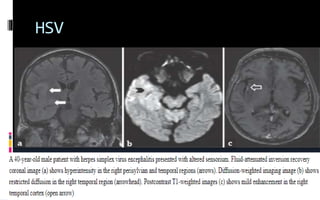
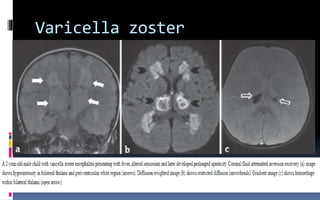
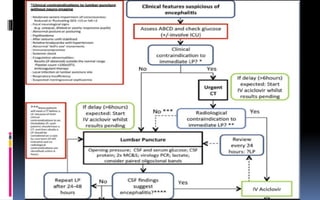
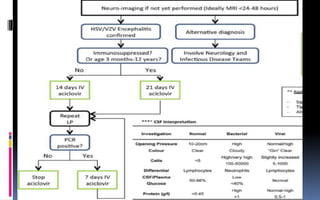
This document provides an overview of acute viral encephalitis. It defines encephalitis and meningoencephalitis, and discusses the causes, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis and management of viral encephalitis. The most common causes are viruses like herpes simplex virus, varicella zoster virus, enteroviruses, and arboviruses. Diagnosis involves CSF analysis, imaging, and PCR. Management involves supportive care, antiviral drugs like acyclovir, and controlling raised intracranial pressure. Prognosis depends on factors like age, severity of symptoms, and time to treatment initiation. Rehabilitation is often needed due to potential neurological sequelae. Early diagnosis and treatment are emphasized to