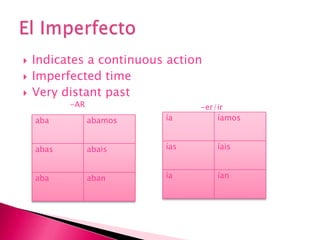
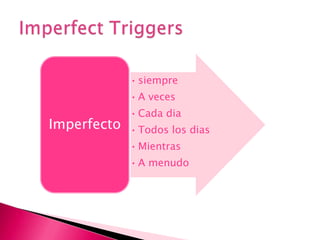
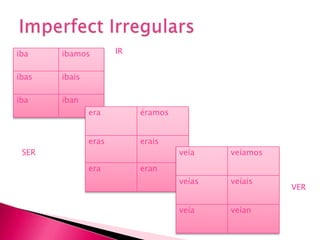
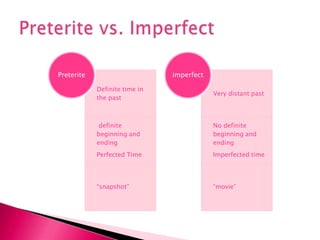
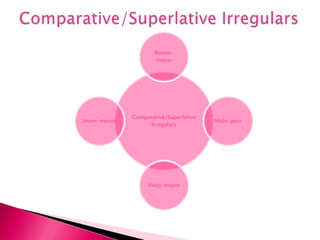
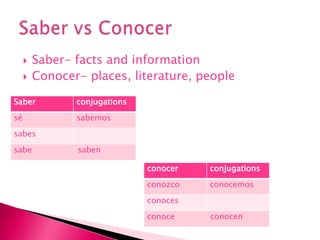
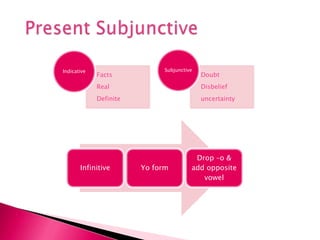
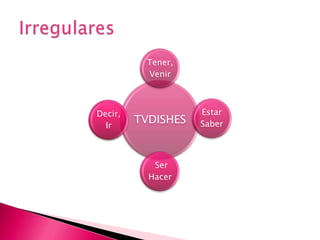
This document provides an outline of grammar topics covered in Spanish grammar books for semesters 1 and 2. It includes sections on verb tenses like the preterite, imperfect, future, and conditional. It also covers topics such as irregular verbs, comparative and superlative forms, uses of ser and estar, por vs para, impersonal se, commands, and the subjunctive mood. The outline serves as a table of contents for learners to understand what will be covered in their Spanish grammar studies over the course of two semesters.