This document discusses hypovitaminosis D (vitamin D deficiency). It covers the roles, metabolism, effects, risk groups, clinical presentation, screening, treatment, and guidelines regarding vitamin D levels. Some key points include:
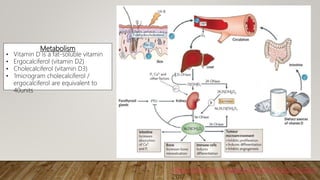
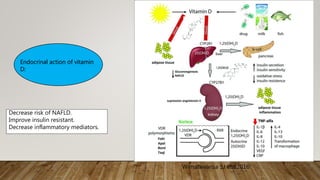
- Vitamin D has important roles in bone health and many other body systems. It is obtained mostly from sun exposure and dietary sources.
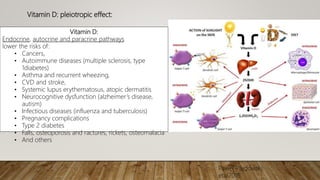
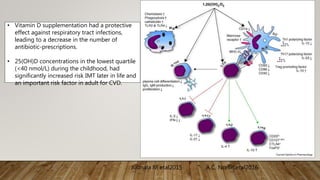
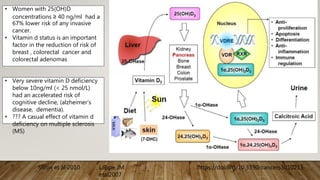
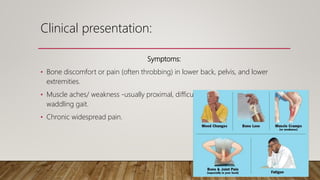
- Deficiency can cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, and is also linked to increased risk of various diseases. Risk groups include pregnant/breastfeeding women and those with limited sun exposure.
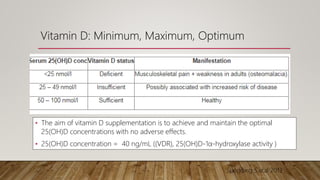
- Screening may be done in symptomatic patients or those at high risk. Treatment involves supplementation to reach/maintain sufficient vitamin D levels,











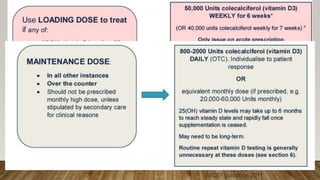
![Maintenance treatment
Should follow correction of deficiency or insufficiency combined with food and lifestyle
advice.
NHSE recommends maintenance therapy for vitamin D deficiency should NOT routinely be
prescribed in primary care 12.
•Colecalciferol tablets 800-2000 unit tablets ONCE daily individualised to patient circumstances.
• Start at lower doses within this range.
• Higher doses (within this range) may be required in Winter months compared to Summer
months.
• 25(OH) vitamin D levels may take up to 6 months to reach steady state and rapidly fall once
supplementation is ceased. Therefore maintenance therapy may need to be long-term.
• If the patient continues to be genuinely symptomatic despite 6 months of maintenance
treatment, then evaluate adherence issues.
• If no adherence issues after 6 months of treatment, then check Vitamin D levels and if still
insufficient consider increase in maintenance dose within parameters described or loading
dose followed by maintenance if appropriate.
•Advise to purchase a supplement suitable to supply 20 – 50micrograms (800 to 2000 units) daily.
•Available in supermarkets and pharmacies: ask community pharmacist for latest advice.
OR
•Calcium + vitamin D (calcium as maximum calcium carbonate 2.5g [equivalent to 1.5g calcium]) and
1000 units daily vitamin D3 when given as combined preparation) for frail, institutionalised people to
prevent falls and for those with osteoporosis/osteopenia if daily recommended intake of calcium not
met](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypovitaminosisd-211223171747/85/Hypovitaminosis-D-21-320.jpg)






