The document provides a summary of Spanish grammar concepts including:
1) Verbs like ser, estar, gustar and hacer along with their uses and conjugations.
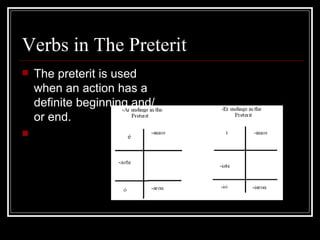
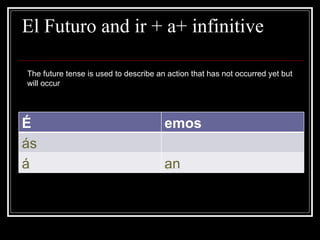
2) How to form the preterit tense and common irregular verb forms.
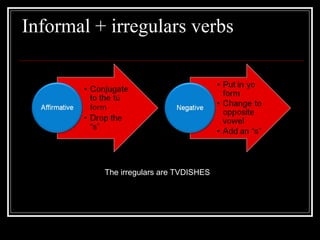
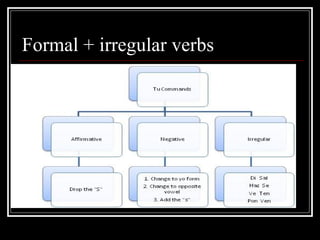
3) The uses of commands, object pronouns, modal verbs, reflexive verbs and the differences between saber and conocer.