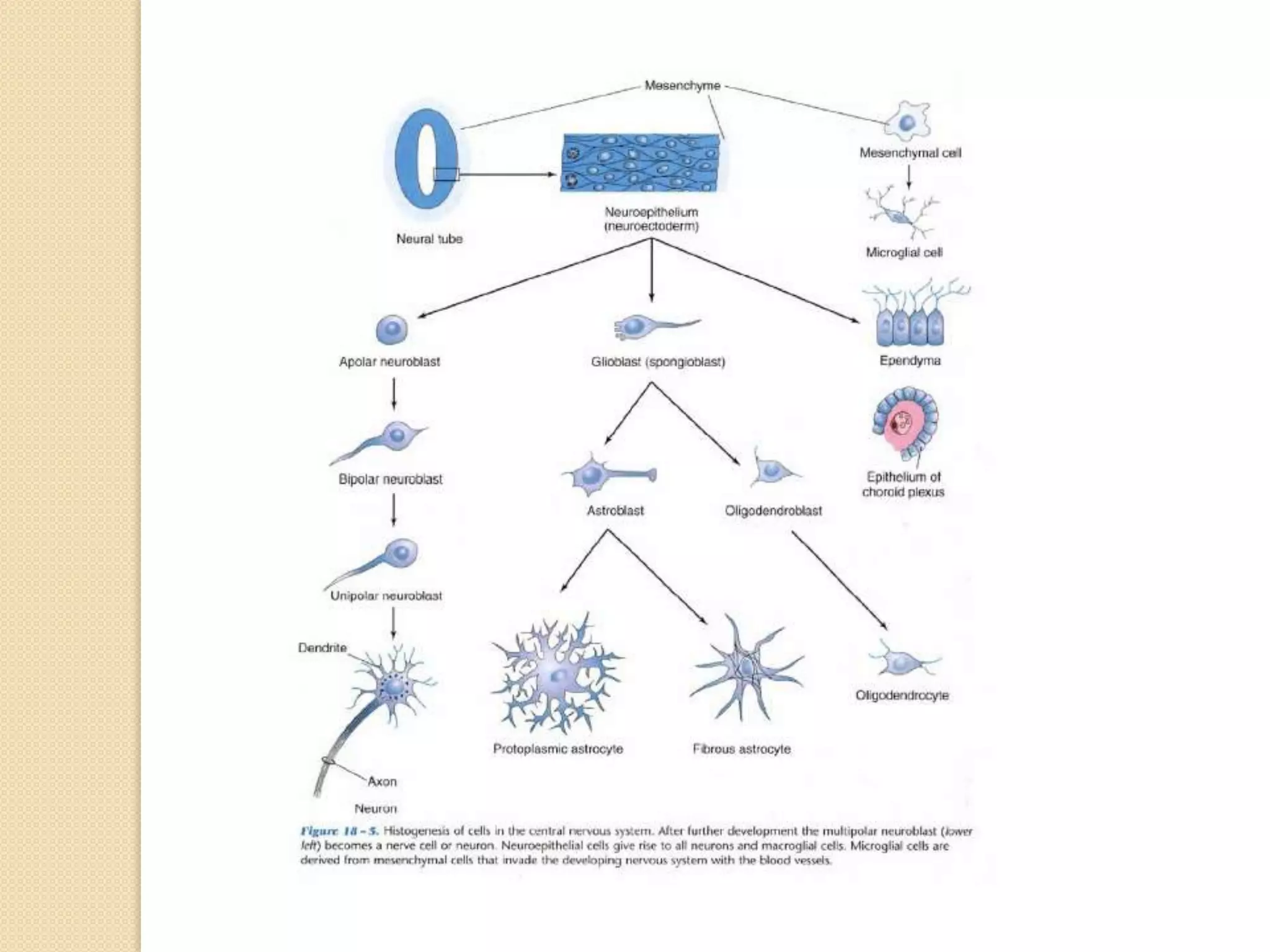
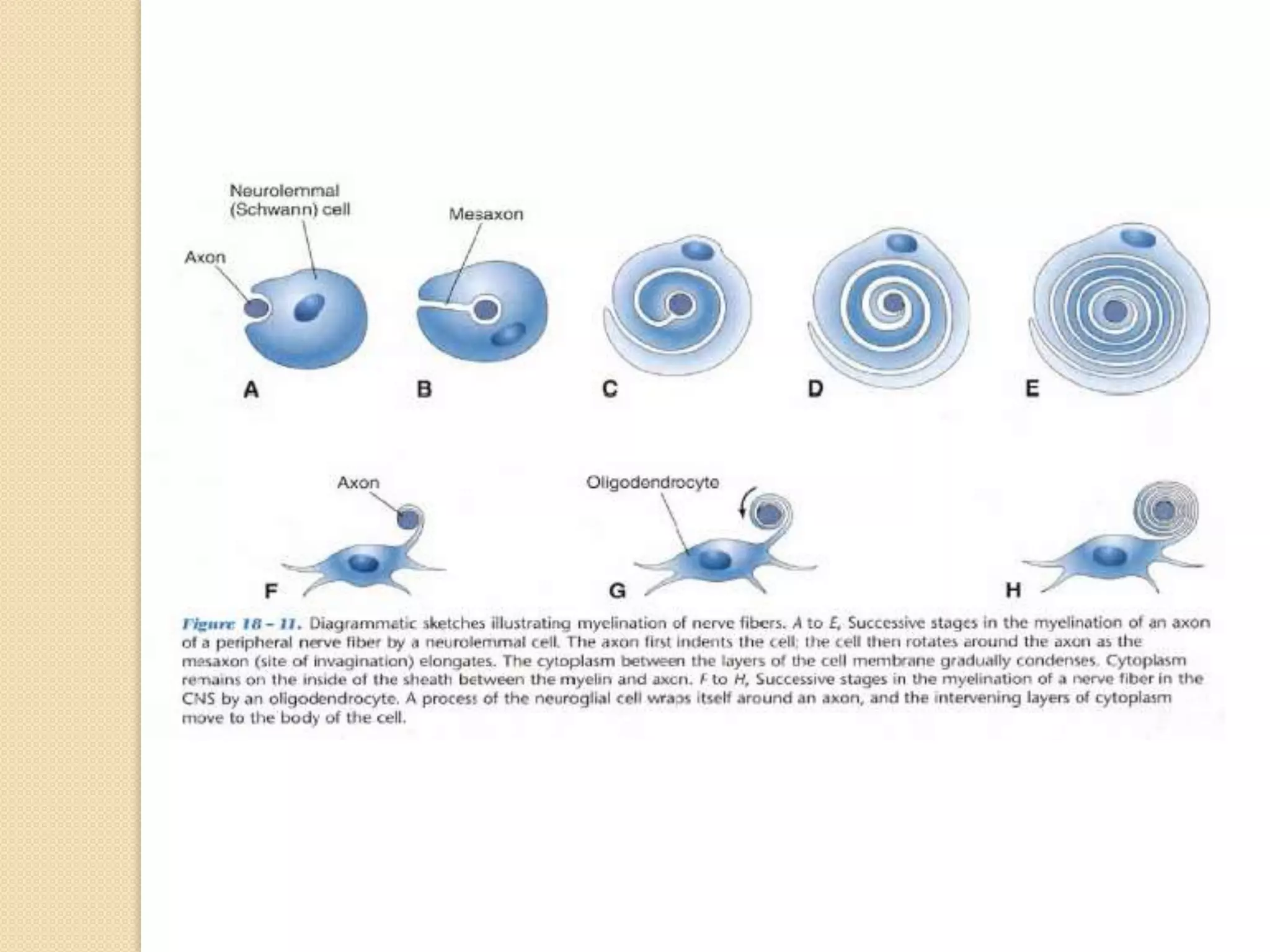
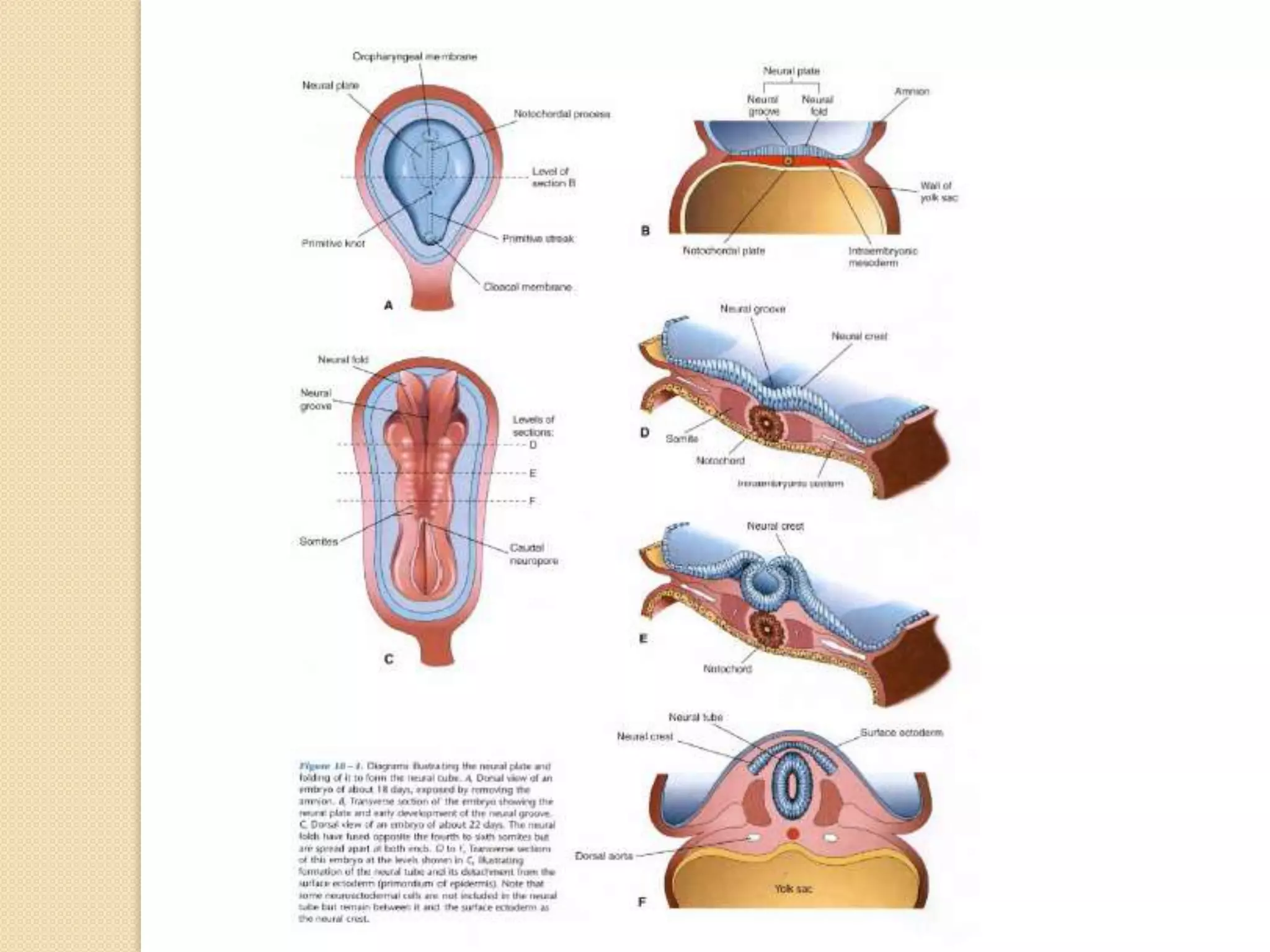
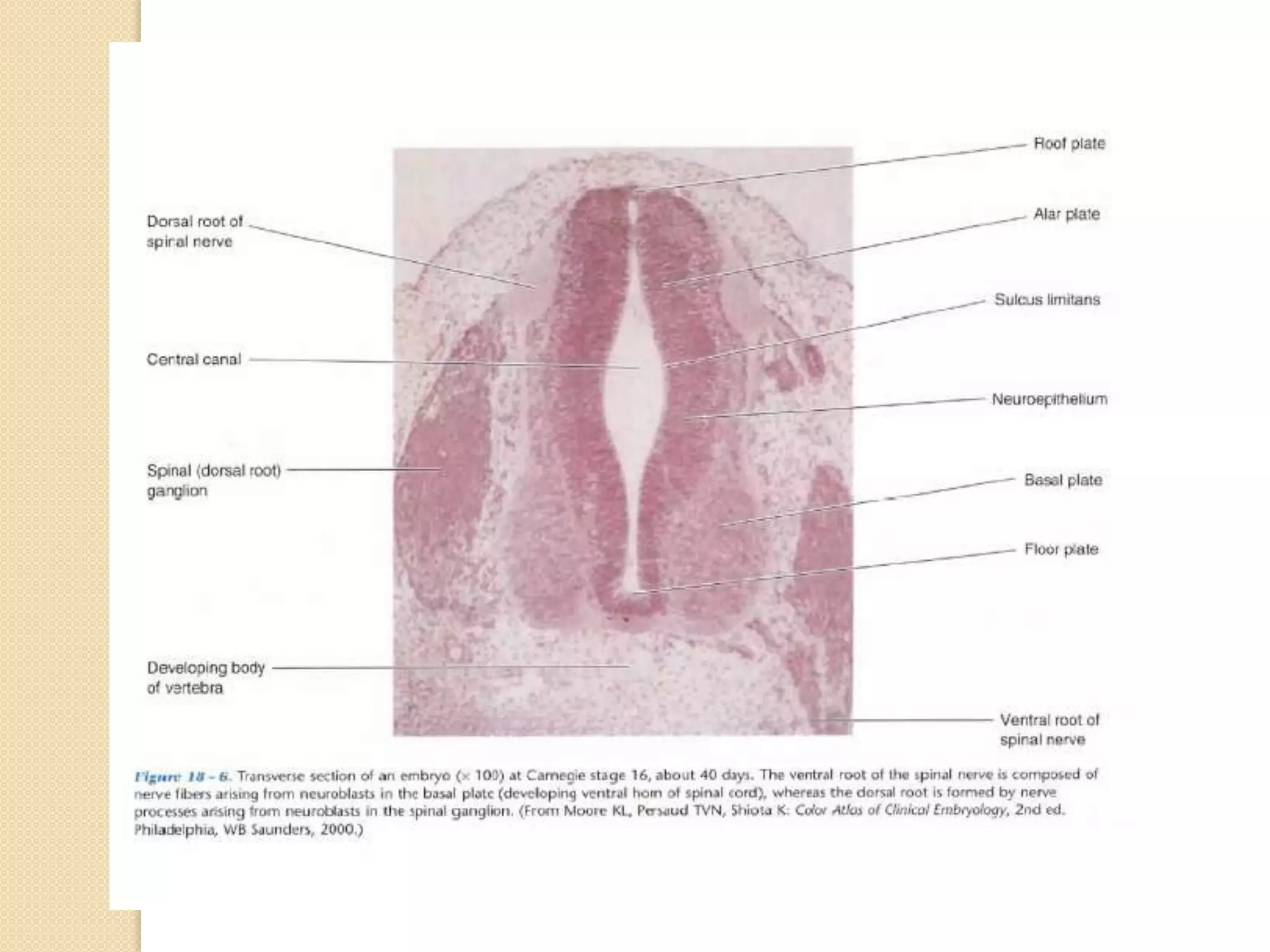
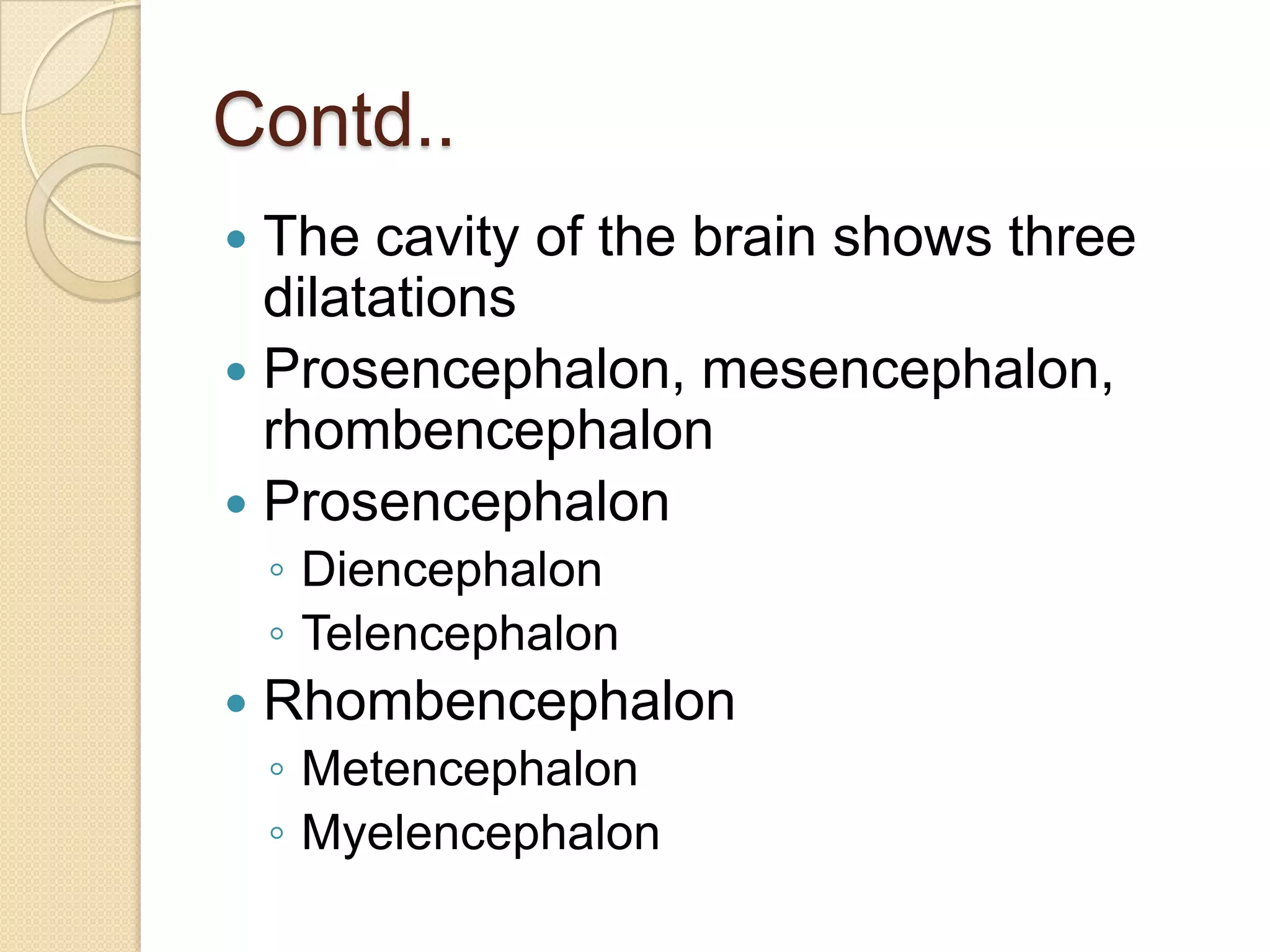
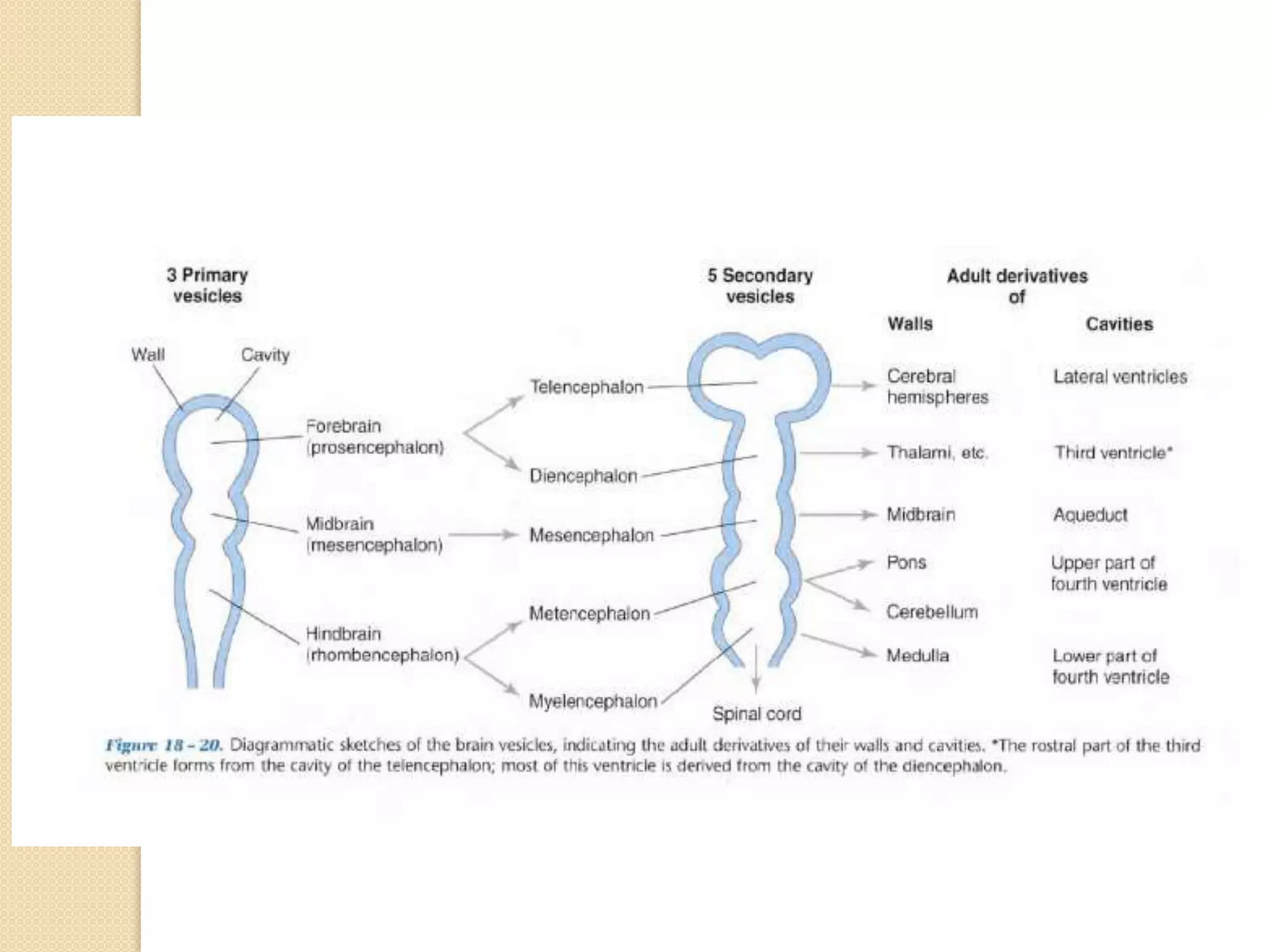
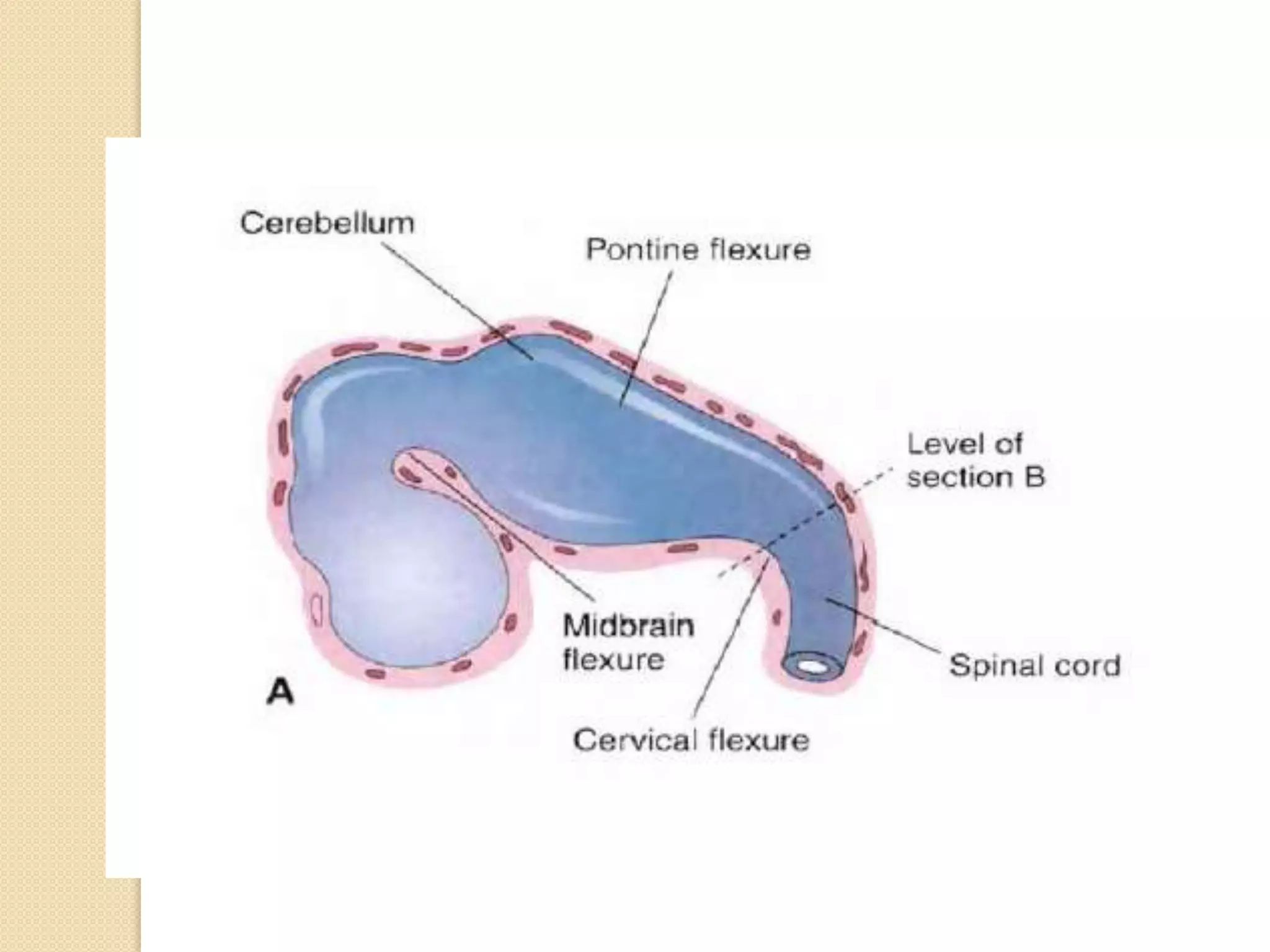
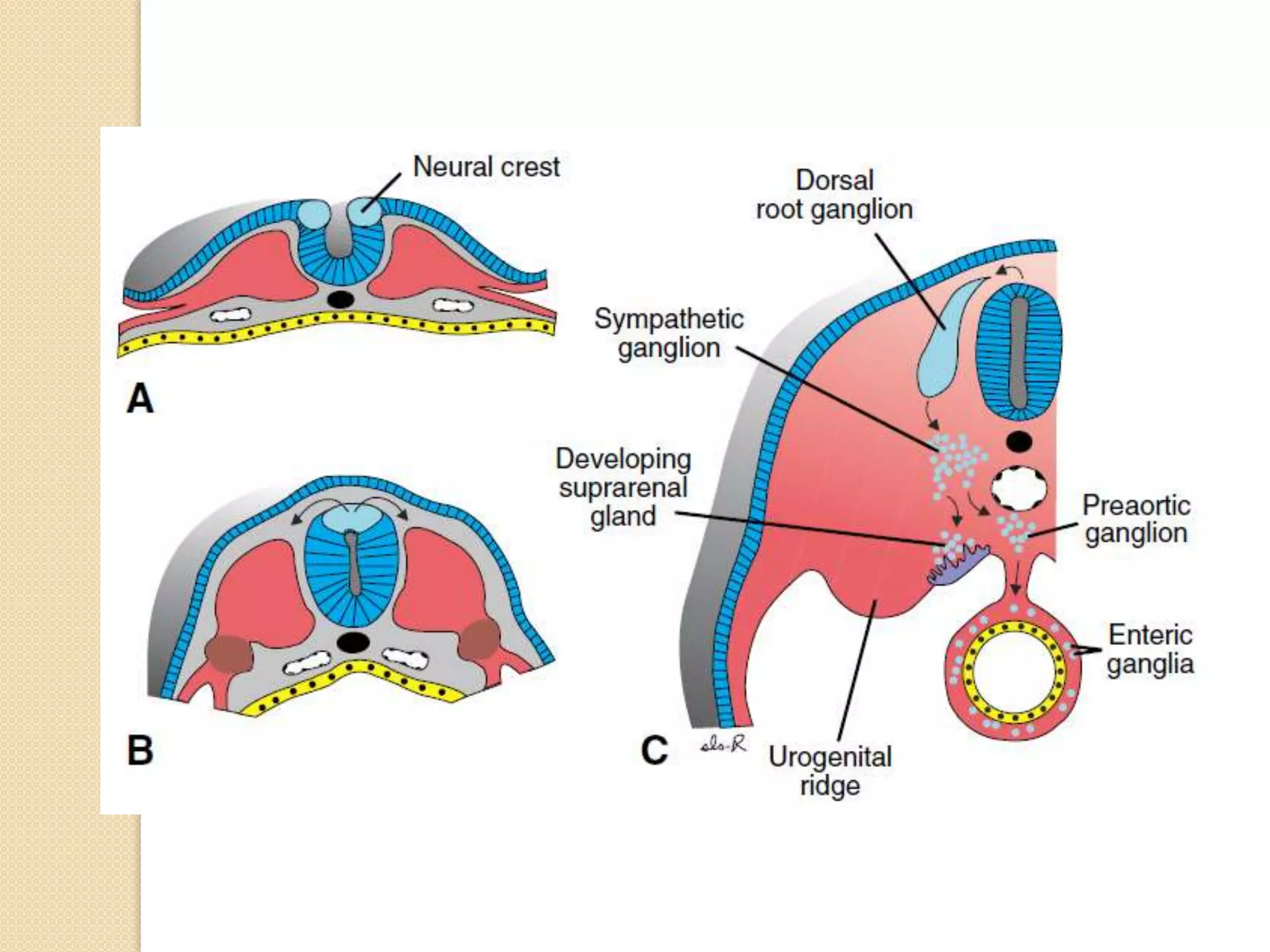
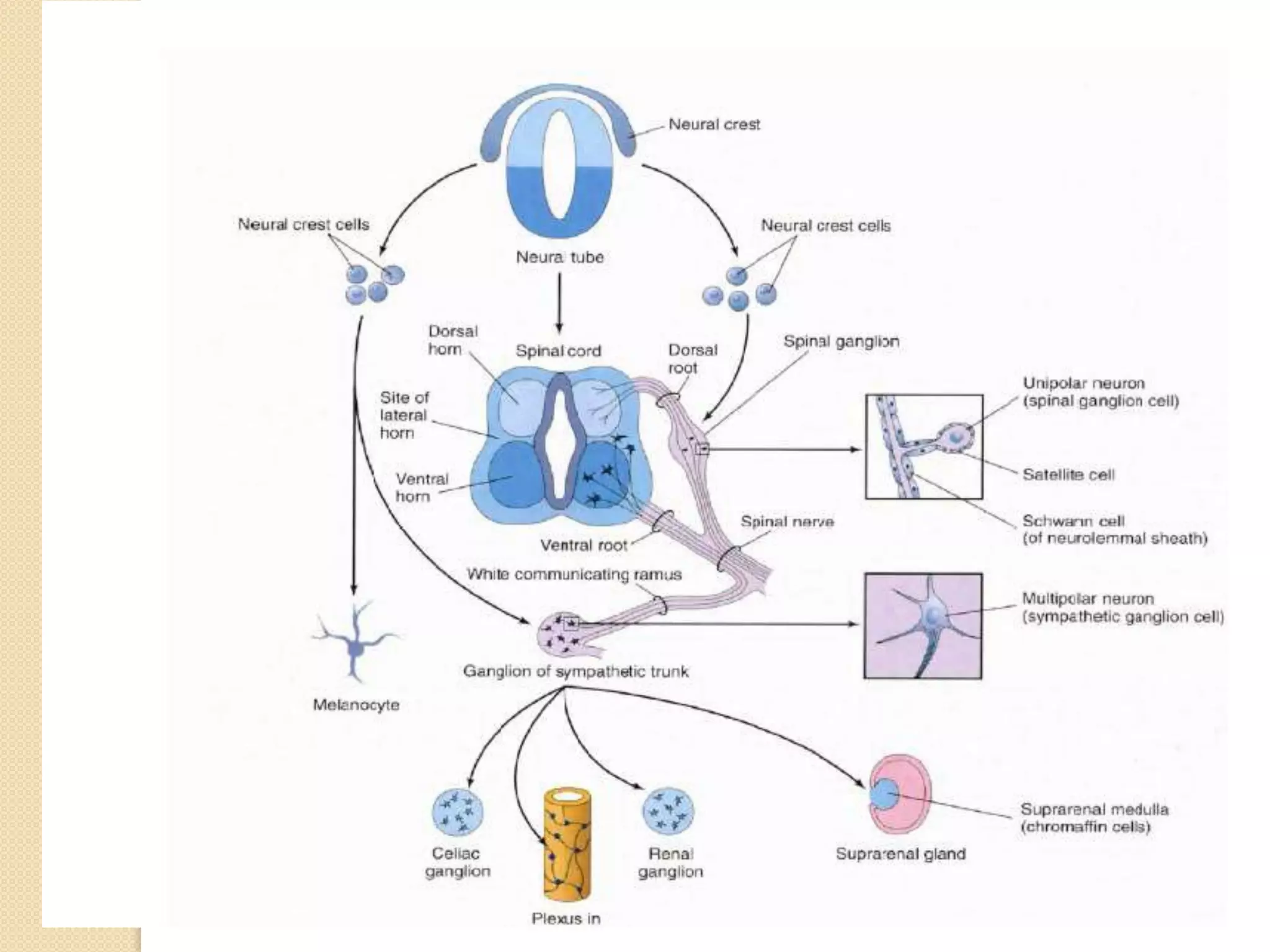
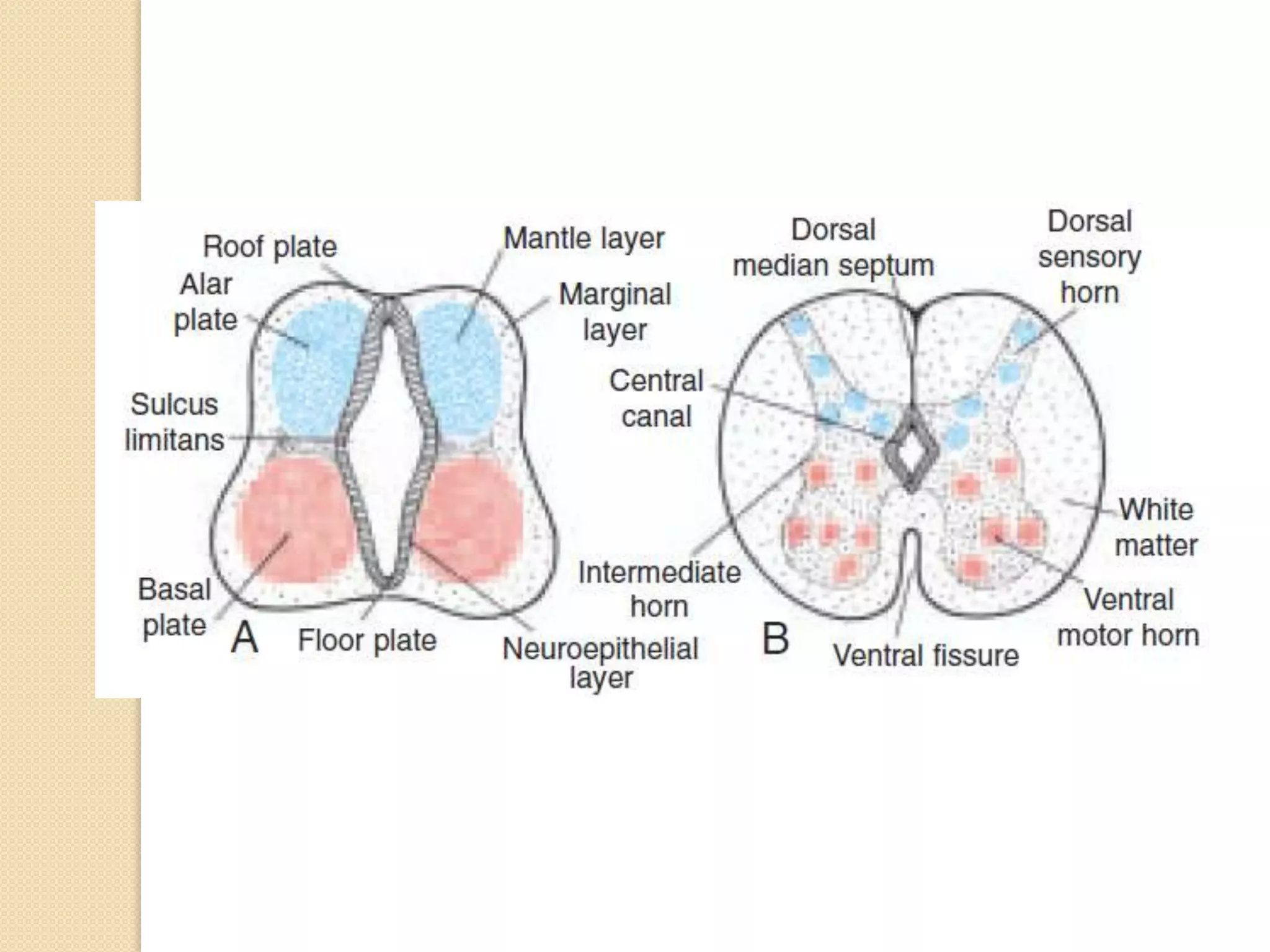
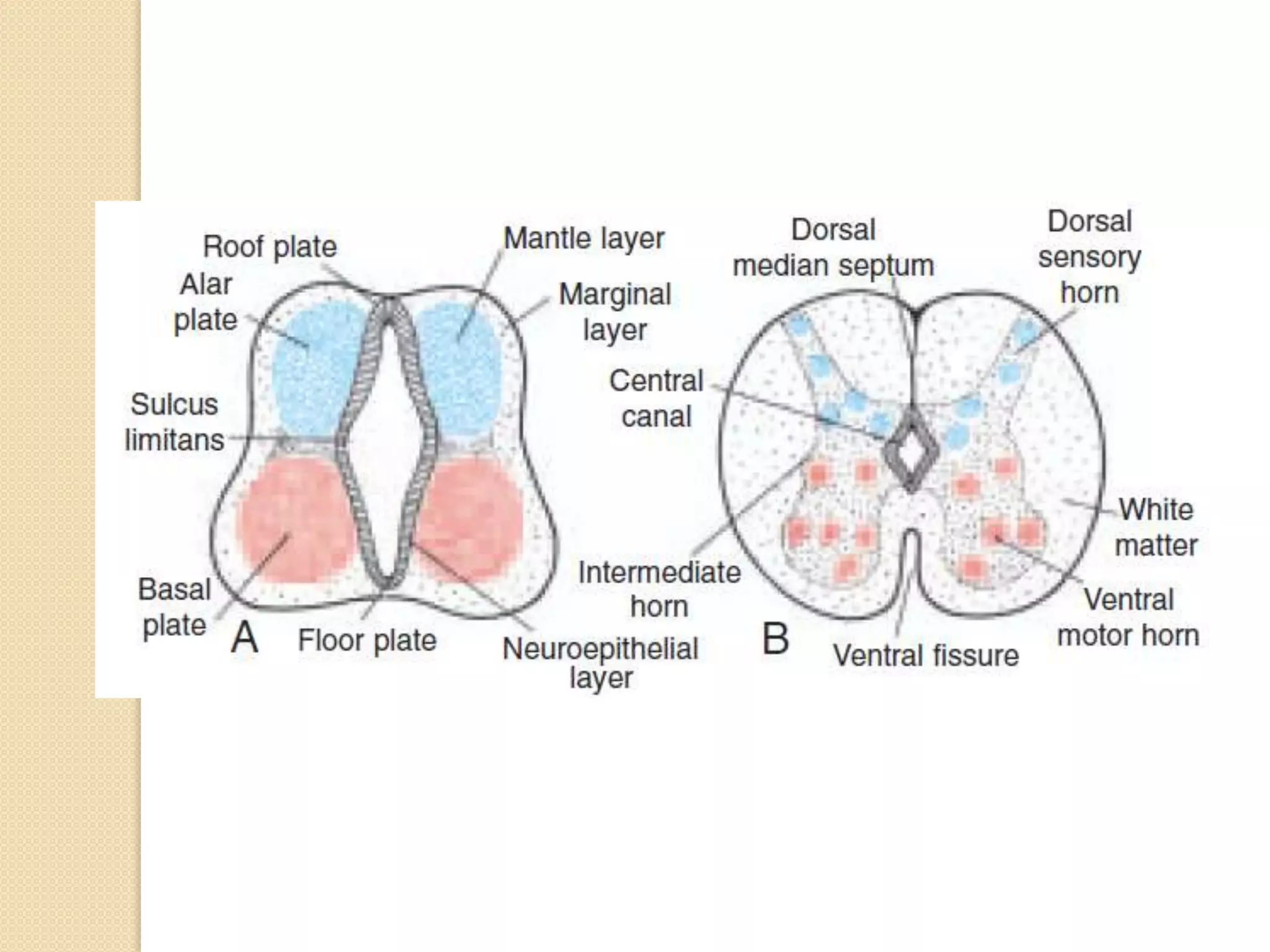
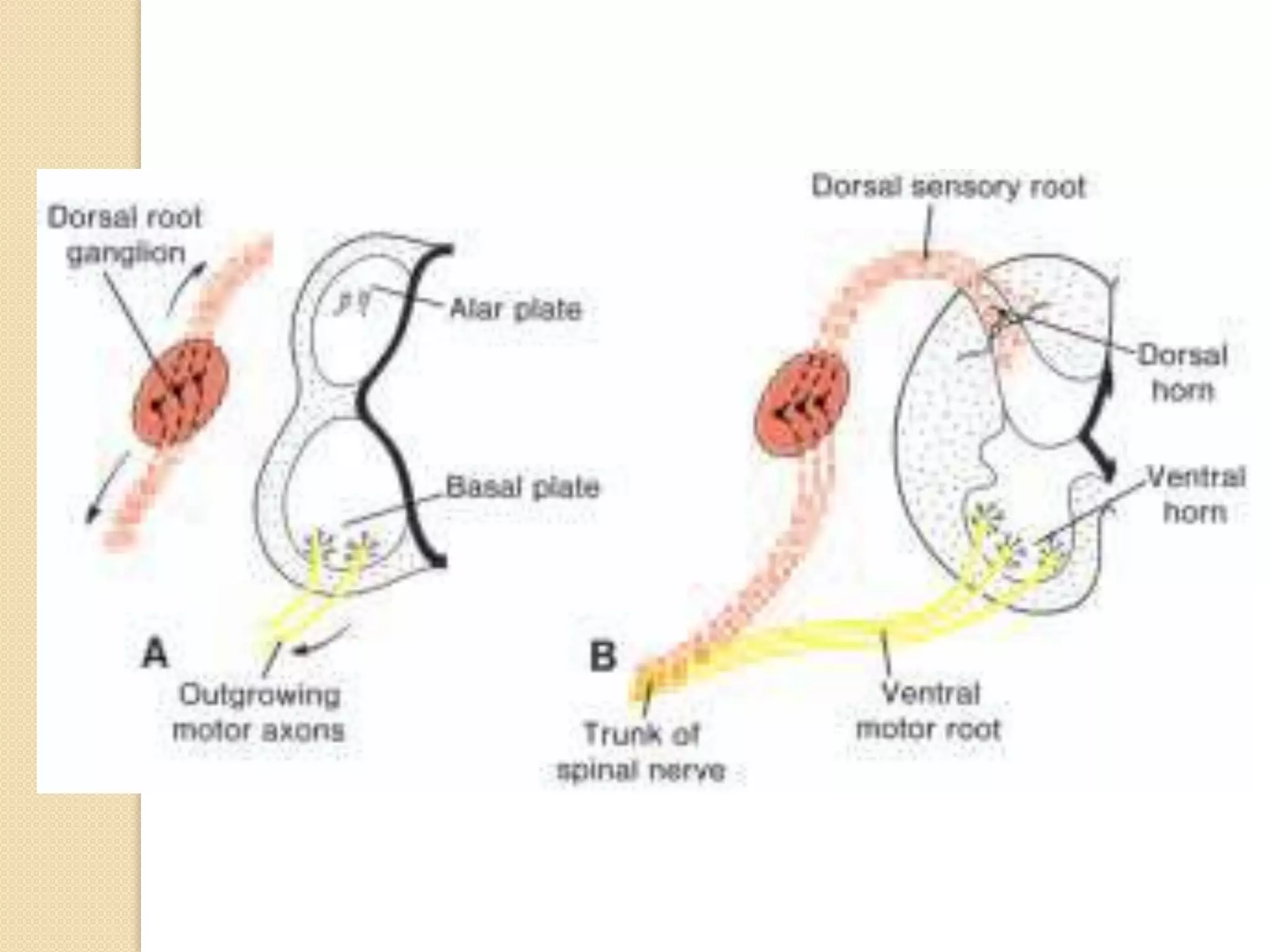
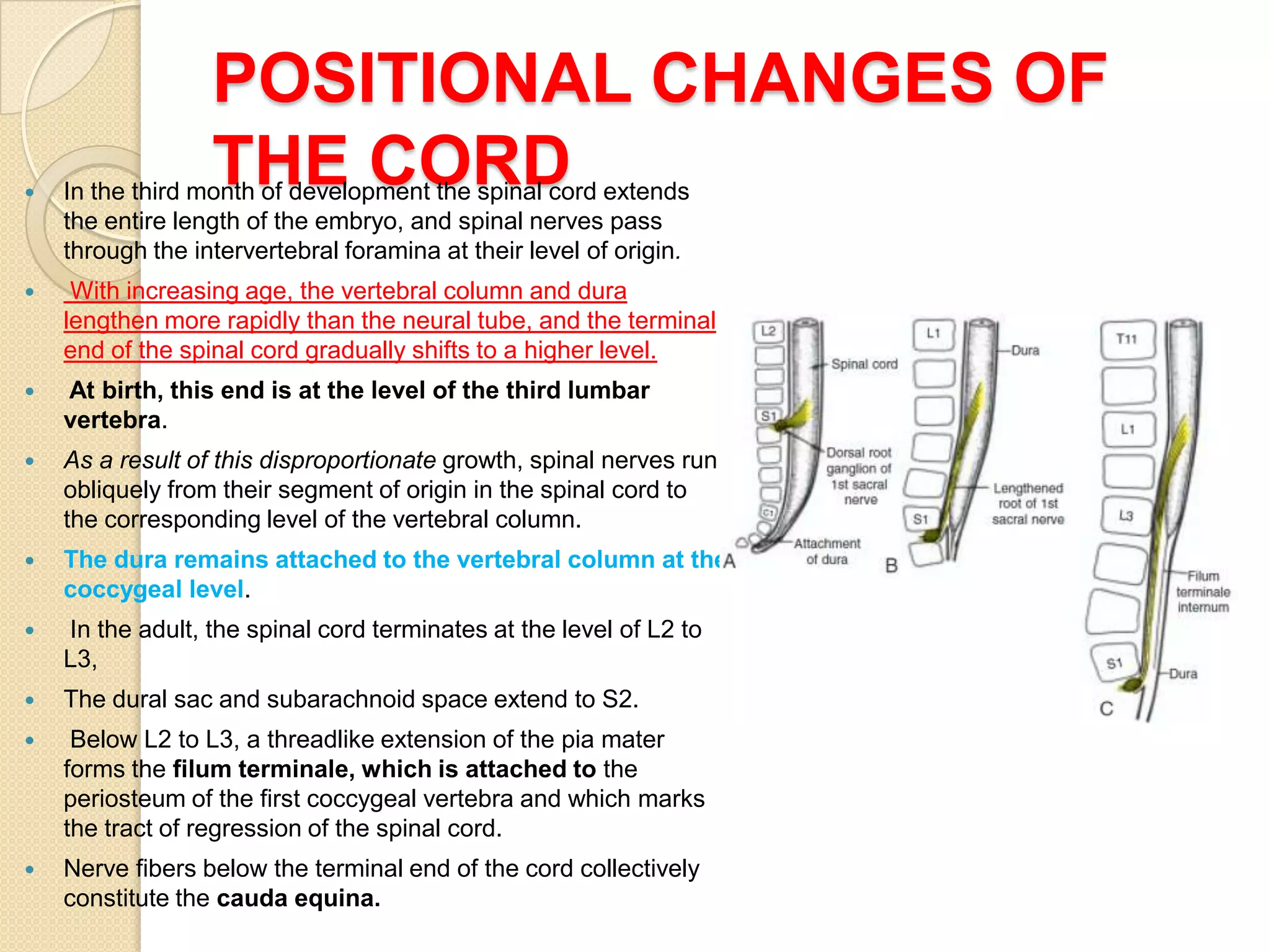
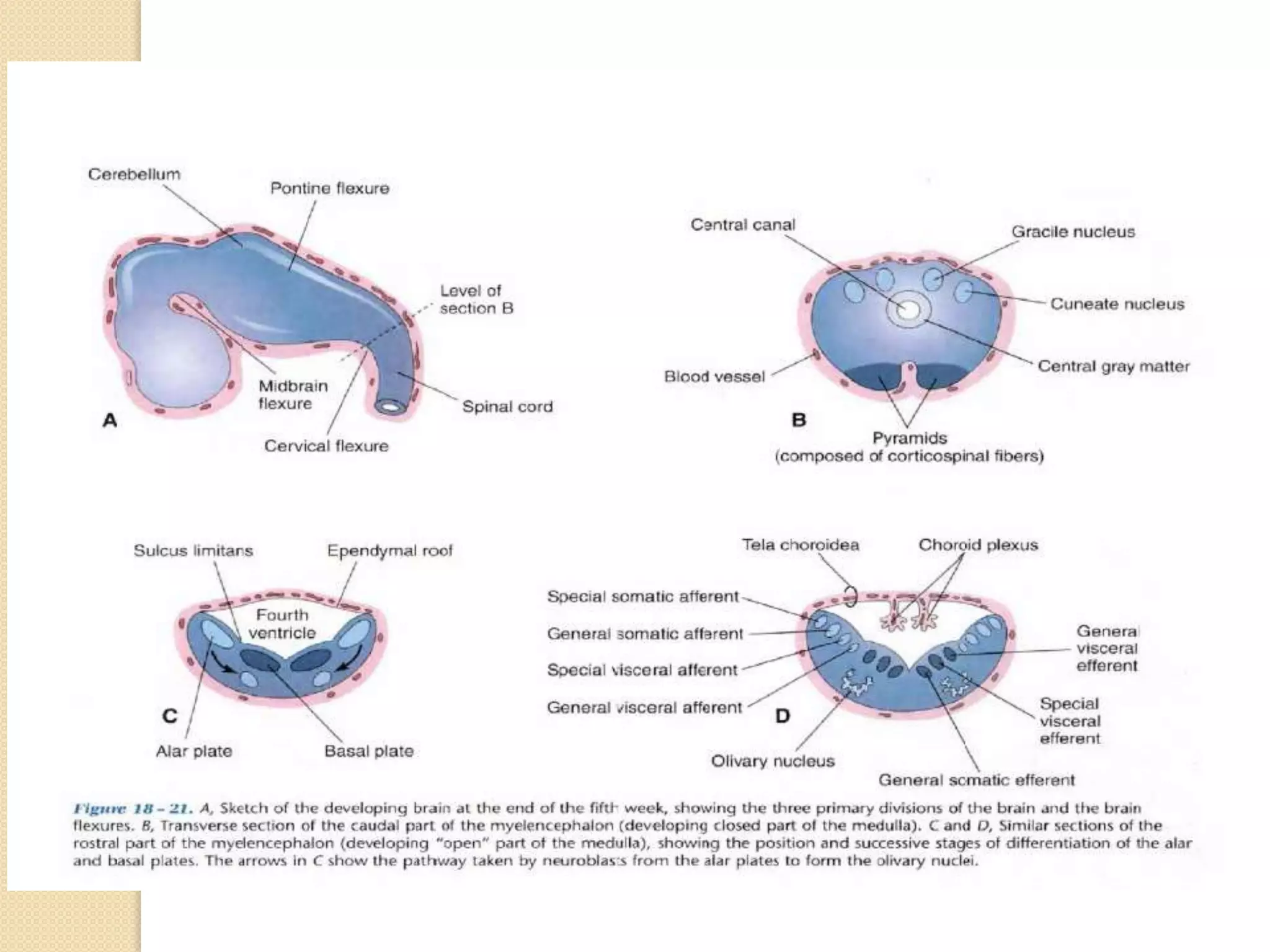
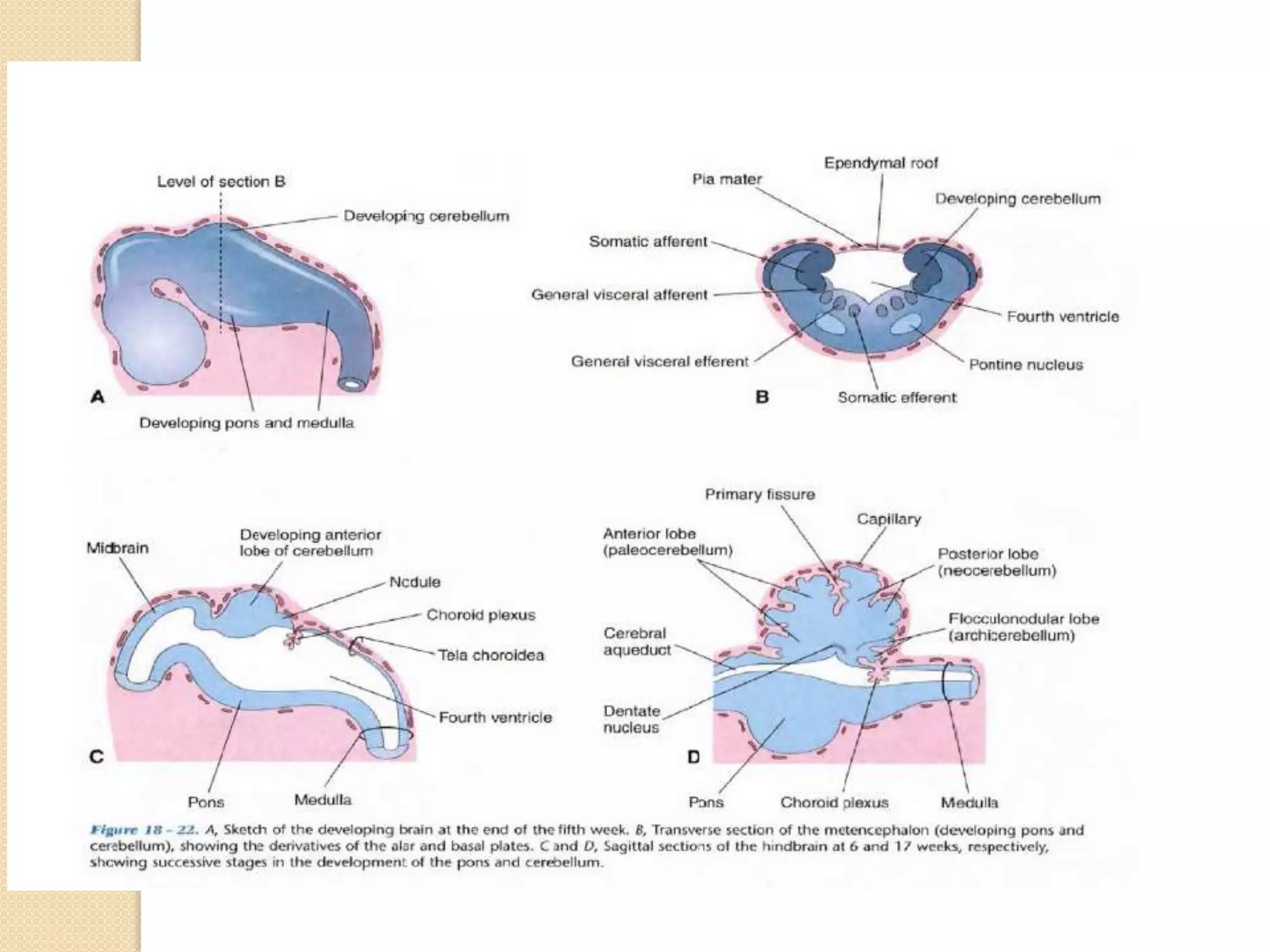
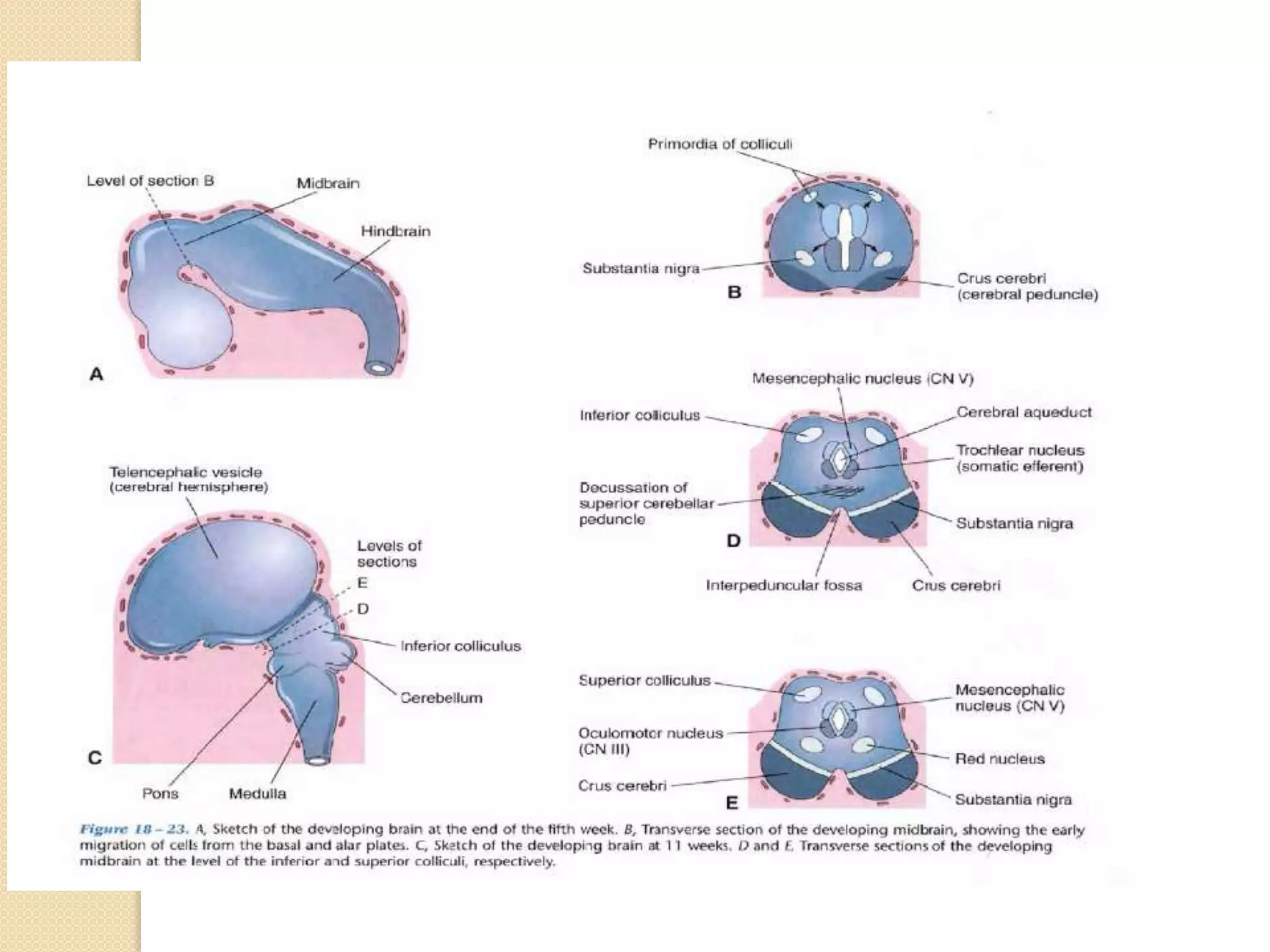
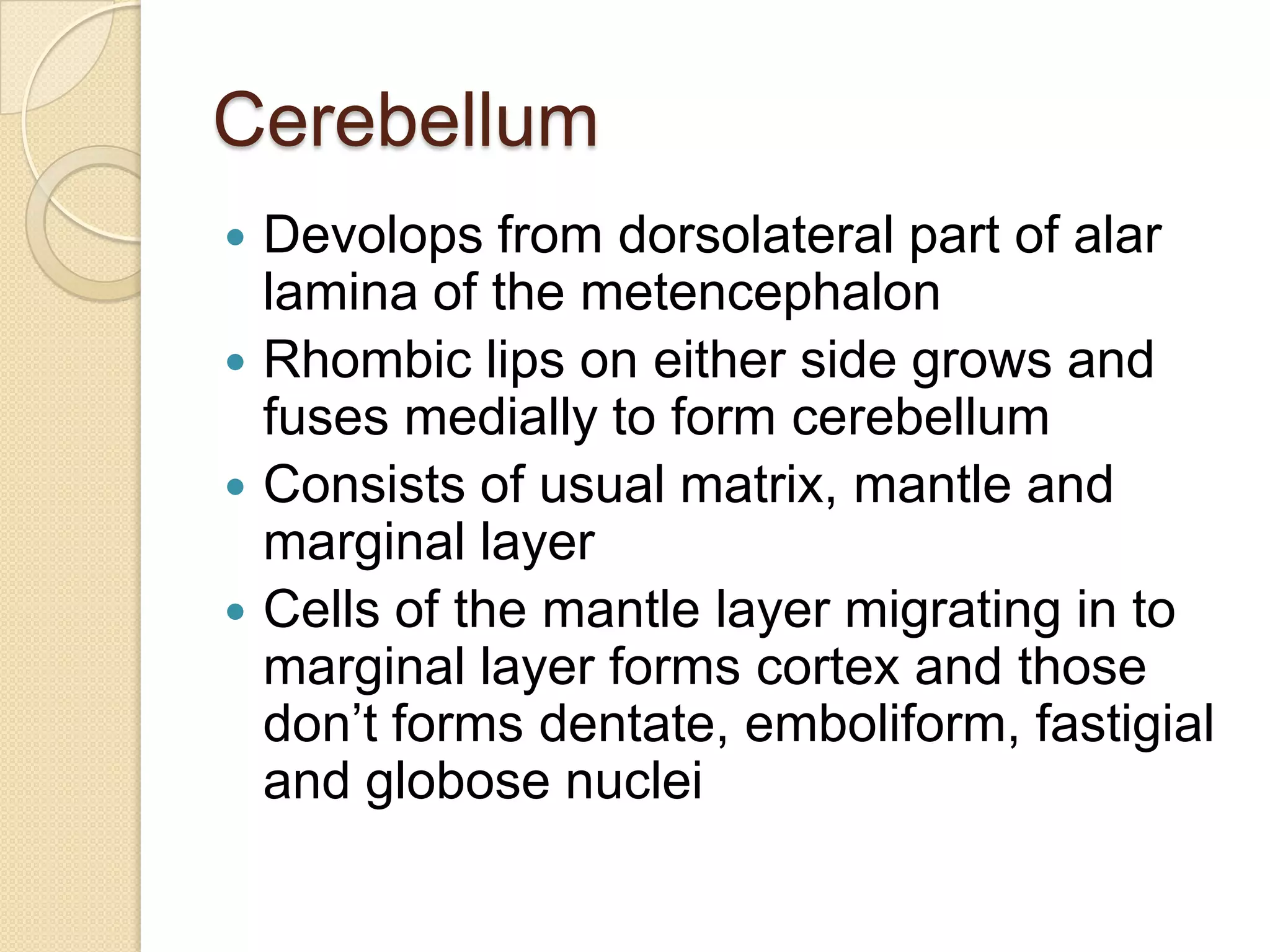
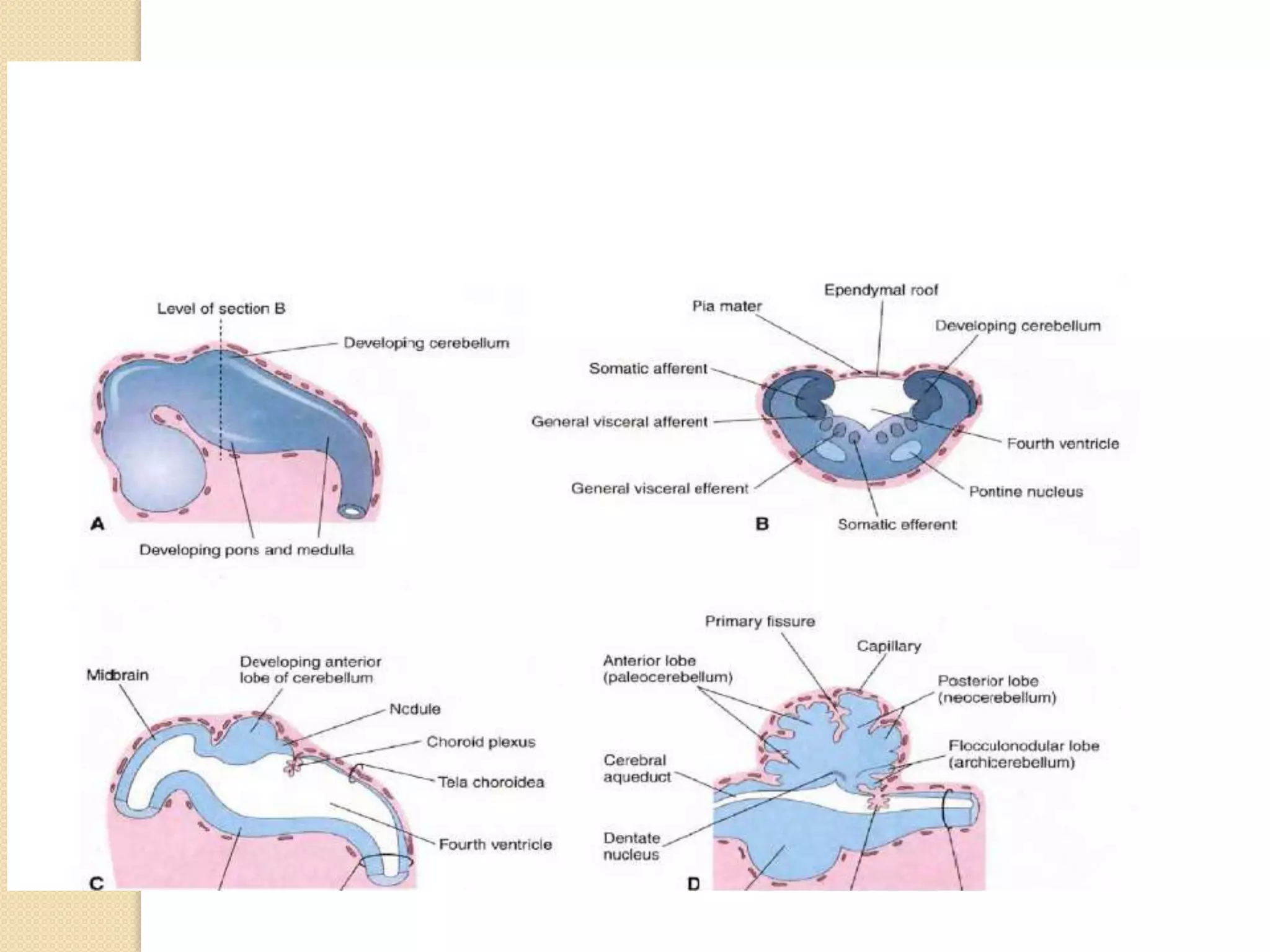
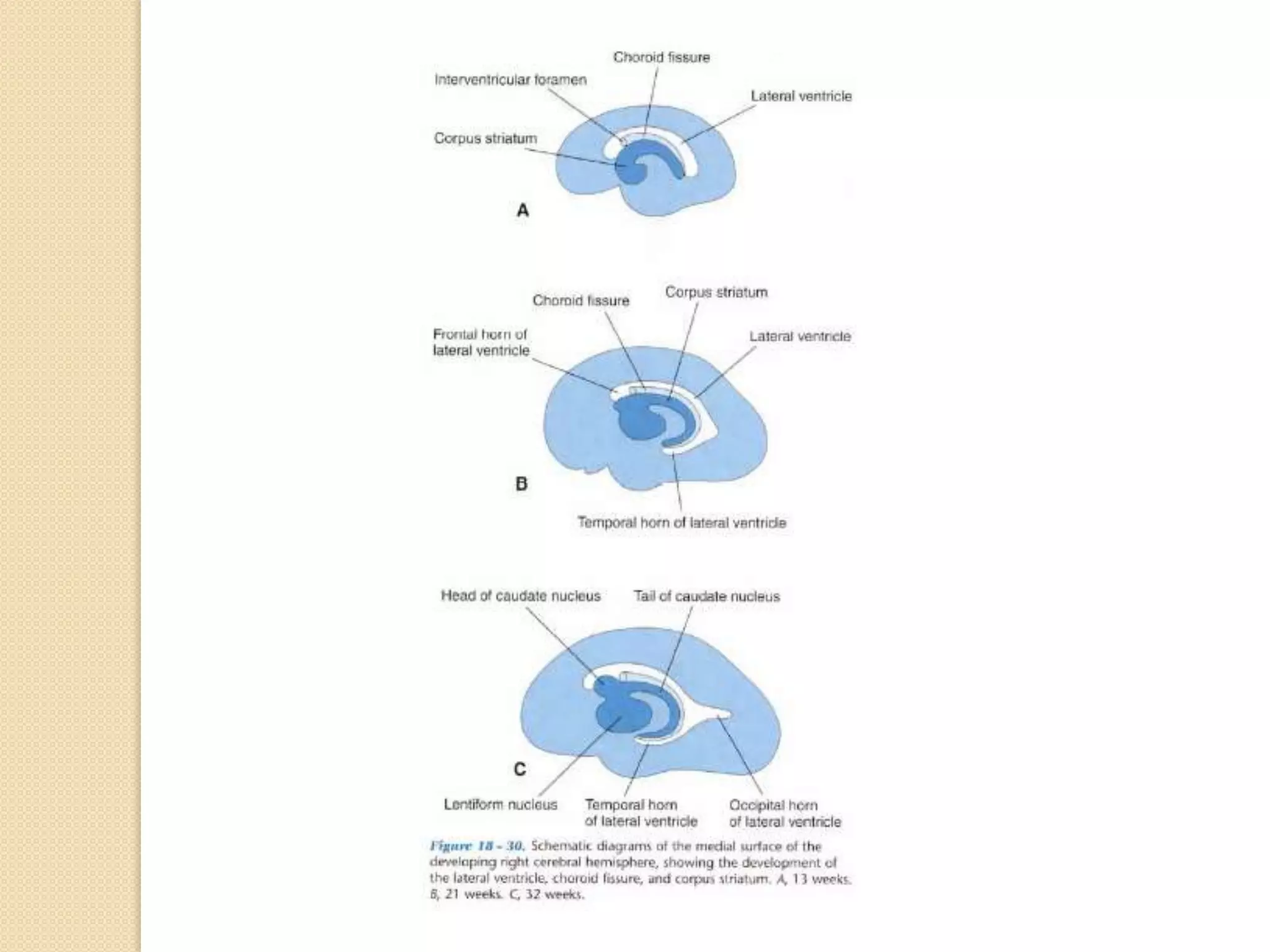
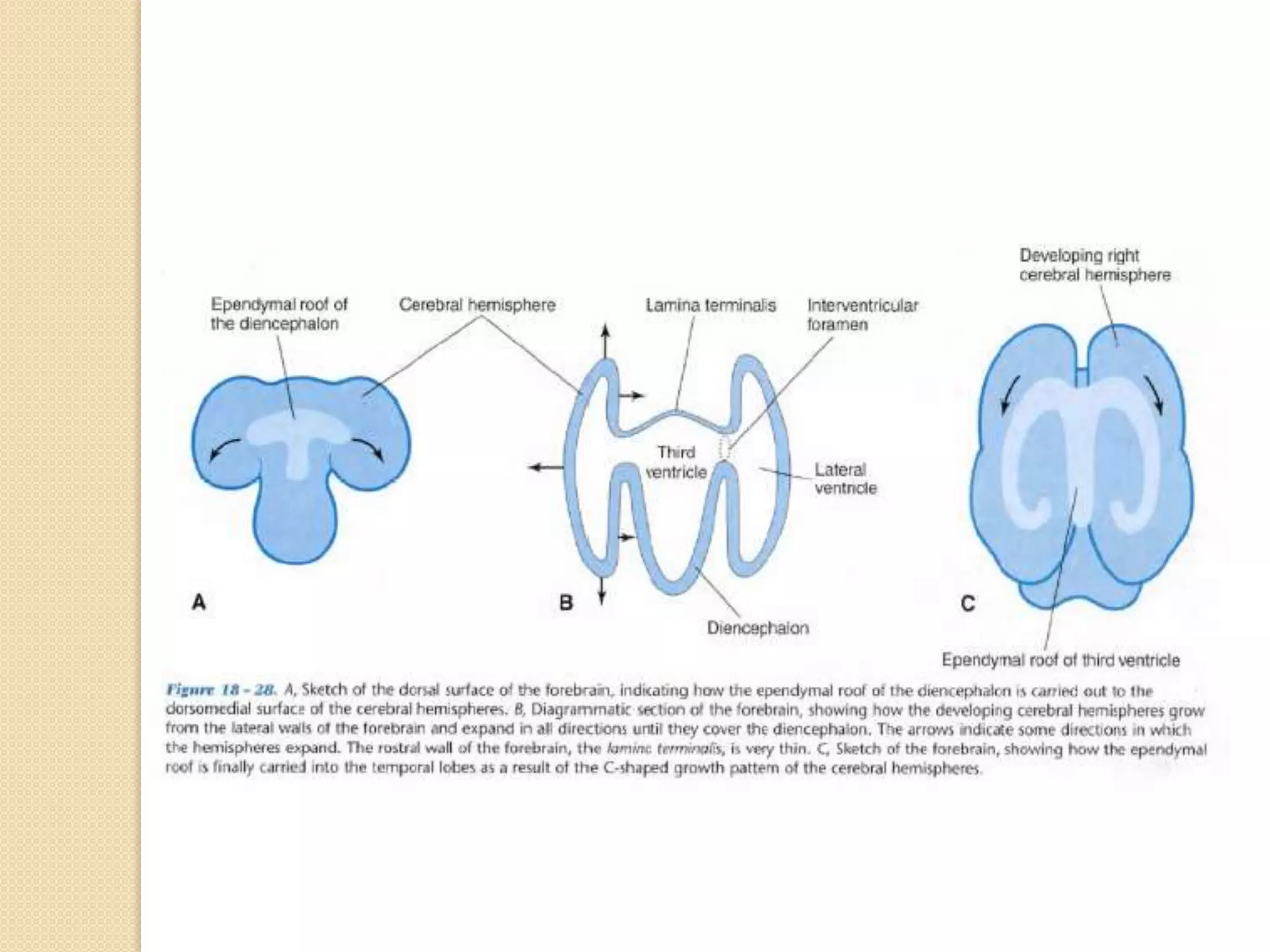
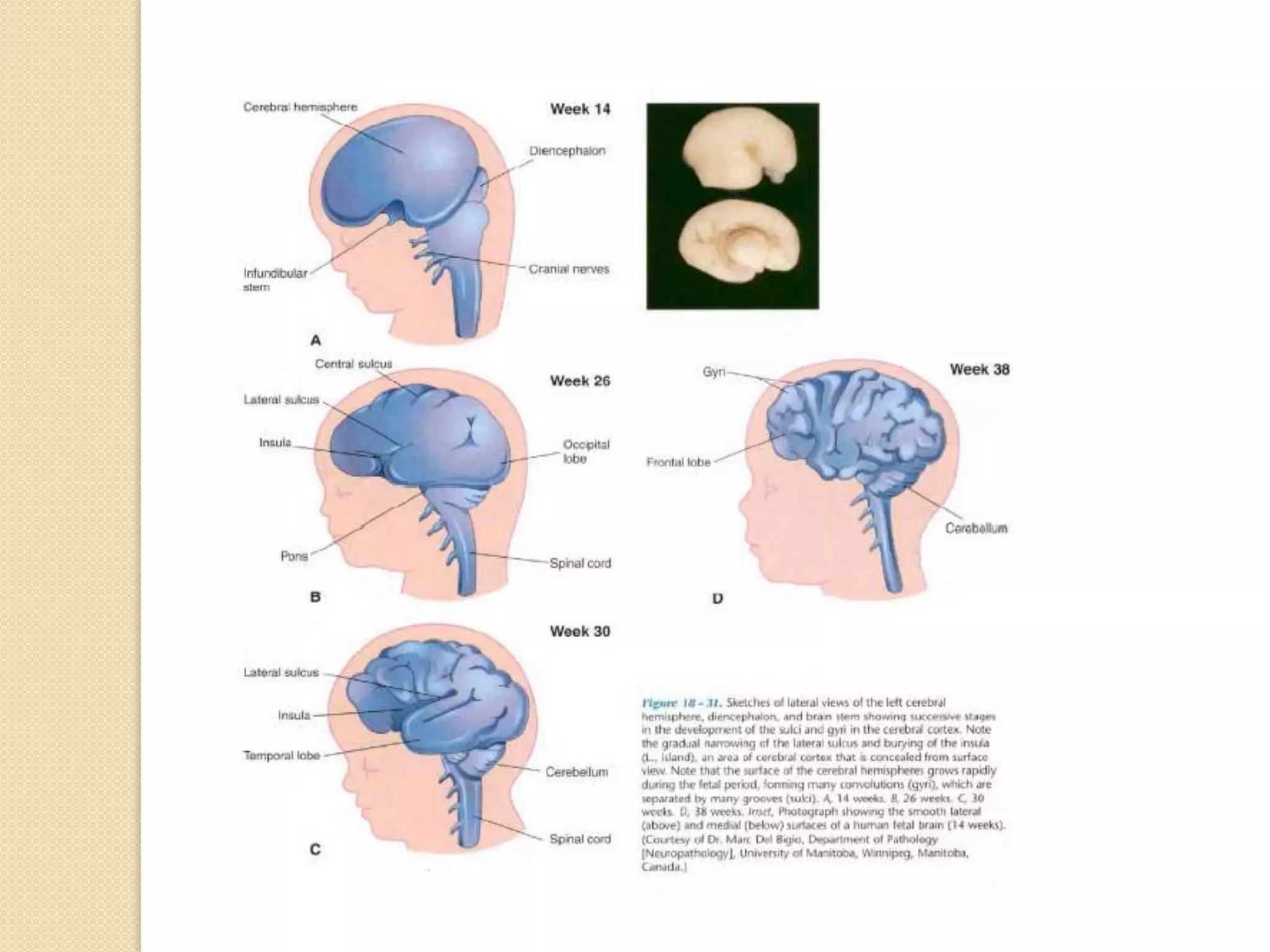
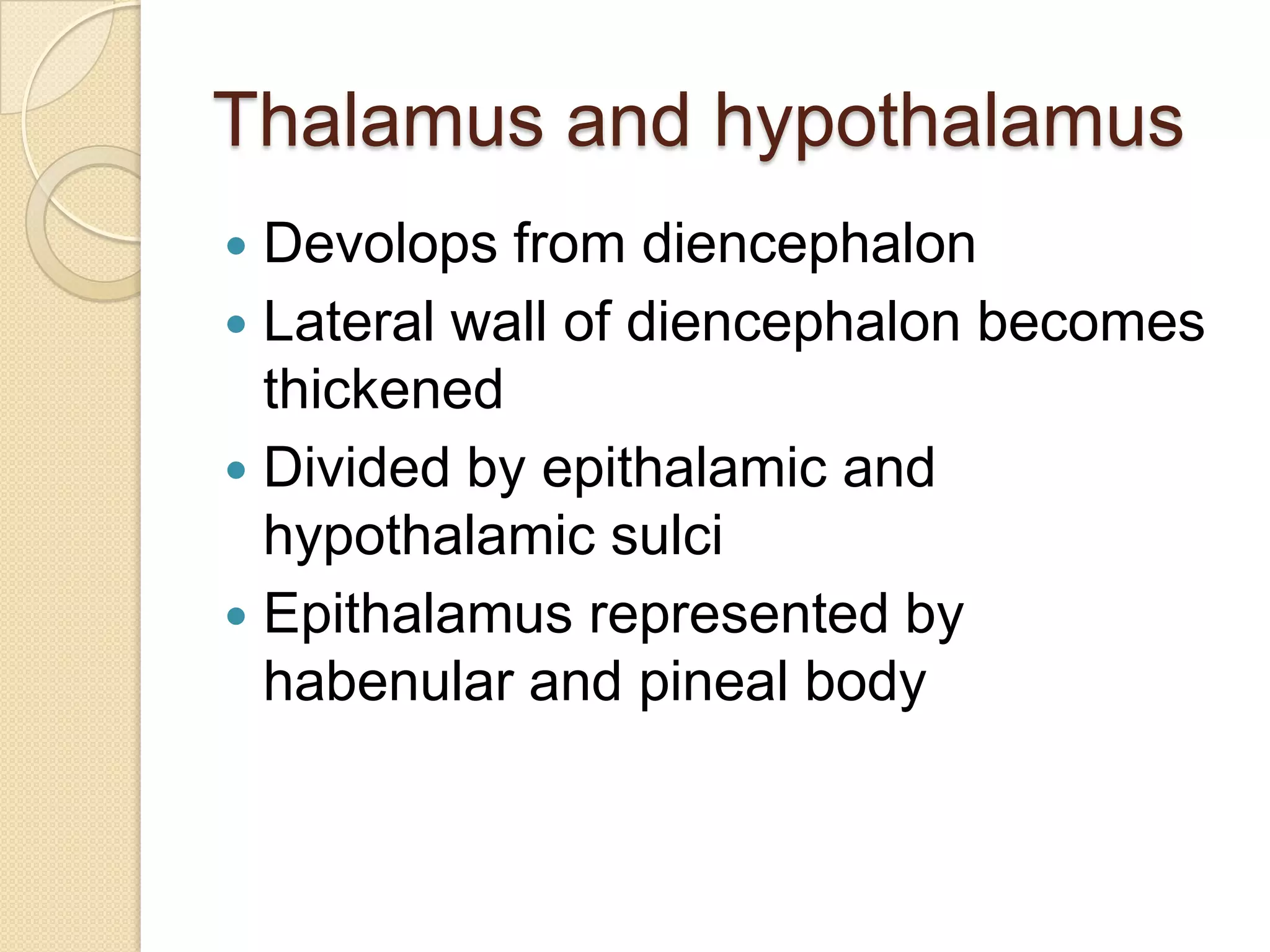
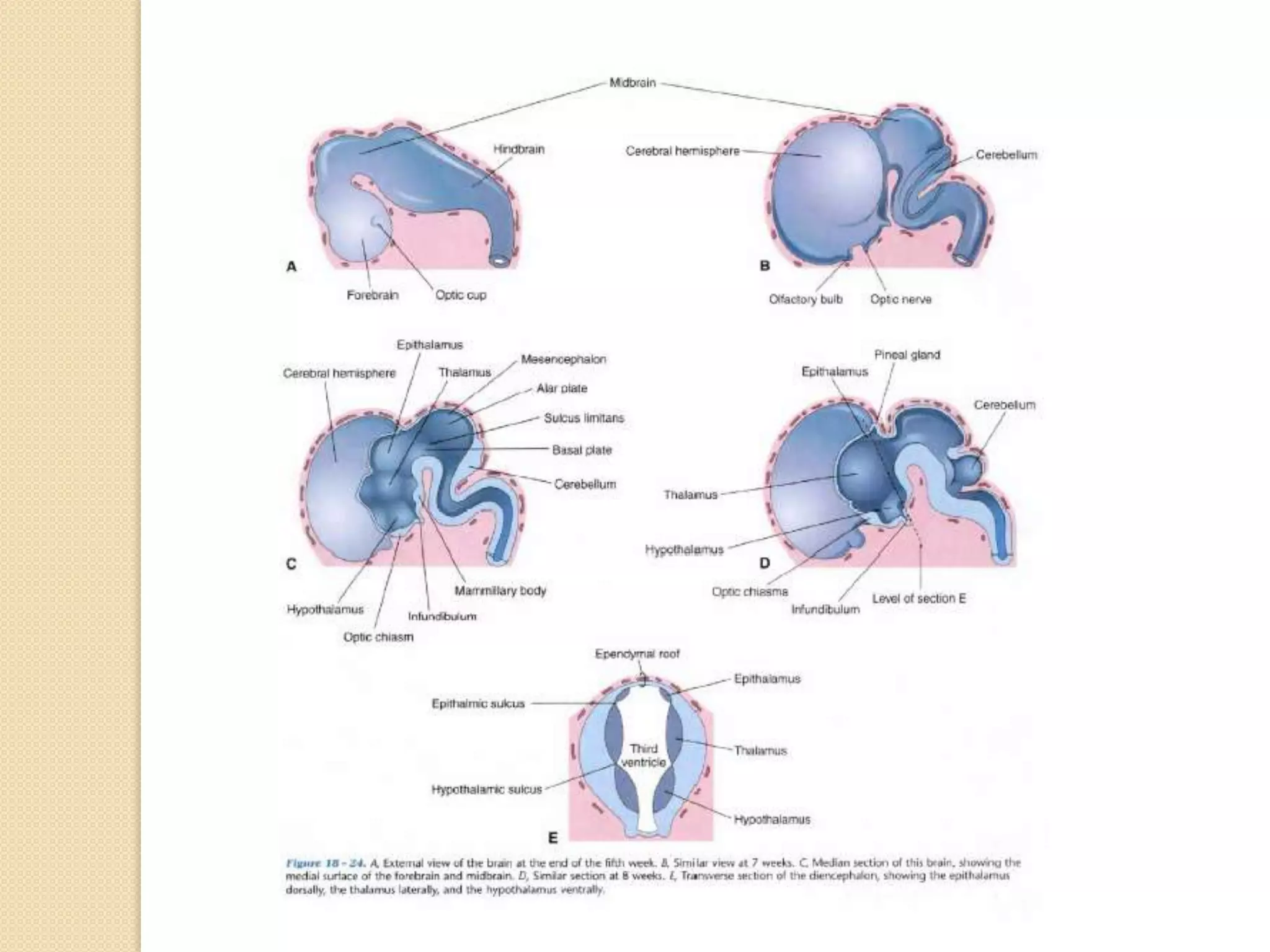
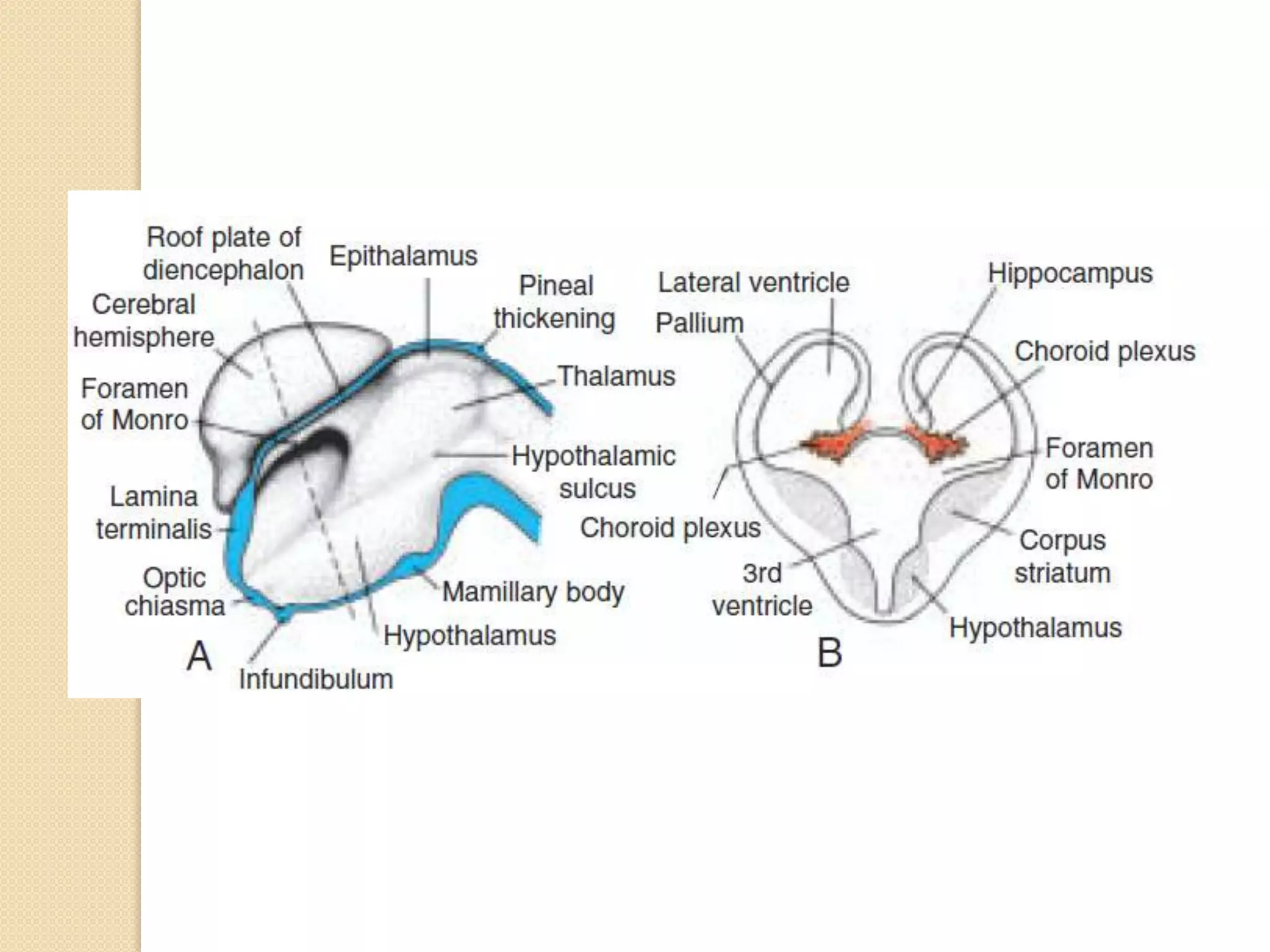
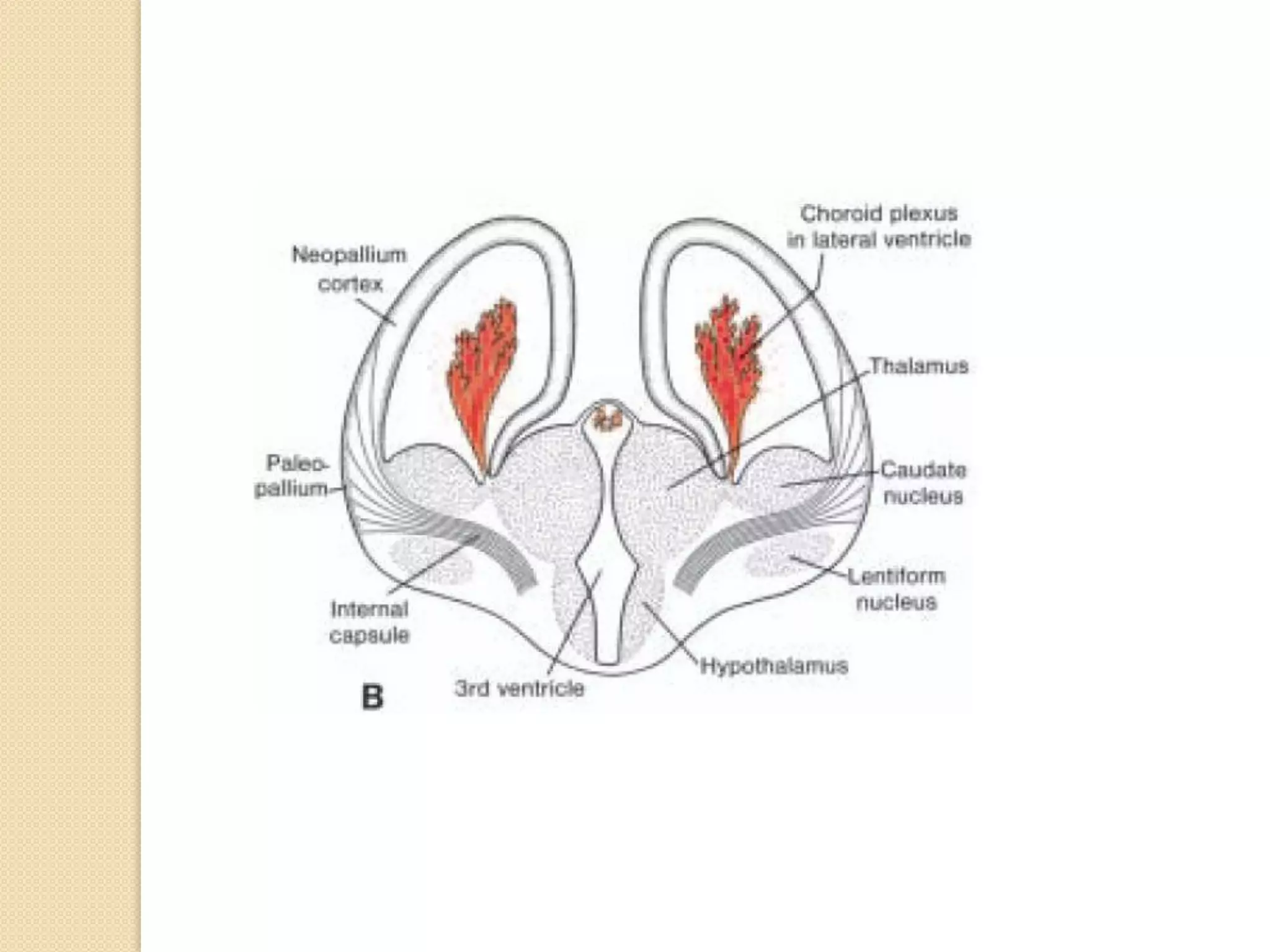
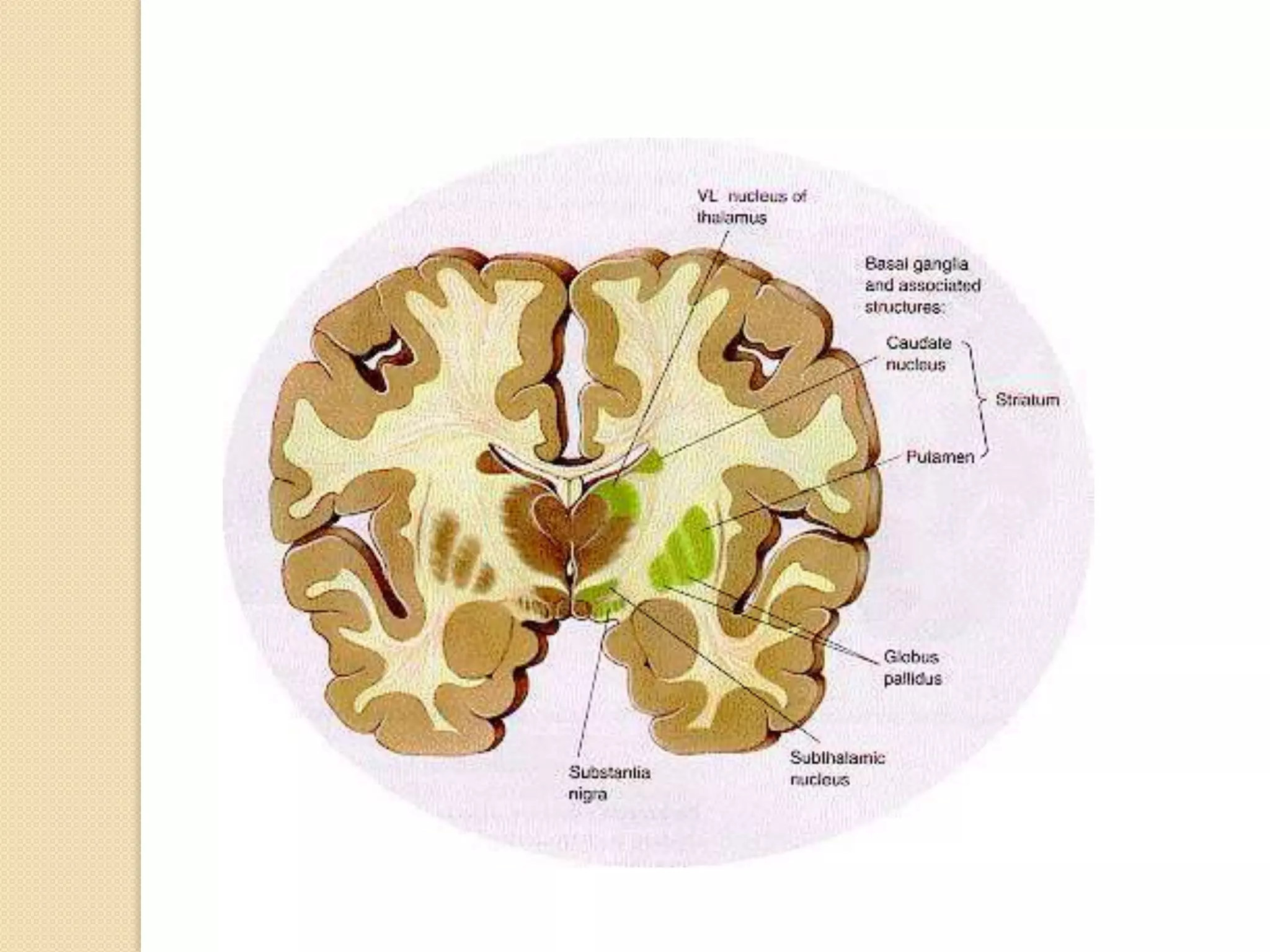
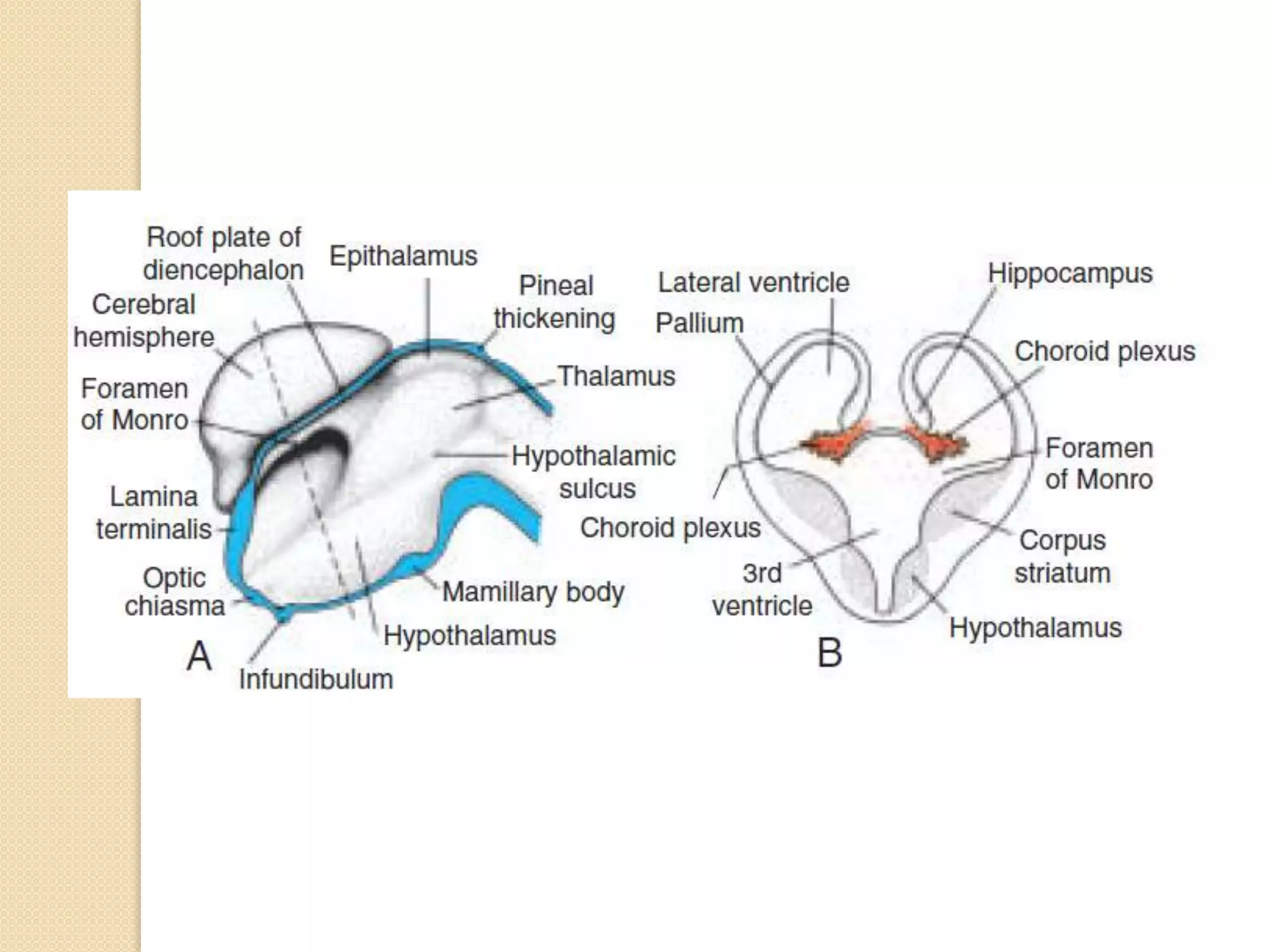
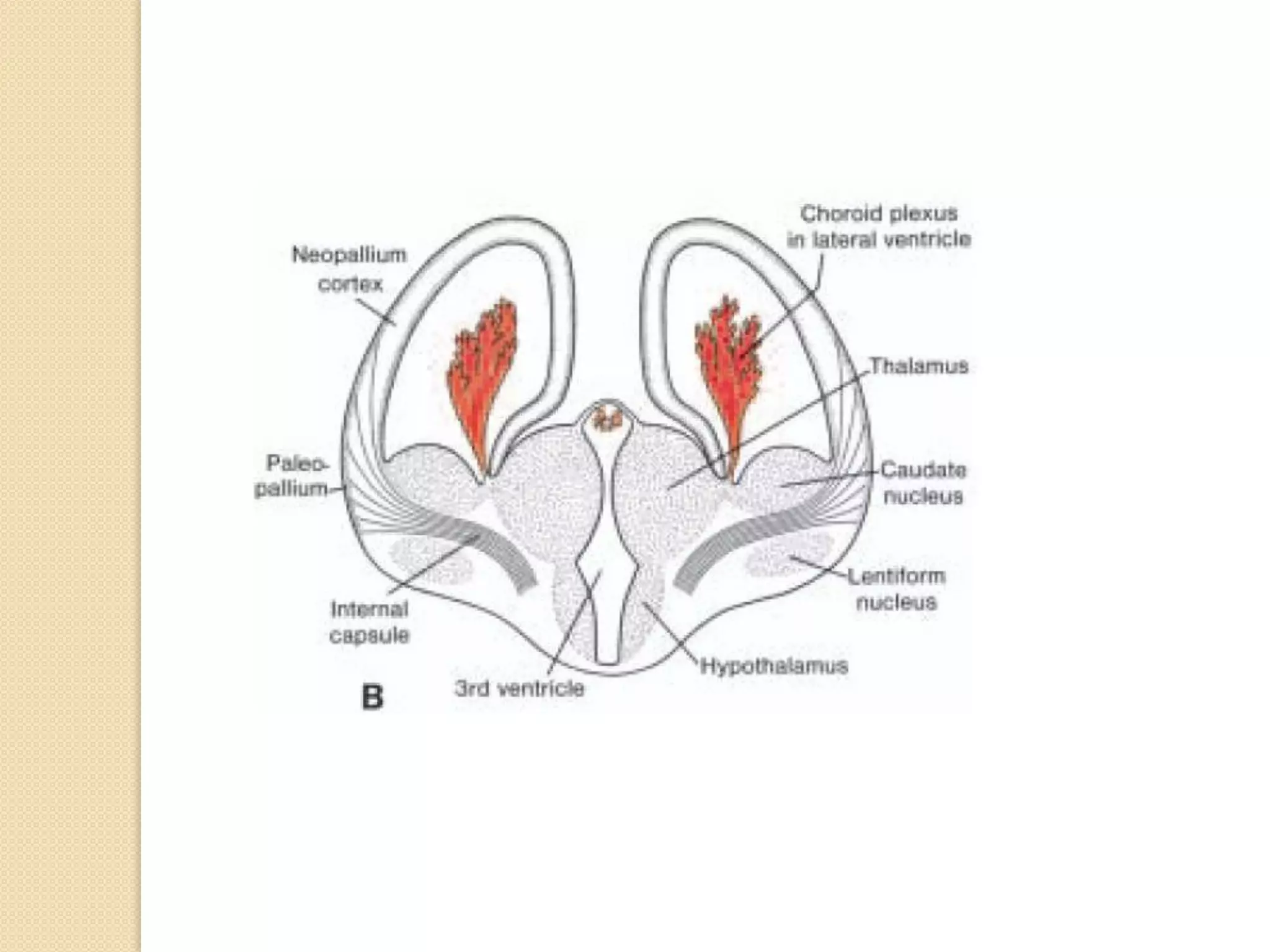
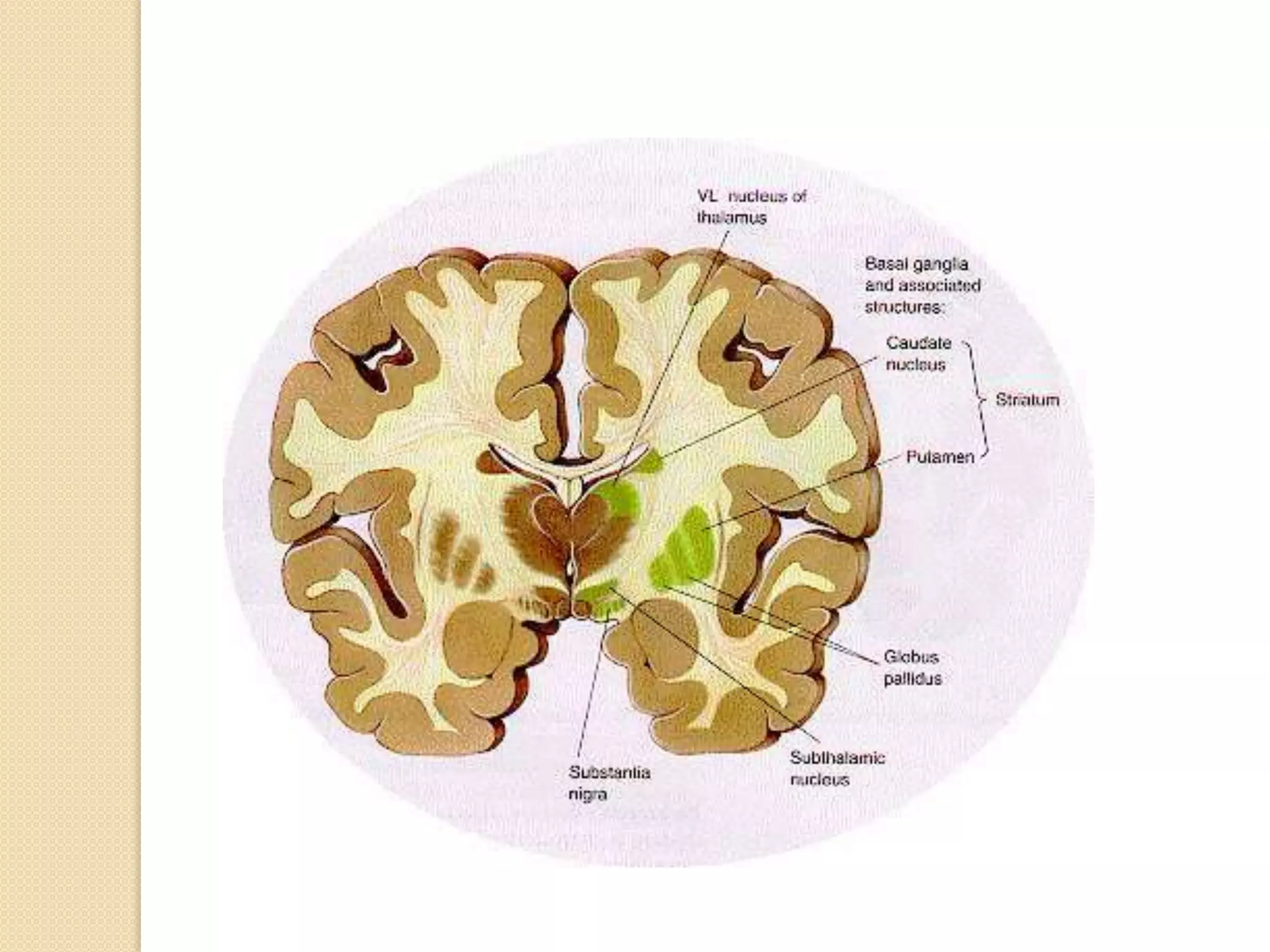
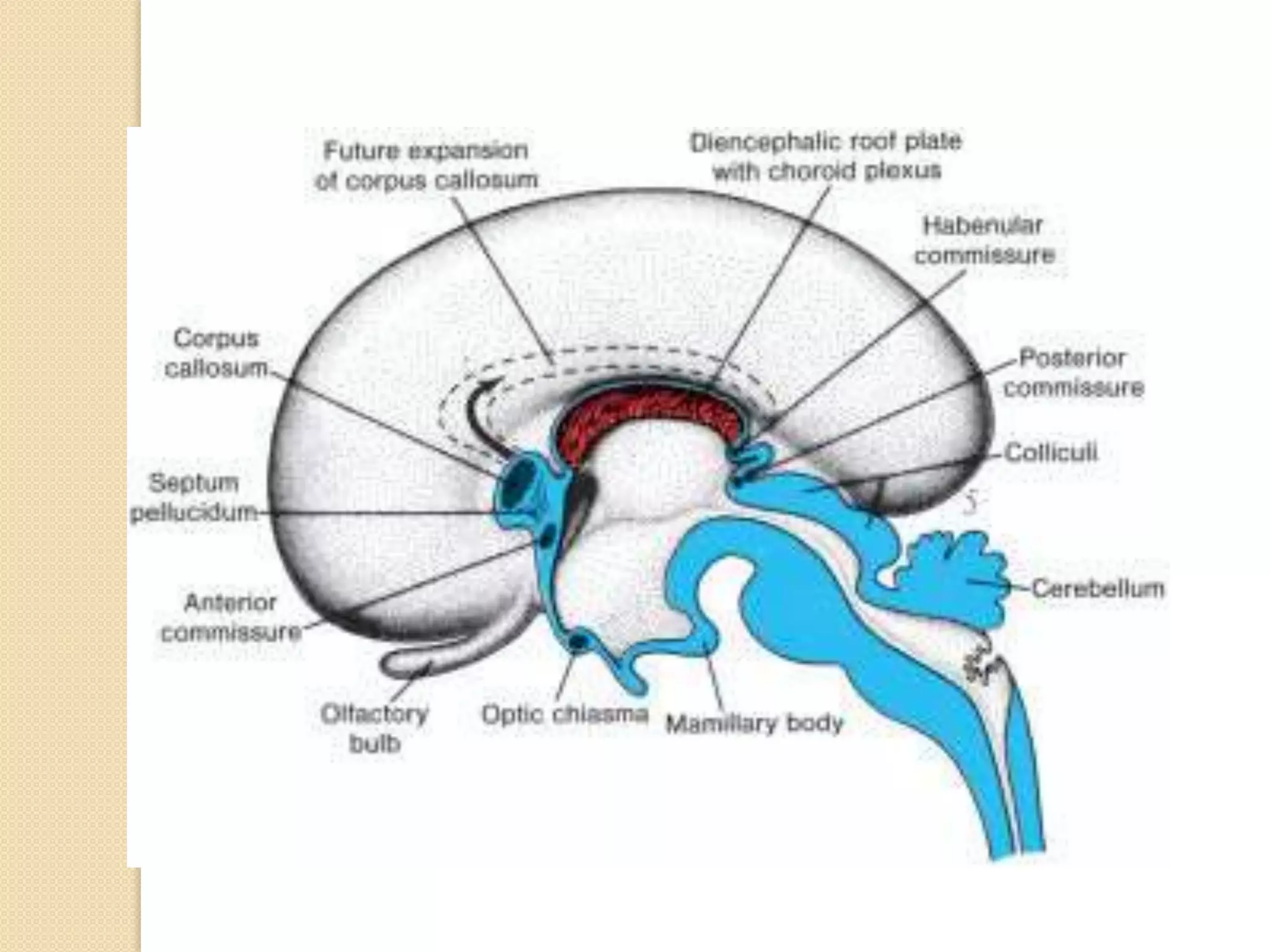
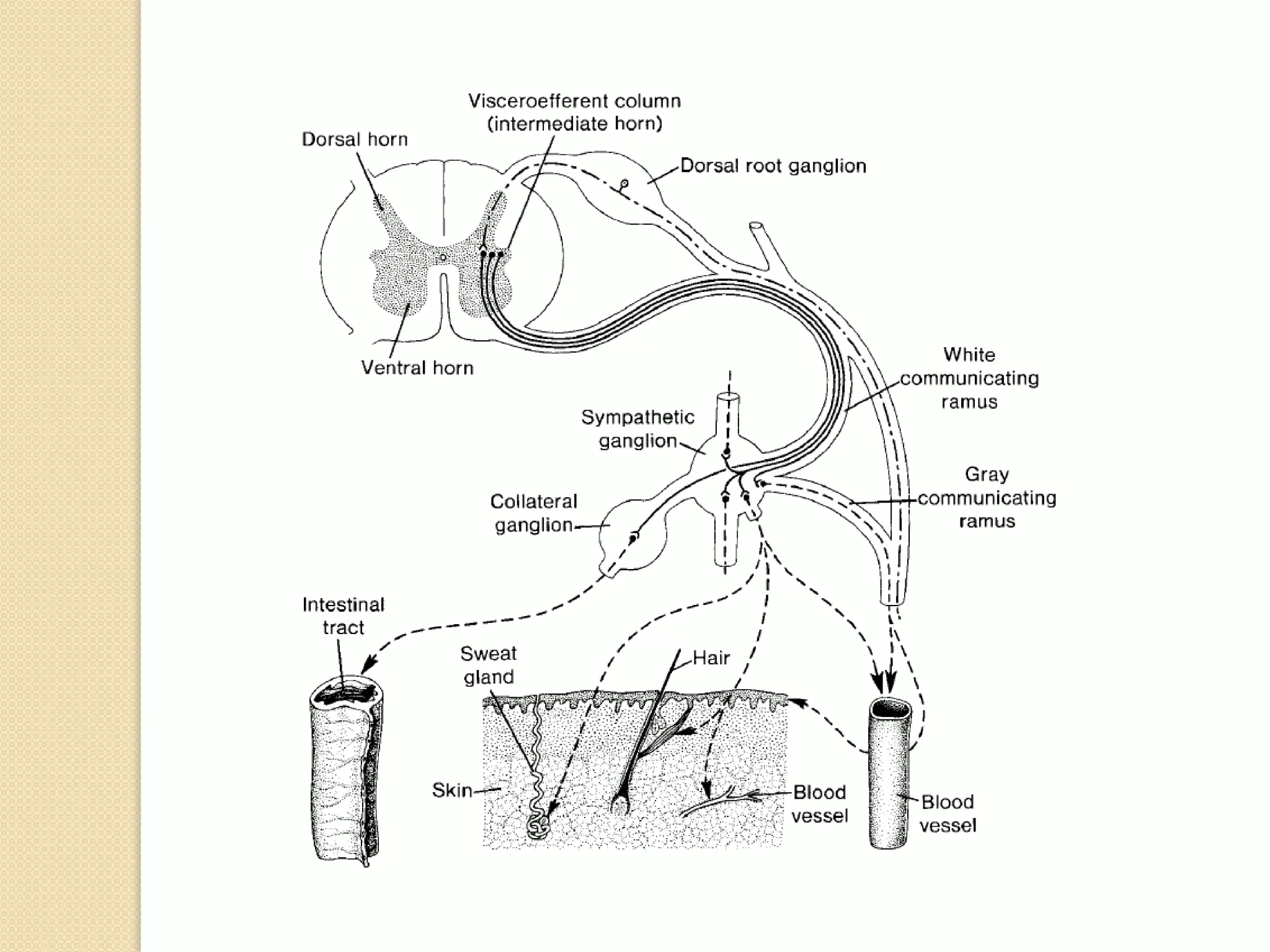
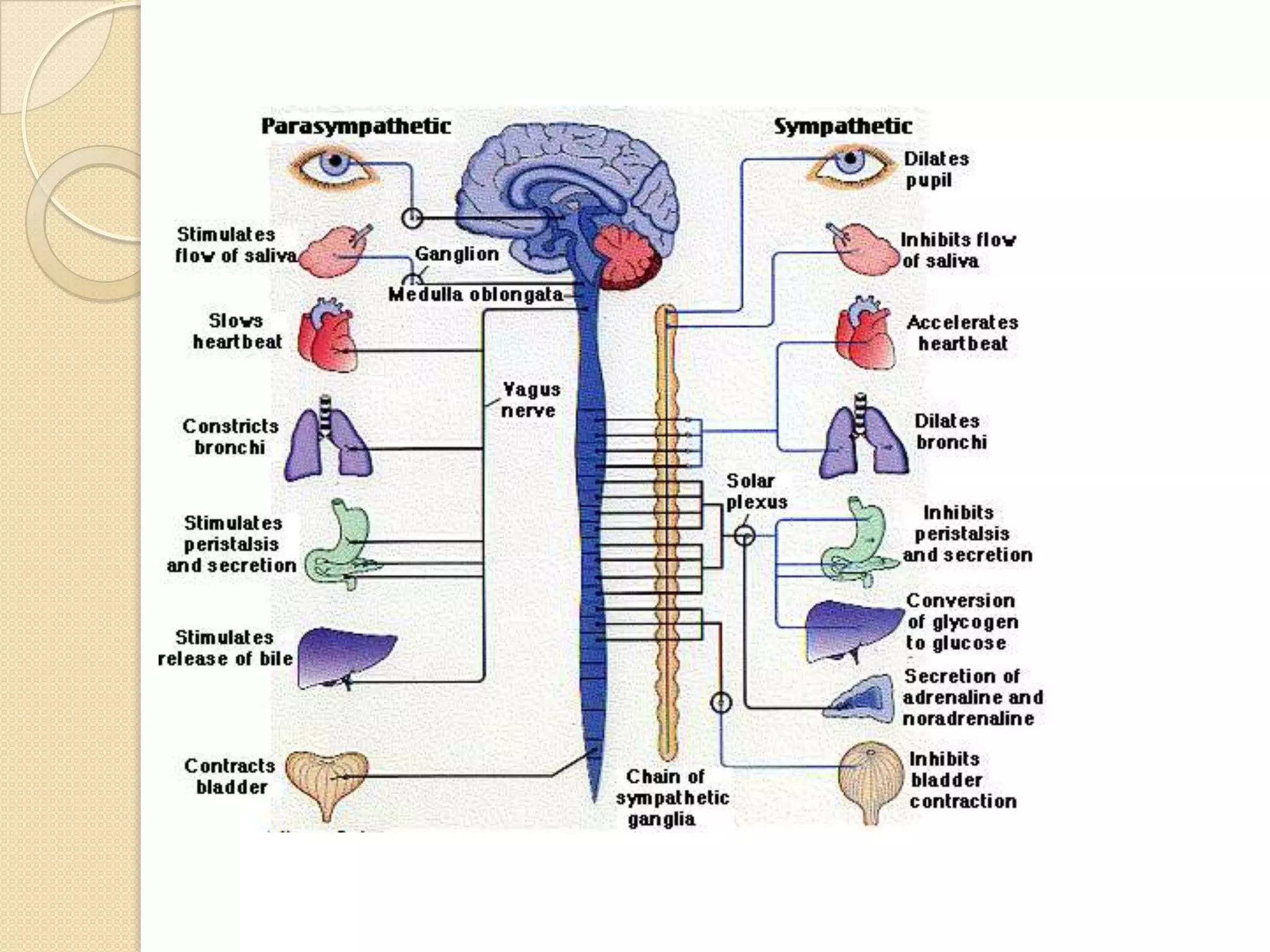
This document provides an overview of the embryology of the nervous system. It discusses how the neural tube forms and divides into various regions including the spinal cord, medulla, pons, midbrain, cerebellum and cerebral hemispheres. It describes how neurons and glial cells develop and migrate within the neural tube. It also covers the formation and development of various structures like the autonomic nervous system, corpus striatum and cerebral cortex.