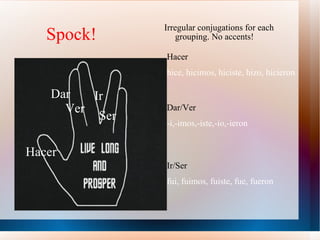
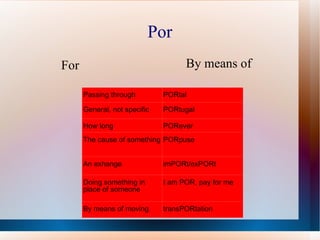
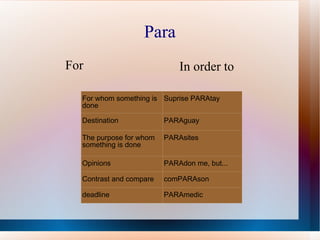
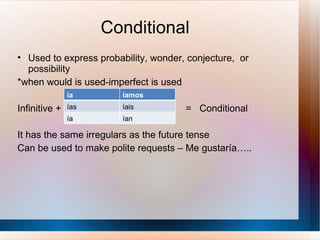
This document provides a summary of key Spanish grammatical concepts across multiple tenses and structures. It includes sections on the preterite and imperfect tenses, triggers that indicate each tense, irregular verb forms, uses of ser vs estar, commands, the subjunctive, and more. Tables of contents and subtitles introduce each new concept discussed in the document.