome Project.