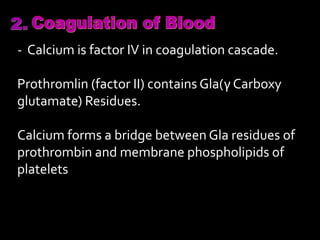
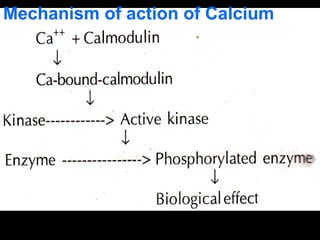
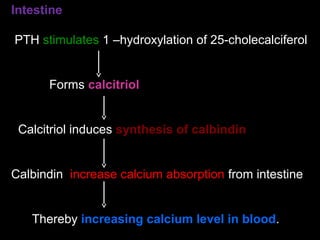
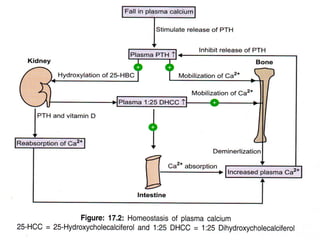
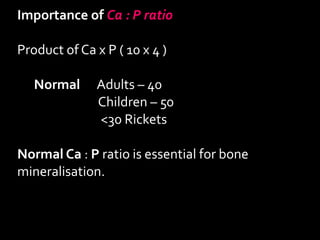
Calcium is essential for many physiological processes in the body. It makes up 1-1.5% of total body weight, with 99% located in bones and teeth. Dietary sources include dairy products, eggs, fish, and leafy greens. The recommended daily intake is 500 mg for adults and 1200 mg for children. Calcium is absorbed in the duodenum and jejunum through an active transport process requiring energy and carrier proteins. Homeostasis is maintained by calcitriol, parathyroid hormone, and calcitonin which regulate absorption from the intestine and resorption from bones. Imbalances can cause hypercalcemia with symptoms like confusion and arrhythmias, or hypocalcemia/