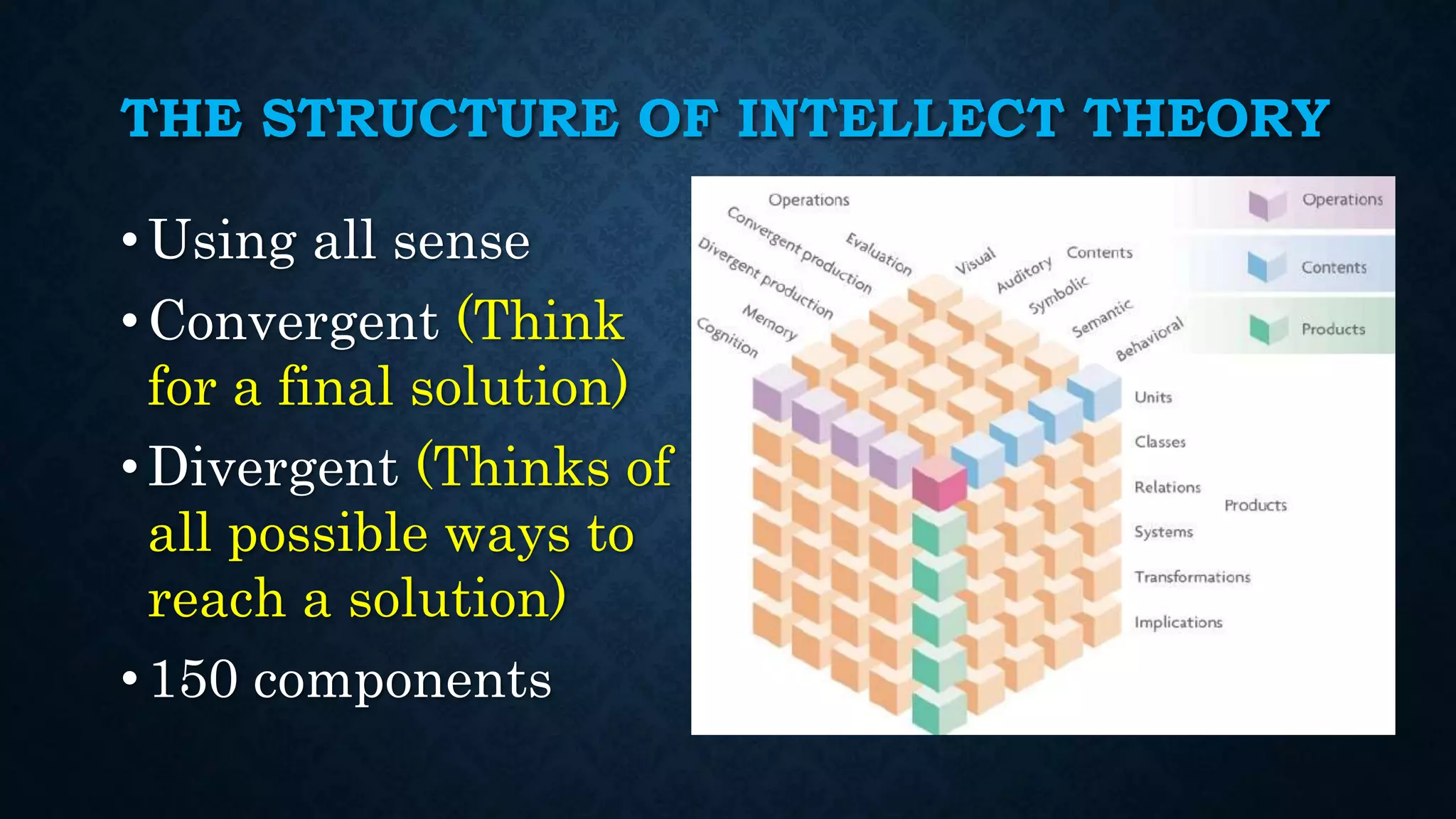
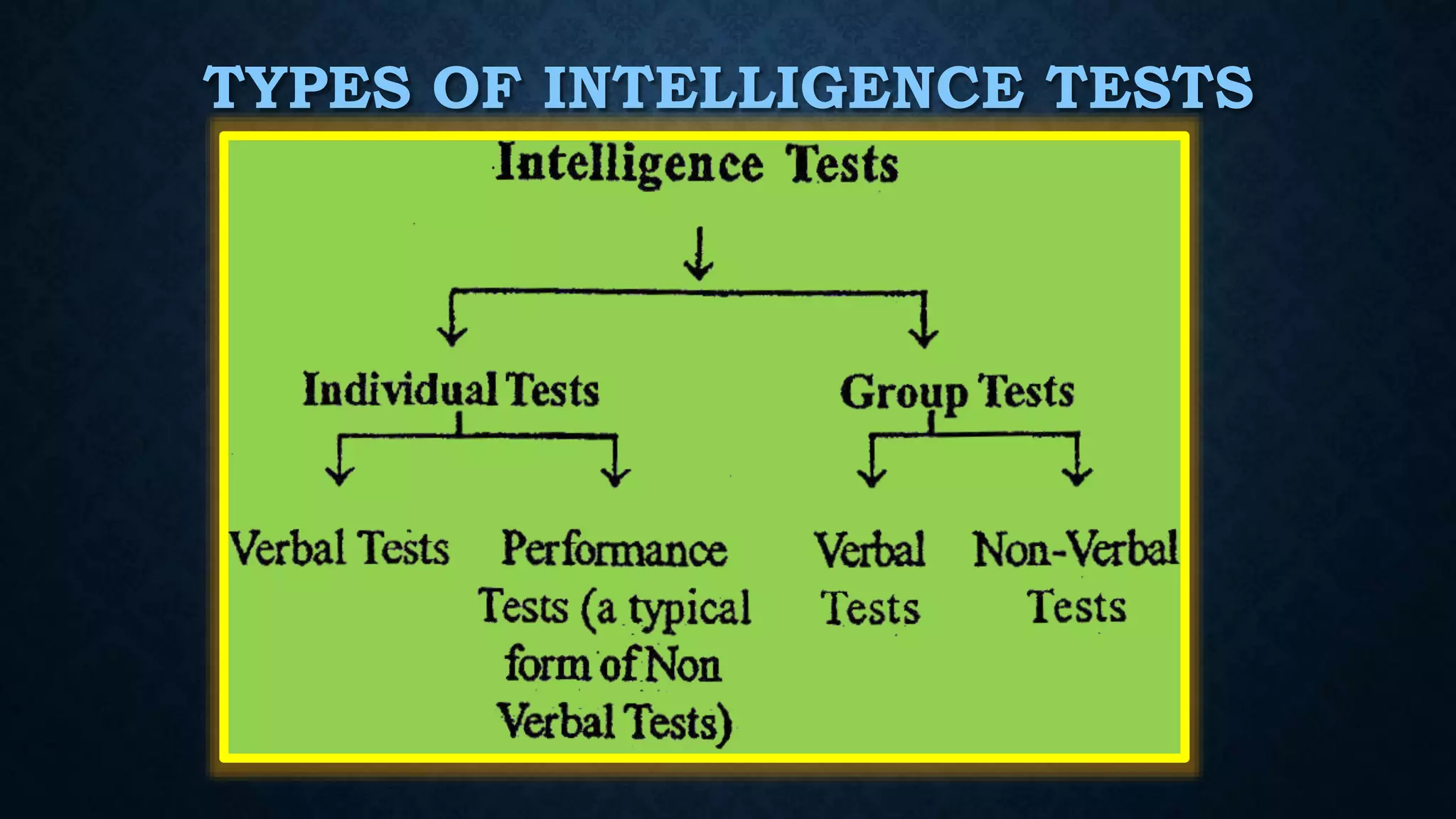
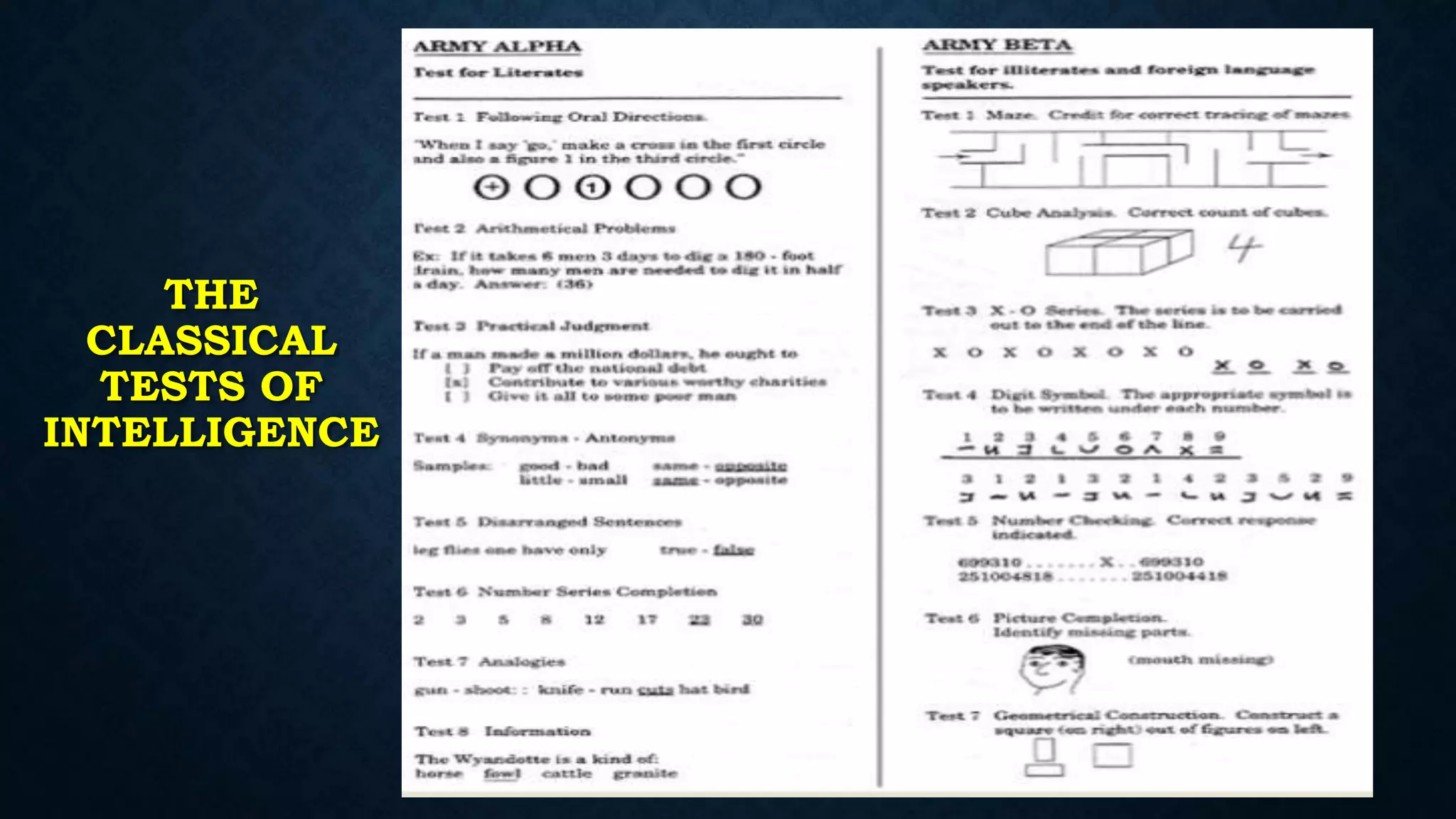
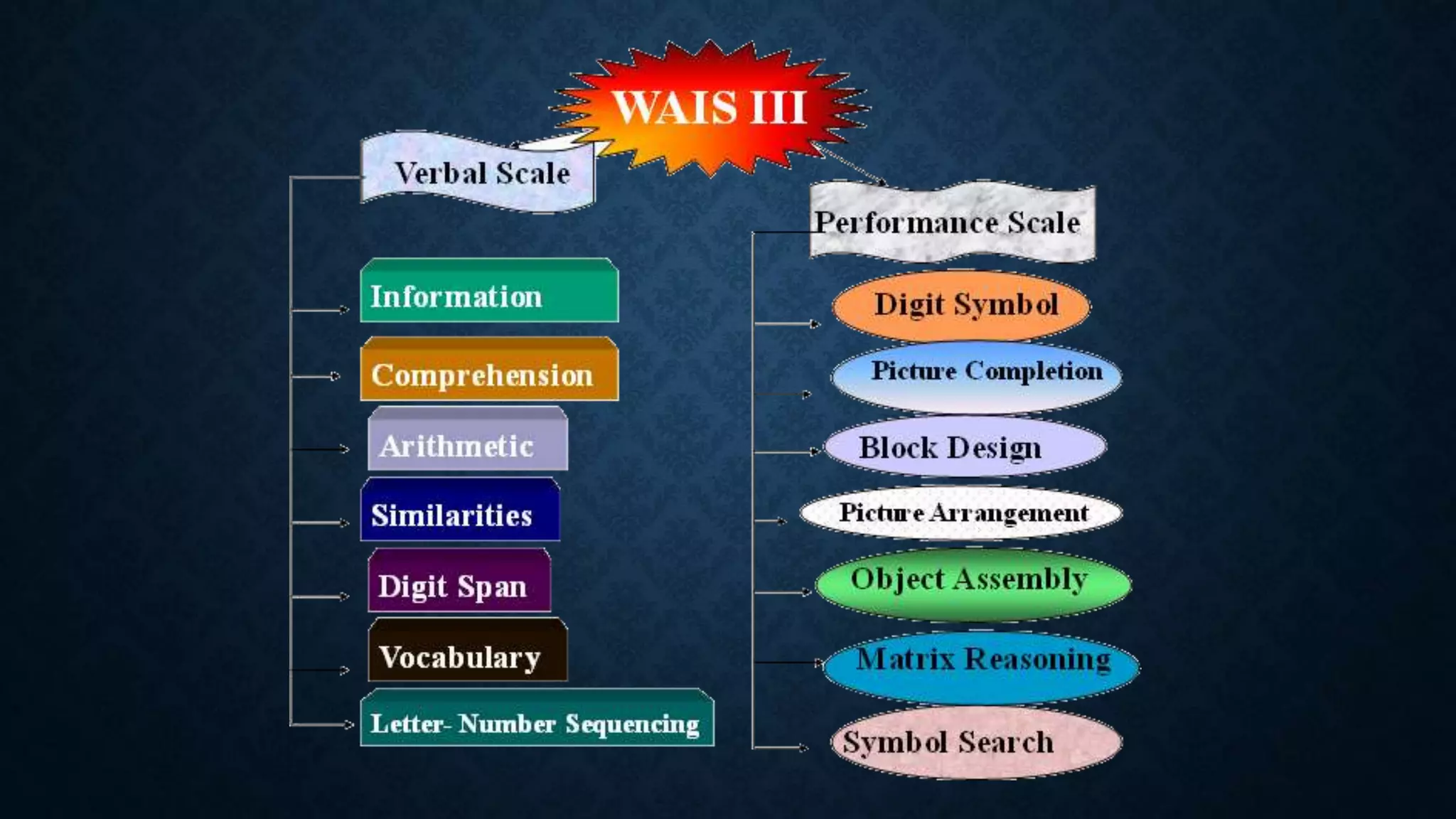
The document provides an extensive overview of intelligence theories, definitions, and assessments, including contributions from notable figures such as Albert Binet and Howard Gardner. It covers a range of intelligence types, including multiple intelligences and the triarchic theory, along with various intelligence tests used in practice. Additionally, it discusses the concept of giftedness, its characteristics, and the environmental and genetic influences on intelligence.