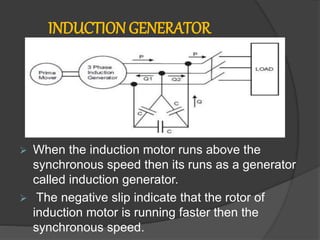
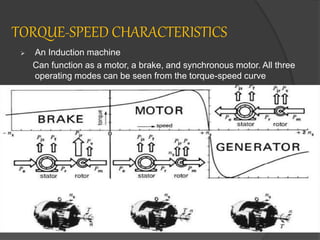
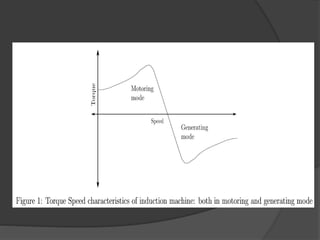
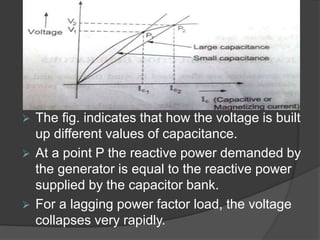
The document discusses induction generators. It explains that an induction generator operates when an induction motor runs above synchronous speed, causing the rotor to spin faster than synchronous speed with negative slip. It operates similarly to an induction motor but delivers power to a load instead of drawing power. Reactive power must be supplied by a capacitor bank to develop the rotating magnetic field since induction generators are not self-excited. Induction generators have advantages of simple and rugged construction but disadvantages of lower efficiency and inability to regulate voltage without external sources. They are well suited for variable speed applications like wind turbines.