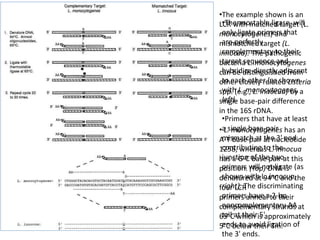
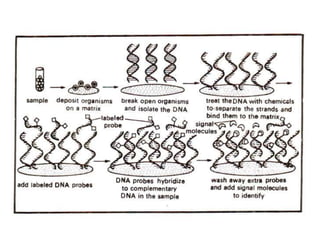
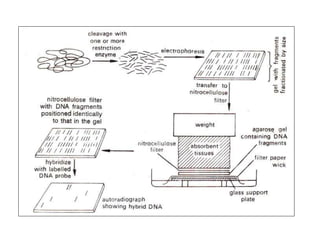
Ligase chain reaction (LCR) is a technique that can detect single base pair differences in DNA sequences. It uses a thermostable ligase and primers to exponentially amplify the target sequence if there is a perfect match. Mismatched sequences will not ligate and thus not amplify. LCR has been used to detect genetic diseases, bacteria, viruses, and other sequences. Molecular probes are labeled DNA or RNA fragments that can identify complementary sequences. They are often labeled with radioactive isotopes or non-radioactive molecules like biotin or digoxigenin for detection. Molecular probes have applications in research, diagnostics, and forensics.