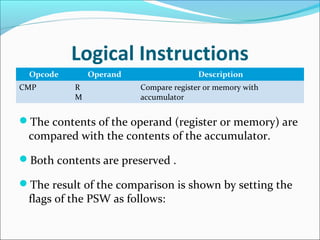
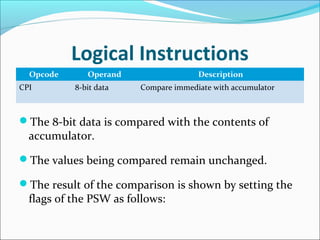
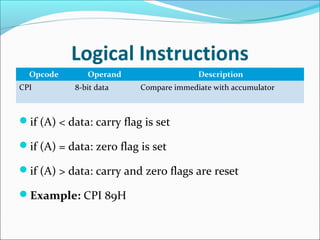
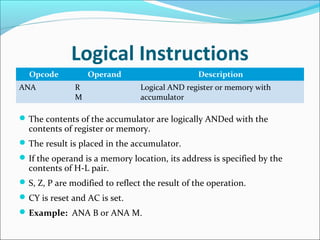
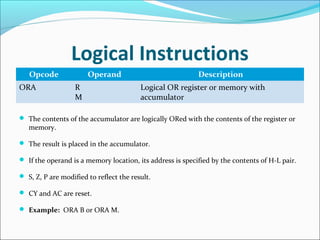
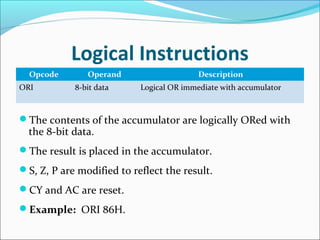
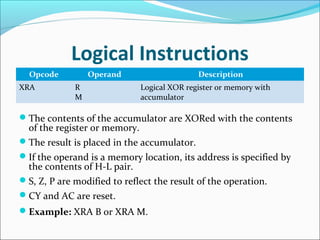
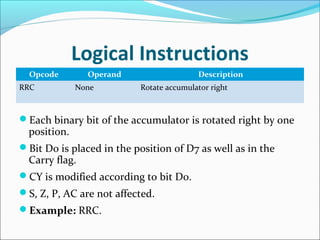
The document provides an overview of the logical instruction set of the 8085 microprocessor, which includes 246 instructions classified into various categories such as data transfer, arithmetic, branching, control, and logical instructions. It details the operations performed by logical instructions, including AND, OR, XOR, rotate, compare, and complement, emphasizing how these operations interact with the accumulator and affect status flags. The document also includes examples of each instruction type and summarizes the role of compare and rotate instructions in manipulating data stored in registers and memory.