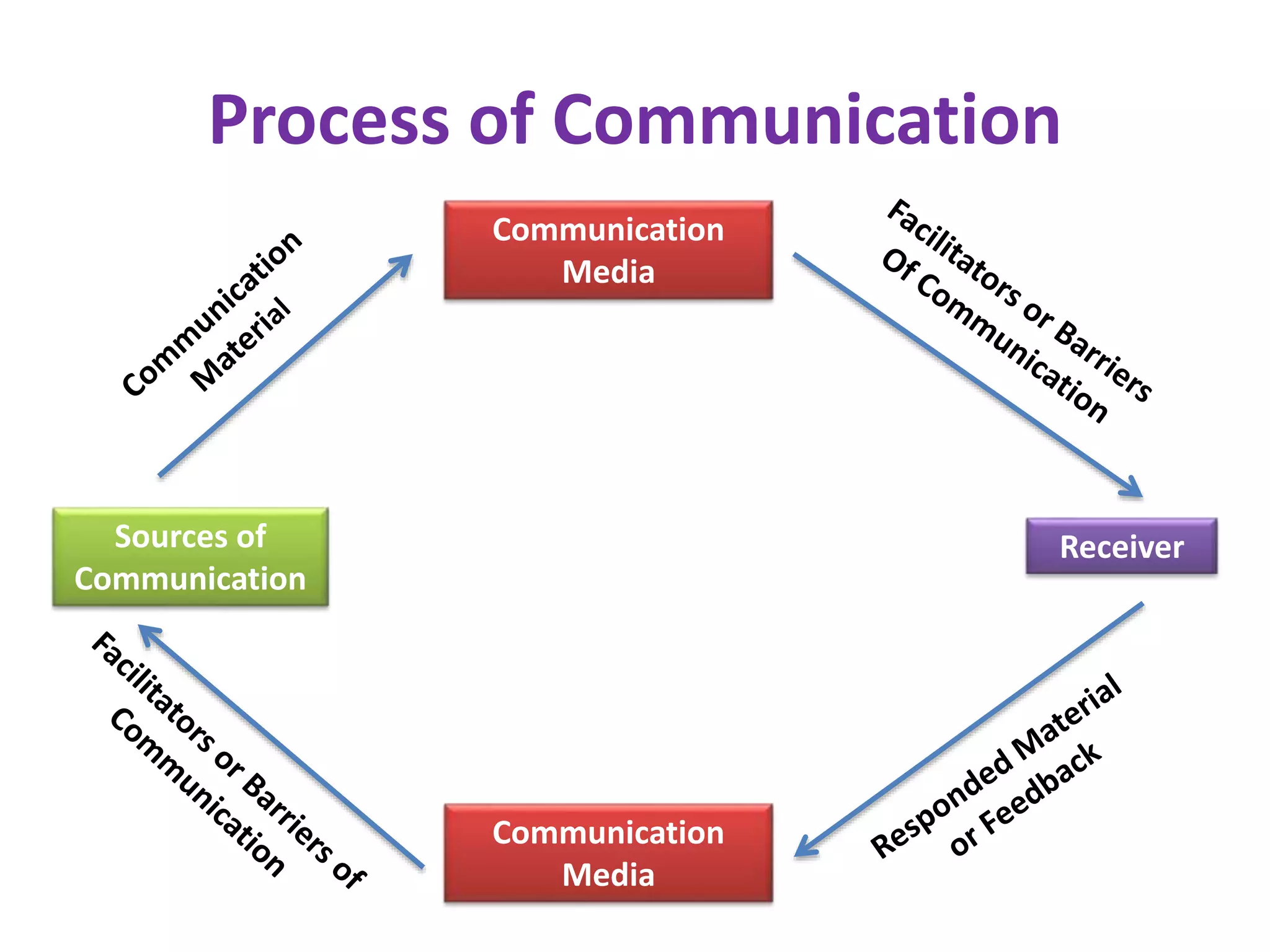
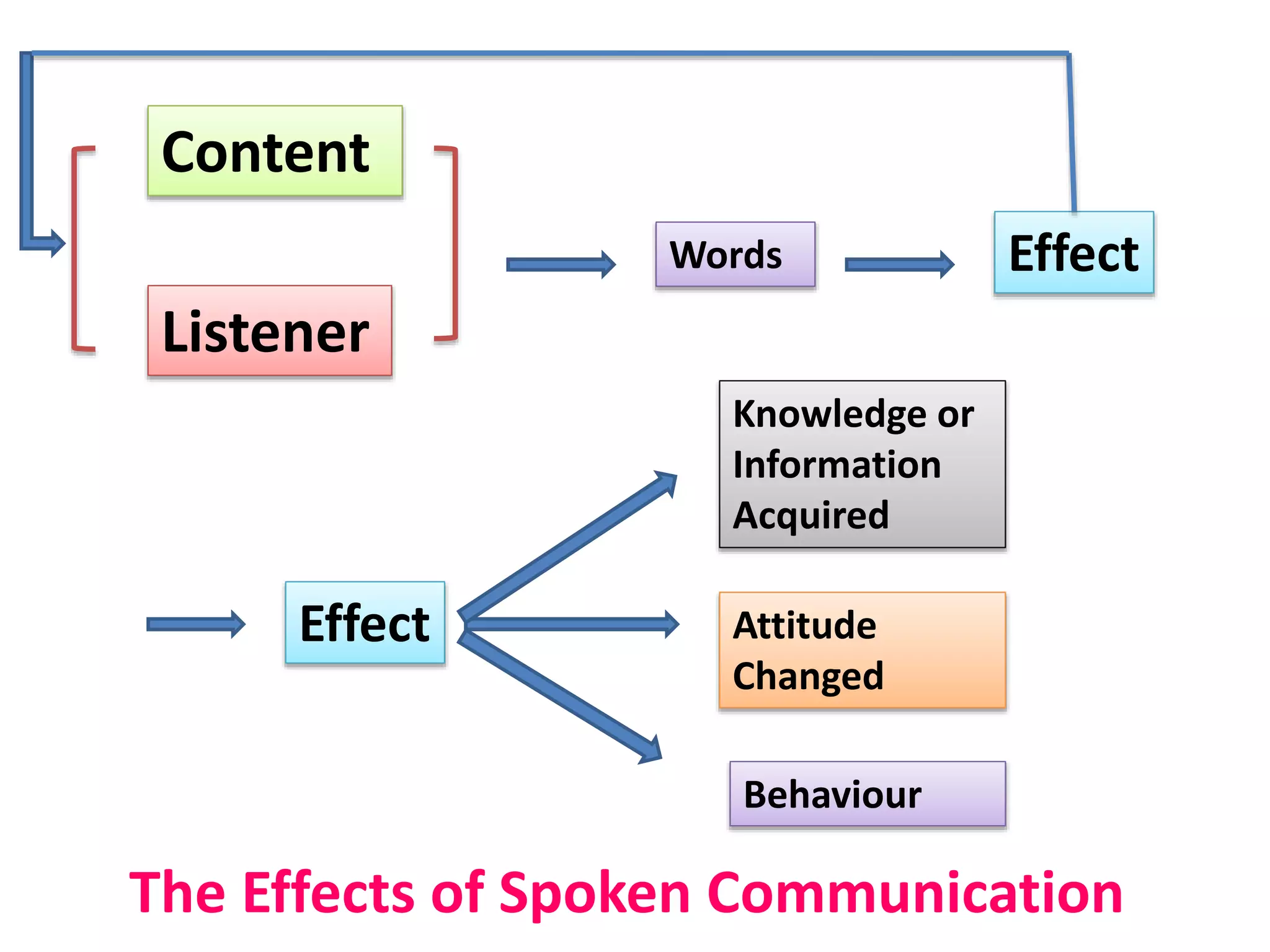
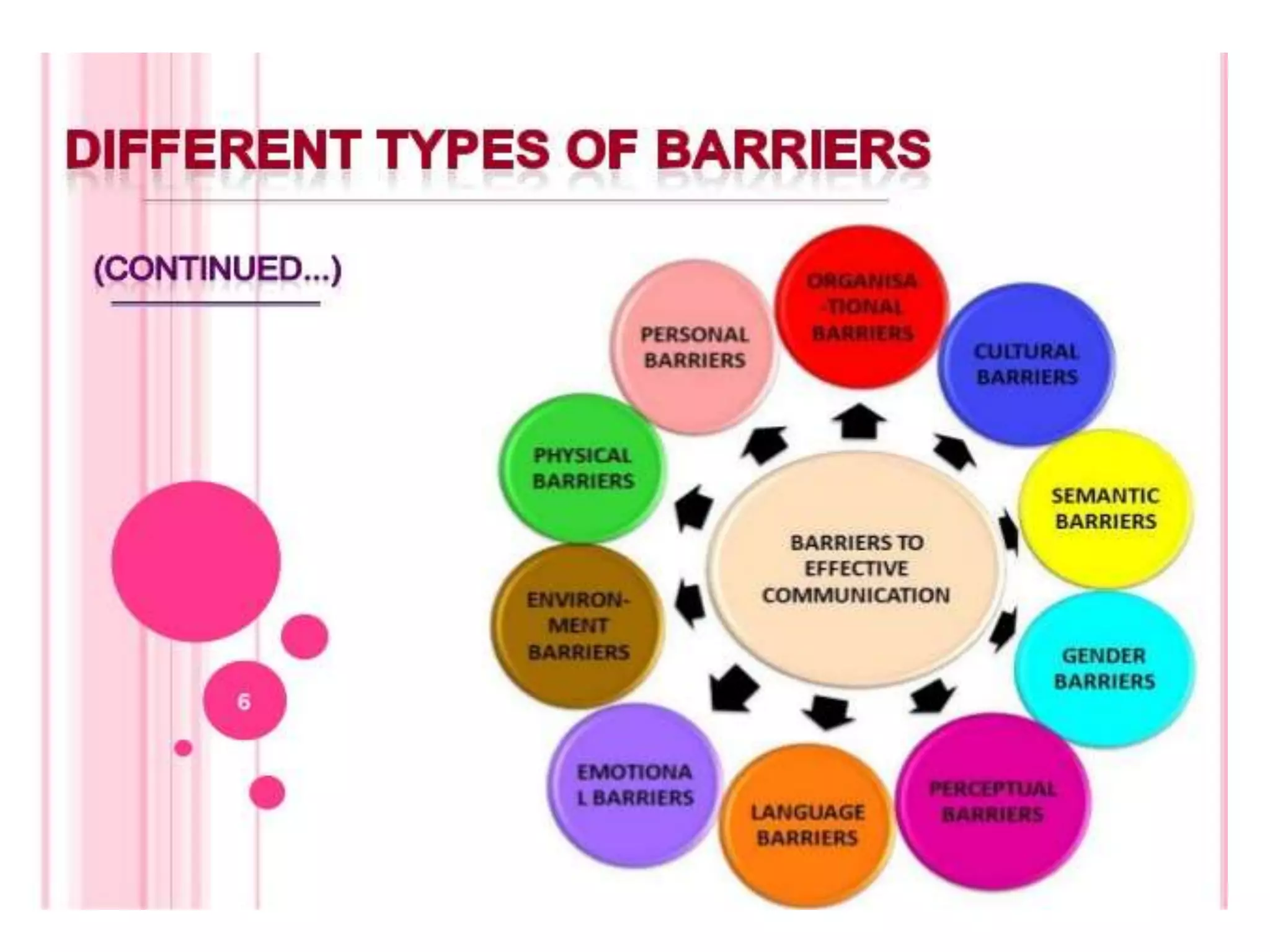
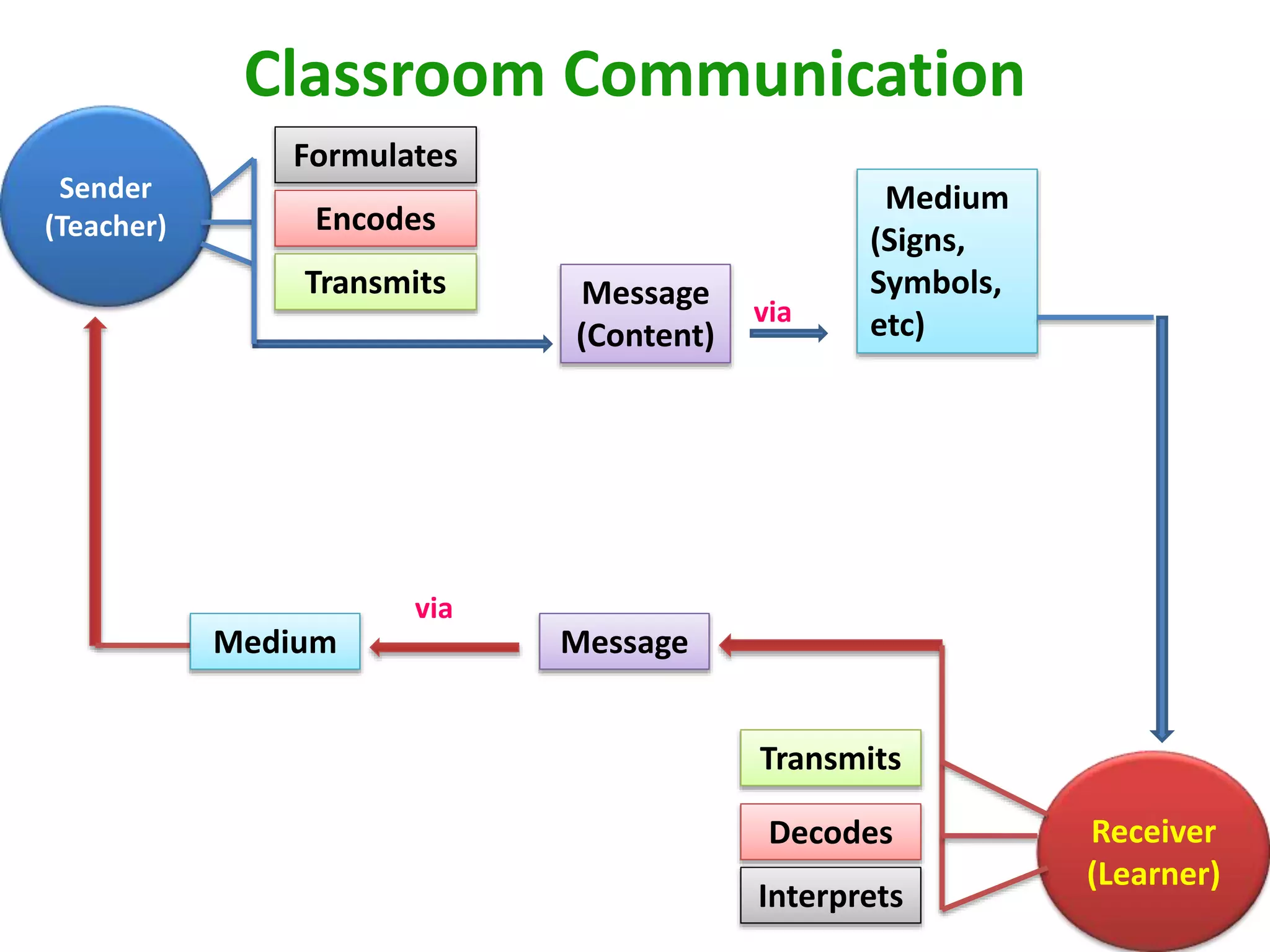
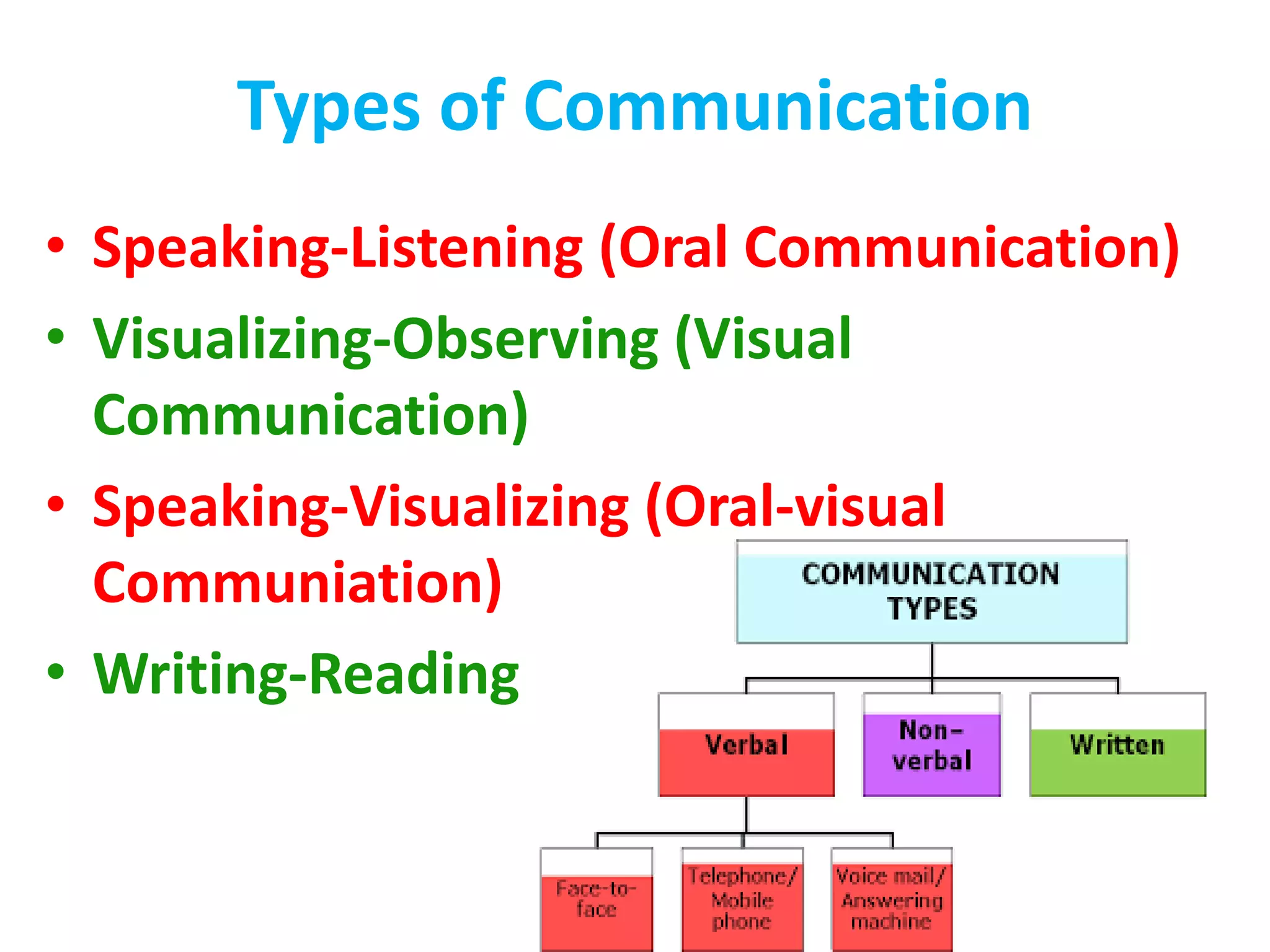
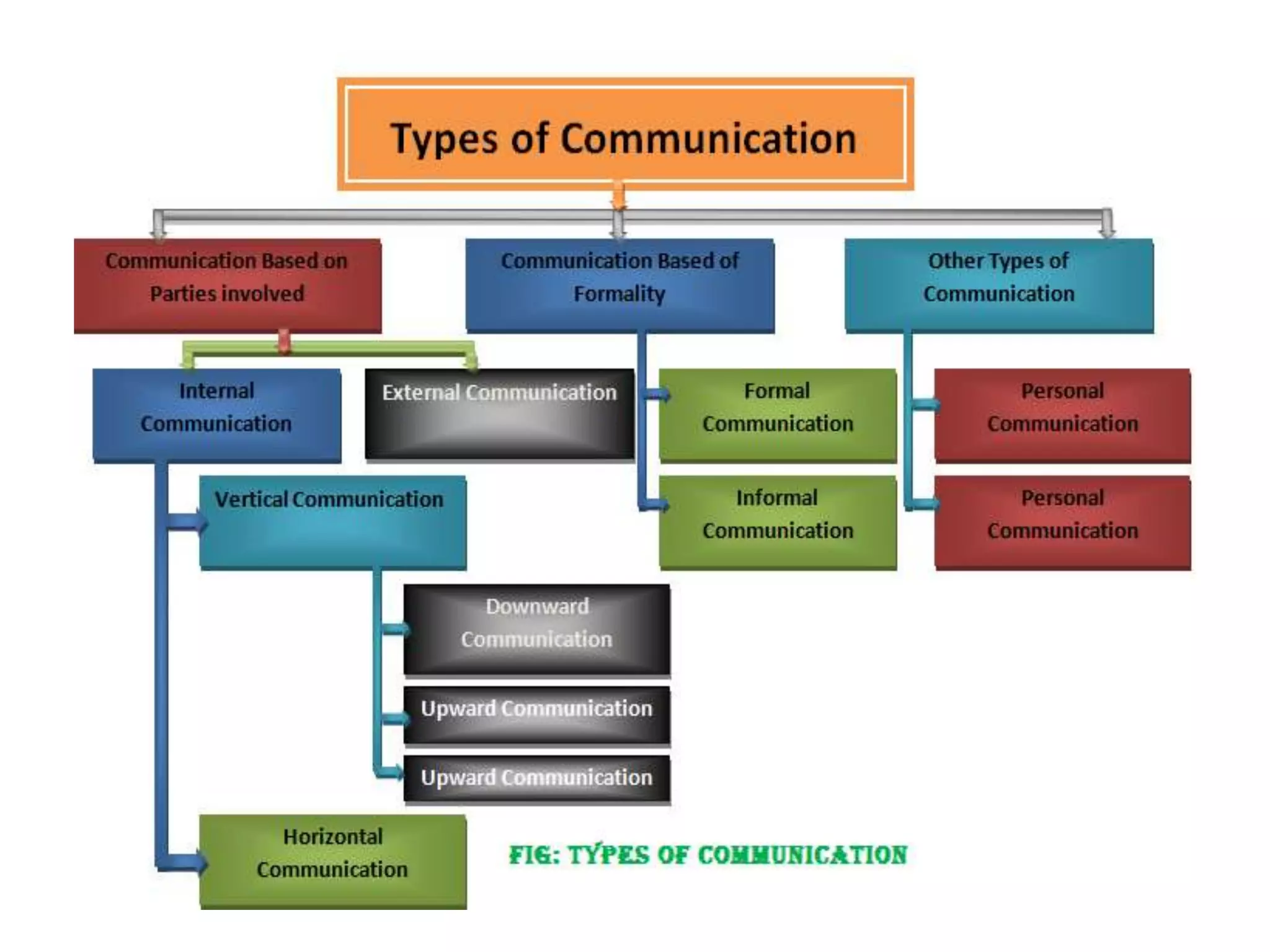
This document discusses communication and interaction in education. It defines communication as the sharing of ideas and feelings between two or more people. The key elements of the communication process are identified as the source, message, channel, and receiver. Barriers to communication include both internal factors like health issues and external factors like environmental distractions. Effective classroom communication involves two-way interaction between the teacher and students using various channels like verbal and non-verbal methods. The document also outlines different types of communication and strategies to improve communication in the classroom.