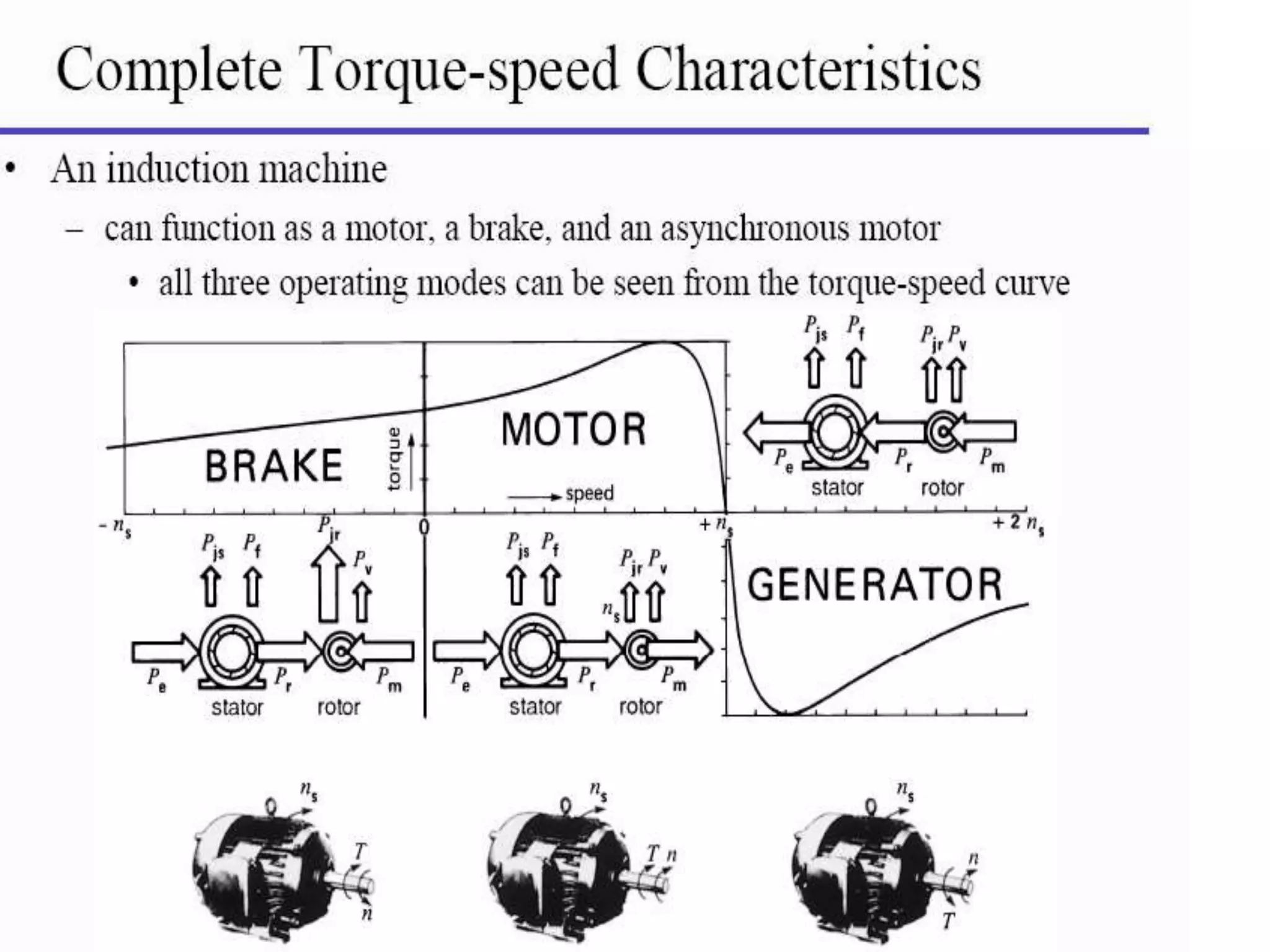
This document summarizes the principles and operation of an induction generator. It explains that an induction generator operates when the rotor spins faster than synchronous speed, inducing a current in the stator. Reactive power is required from an external capacitor bank to generate a rotating magnetic field. Induction generators are simpler and cheaper than other generators but have lower efficiency and cannot independently regulate voltage levels. Their applications include use in variable-speed wind turbines and dynamic braking systems.