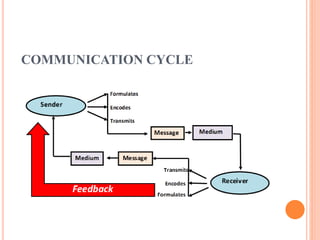
This document provides an overview of communication, including its definition, components, types, steps, factors affecting it, and barriers. Communication is defined as the mutual exchange of facts, thoughts, or emotions between a sender and receiver. The key components are the sender, message, medium, receiver, and feedback. Types of communication include speaking-listening, writing-reading, visualizing-observing, and doing-learning. The steps in communication are ideation, encoding, transmission, receiving, decoding, and responding. Factors like the sender's perception and the receiver's readiness can affect communication. Barriers include inaudibility, unfamiliar terms, facilities, language proficiency, environment, and speech speed.