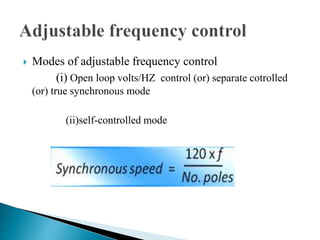
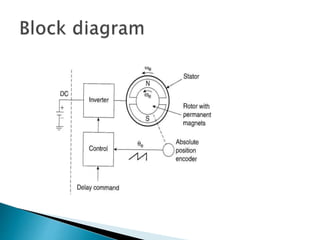
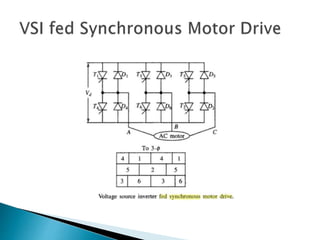
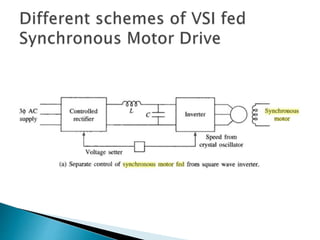
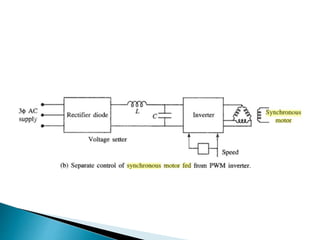
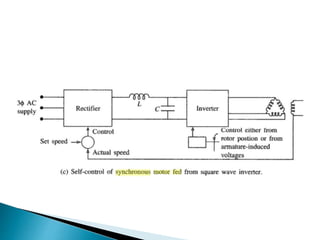
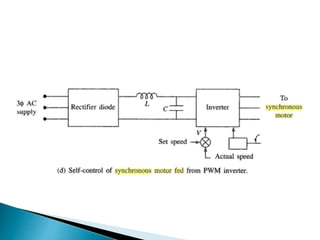
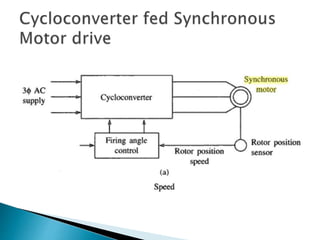
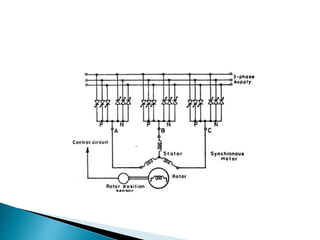
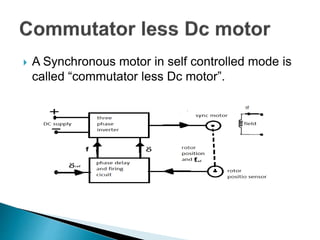
The document discusses synchronous motors used to drive textile and paper mill equipment. It describes different types of synchronous motors including wound field, permanent magnet, synchronous reluctance, and hysteresis motors. It explains that synchronous motors can operate in an adjustable frequency control mode called self-controlled mode, where the supply frequency is controlled by an inverter receiving signals from a frequency controlled oscillator. In this mode, the motor exhibits constant torque behavior up to base speed and flux weakening at higher speeds, with fast transient response similar to a DC motor but smaller rotor inertia.