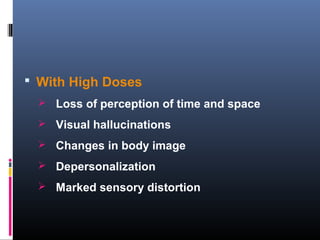
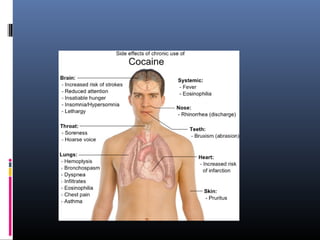
This document discusses several deliriant poisons, including Dhatura, Atropa belladonna, Hyoscyamus niger, Cannabis indica, and cocaine. It provides detailed information on the characteristics, active principles, absorption, effects, symptoms, treatment and medicolegal aspects of Dhatura and Cannabis in particular. For Dhatura, it outlines signs like dry mouth, dilated pupils, and delirium. Cannabis preparations like bhang, ganja and charas are described along with their varying potency and psychological effects from euphoria to hallucinations.