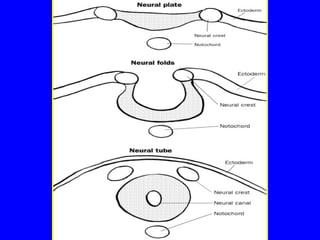
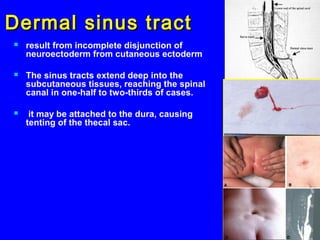
This document discusses congenital anomalies of the central nervous system, including their etiology, primary neurulation, neural tube closure, and specific disorders. Key points include: Folic acid deficiency and infections like rubella can cause anomalies. Primary neurulation occurs around 3-4 weeks and involves the neural tube, epidermis, and neural crest. Neural tube closure begins in the cervical region and finishes around day 29. Specific disorders result from failures of these processes and include anencephaly, meningocele, myelomeningocele, encephalocele, and Chiari malformation. Diagnosis involves imaging like MRI and treatment may involve surgical repair or decompression.