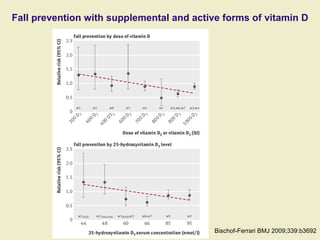
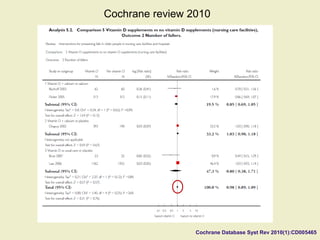
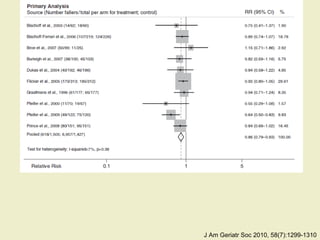
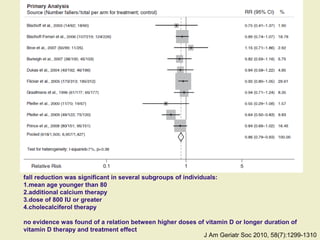
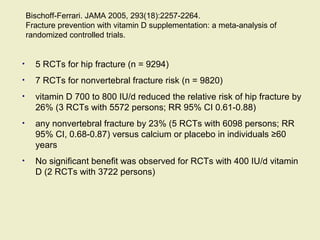
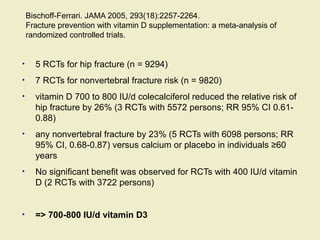
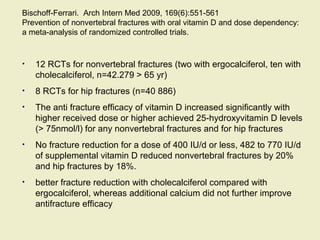
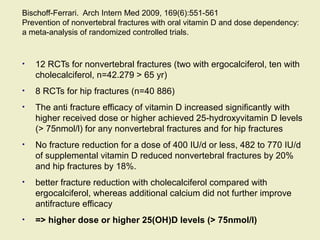
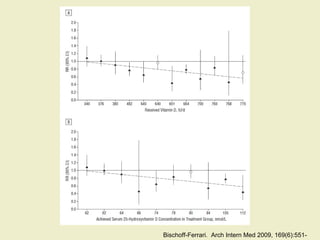
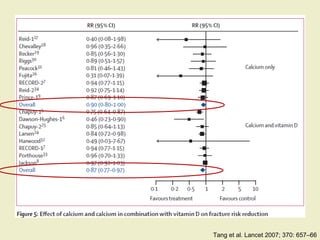
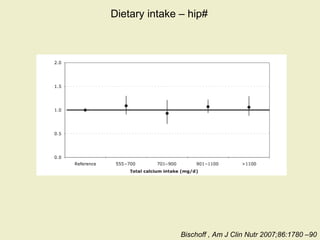
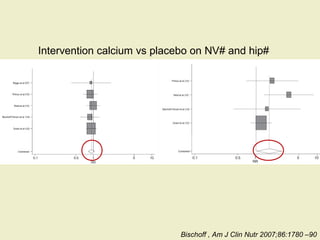
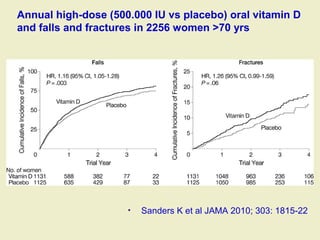
Vitamin D supplementation, especially at doses of 700-800 IU/day of cholecalciferol, has been shown to reduce the risk of hip fractures and nonvertebral fractures when combined with calcium intake of at least 500 mg/day. Several meta-analyses found the greatest benefits in individuals with vitamin D levels <50 nmol/L or calcium intake <700 mg/day. While vitamin D alone showed no significant fracture reduction, supplementation that achieved 25(OH)D levels >75 nmol/L or included additional calcium intake was more effective in preventing fractures.