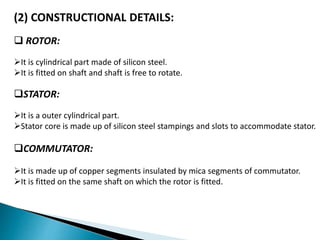
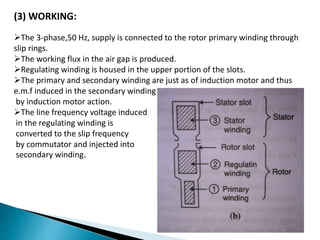
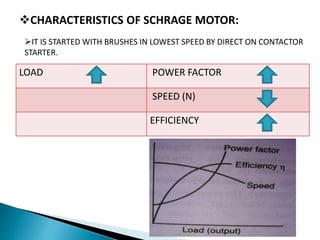
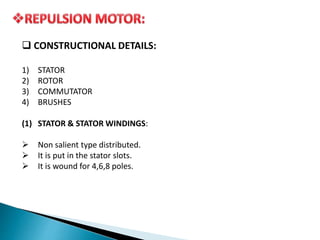
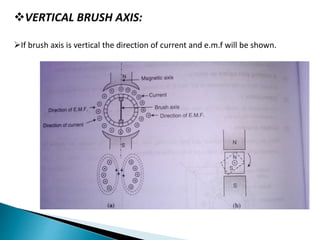
This presentation compares and contrasts two types of motors: the three phase schrage motor and the repulsion motor. The three phase schrage motor uses a commutator to produce unidirectional torque and can operate on AC or DC supply. It has a complicated structure but allows for easy speed and power factor control. The repulsion motor has a stator, rotor, commutator and brushes. It works by inducing voltage in the rotor conductors using the stator flux. Speed is varied by shifting the brushes. Both motors have applications in industrial machinery where variable speed is important.