This document provides an overview of key grammar concepts in Honors Spanish 2 including:
1. A table of contents outlining topics such as verbs like gustar, preterite tense conjugations, irregular verbs, commands, and reflexive verbs.
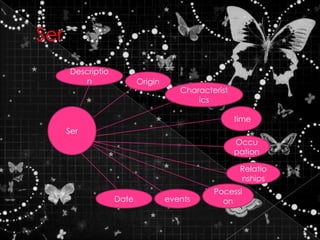
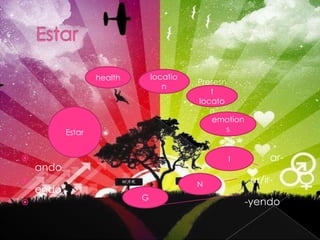
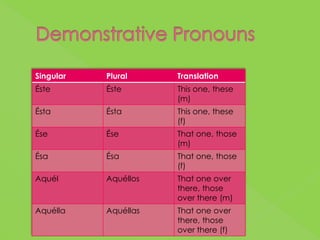
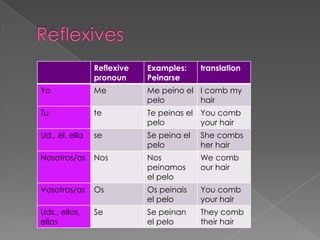
2. Descriptions and examples of concepts like estar vs ser, making commands, using the imperfect tense, DOP and IOP pronoun placement, and saber vs conocer.
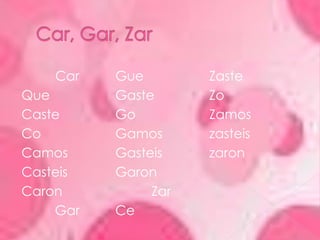
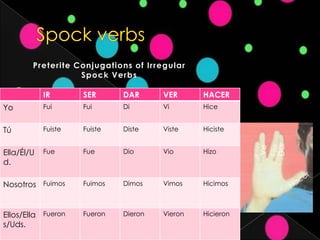
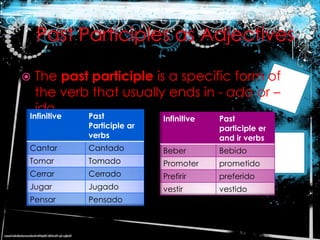
3. Lists of irregular verb conjugations in the preterite tense and cucaracha, snake, and spock verbs along with their forms.