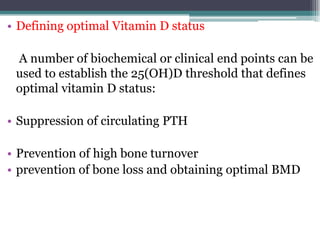
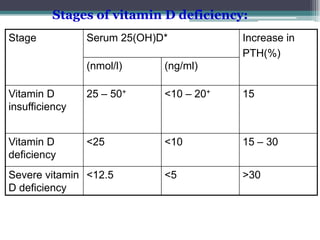
This document discusses the role of calcium and vitamin D in reducing fracture risk. It notes that osteoporotic fractures are increasing with aging and are associated with morbidity, disability, and mortality. Adequate calcium and vitamin D intake helps maximize bone mineral density and prevents falls. The document reviews clinical trials on calcium and vitamin D supplementation for fracture prevention and concludes that daily supplementation of 800 IU of vitamin D and 1000 mg of calcium can effectively reduce fracture risk, especially in institutionalized elderly individuals. Compliance with long-term supplementation is important to maintain benefits.