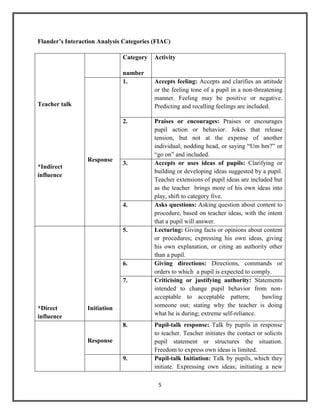
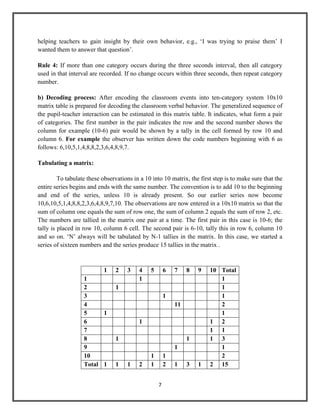
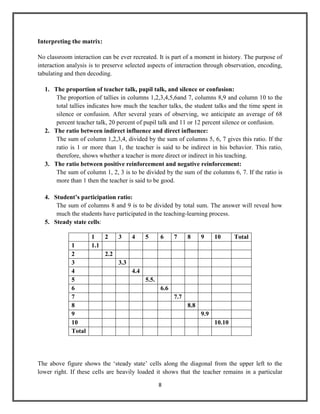
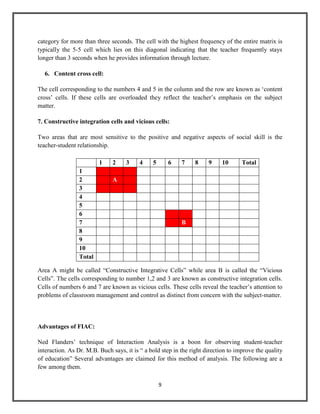
The document discusses Flanders' Interaction Analysis (FIAC), a system for categorizing and analyzing classroom interactions. It describes FIAC's 10 categories for coding teacher and student talk. The categories are divided into indirect and direct teacher influence as well as student talk in response to or initiation of ideas. FIAC involves encoding classroom interactions using the categories, tabulating the data in a matrix, and interpreting the matrix to understand classroom dynamics. Theoretical assumptions underpinning FIAC include the importance of verbal communication and teacher influence in the classroom.