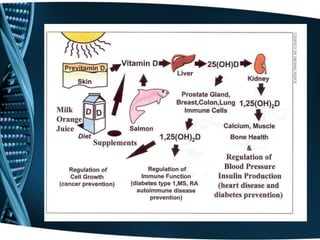
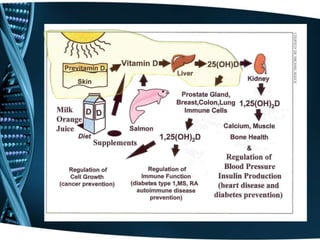
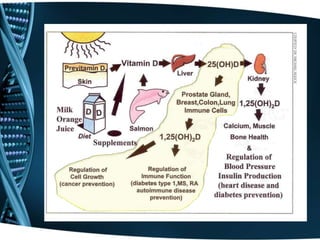
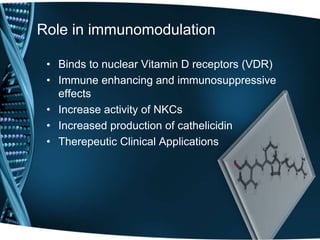
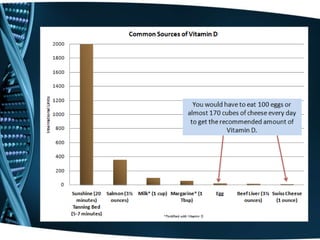
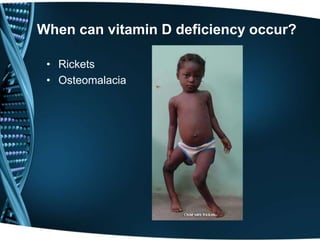
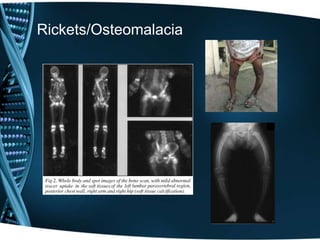
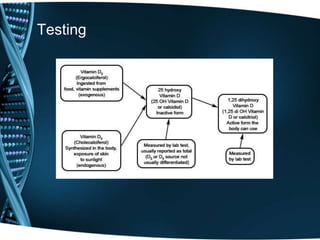
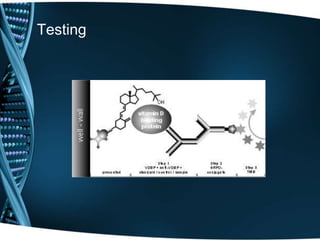
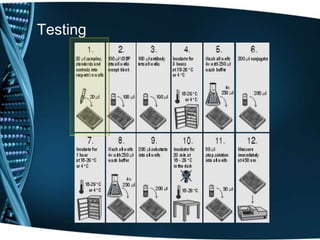
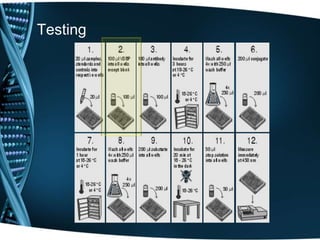
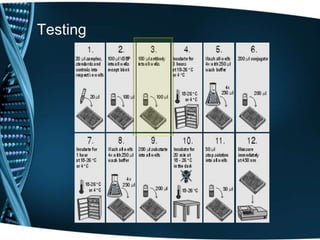
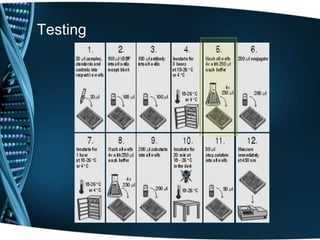
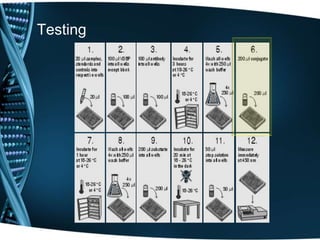
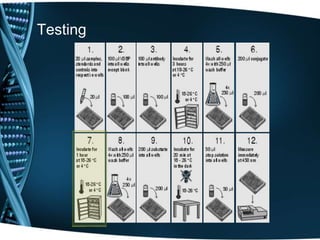
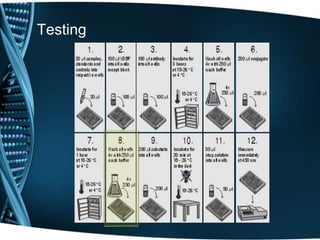
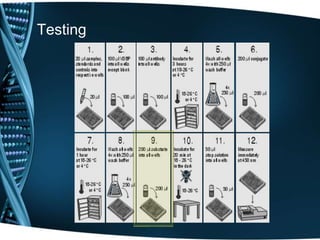
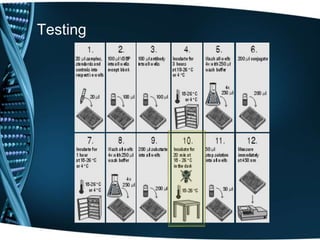
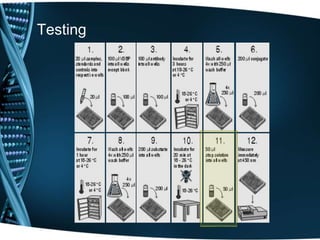
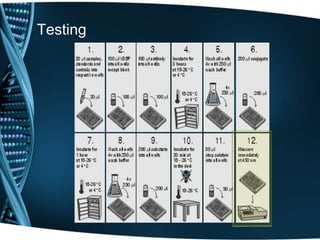
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is obtained through sunlight exposure and dietary sources like fatty fish and fortified foods. It plays an important role in bone and immune health by aiding in calcium absorption and bone mineralization. Testing for vitamin D levels has increased in recent years due to research linking vitamin D deficiency to diseases like cancer, heart disease, diabetes and depression. While vitamin D shows promise for many health benefits, more research is still needed to fully understand its therapeutic potential.