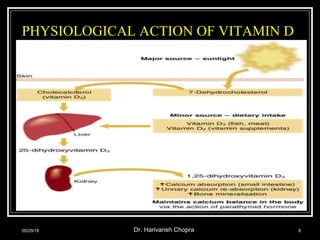
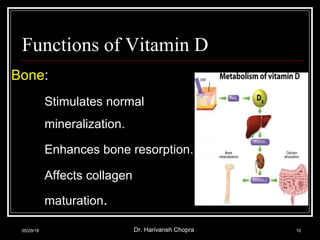
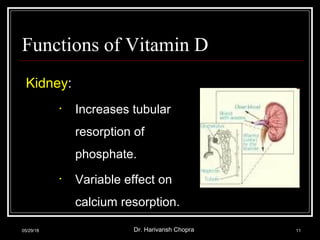
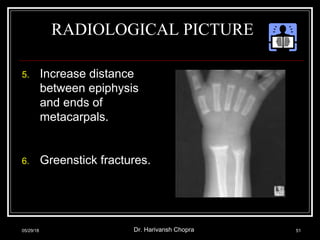
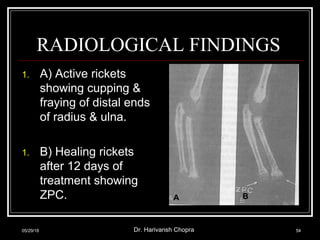
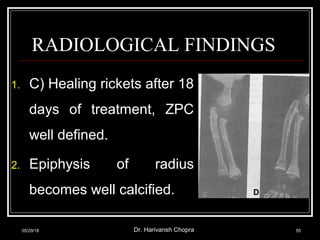
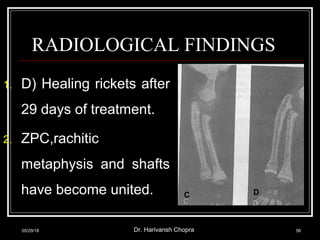
This document discusses vitamin D, including its functions, sources, daily requirements, deficiency, toxicity, and management. Some key points:
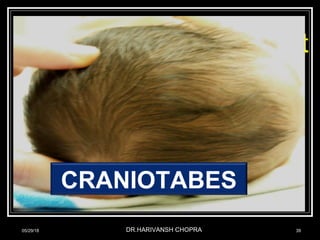
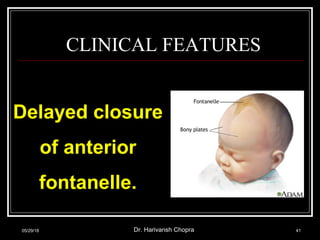
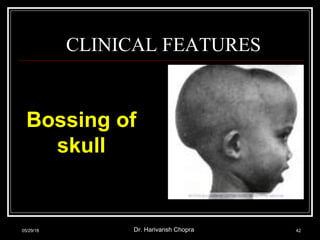
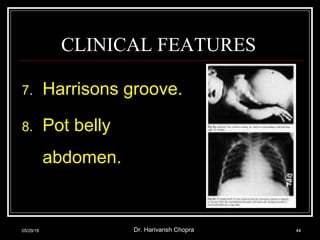
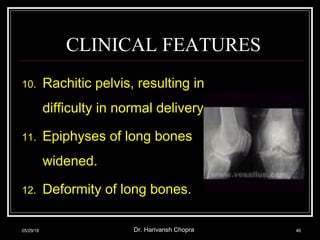
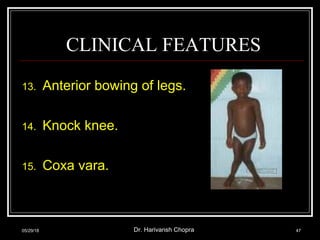
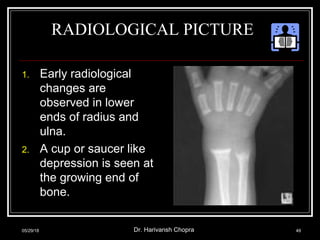
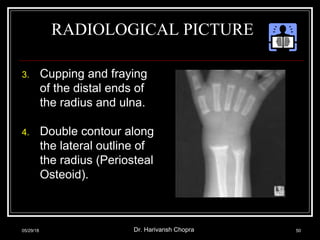
- Vitamin D promotes calcium absorption and is important for bone health. Deficiency can cause rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
- Good dietary sources include fatty fish, fish liver oils, eggs, and dairy. Sun exposure also enables vitamin D production.
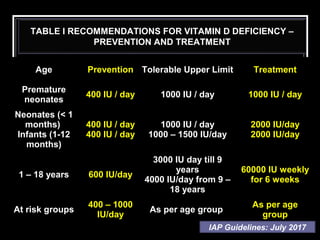
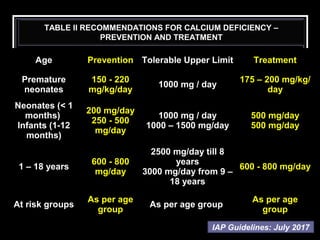
- Recommended daily intake is 10-20 micrograms for adults. Deficiency is managed with high dose vitamin D supplementation. Toxicity risks include excessive intake.