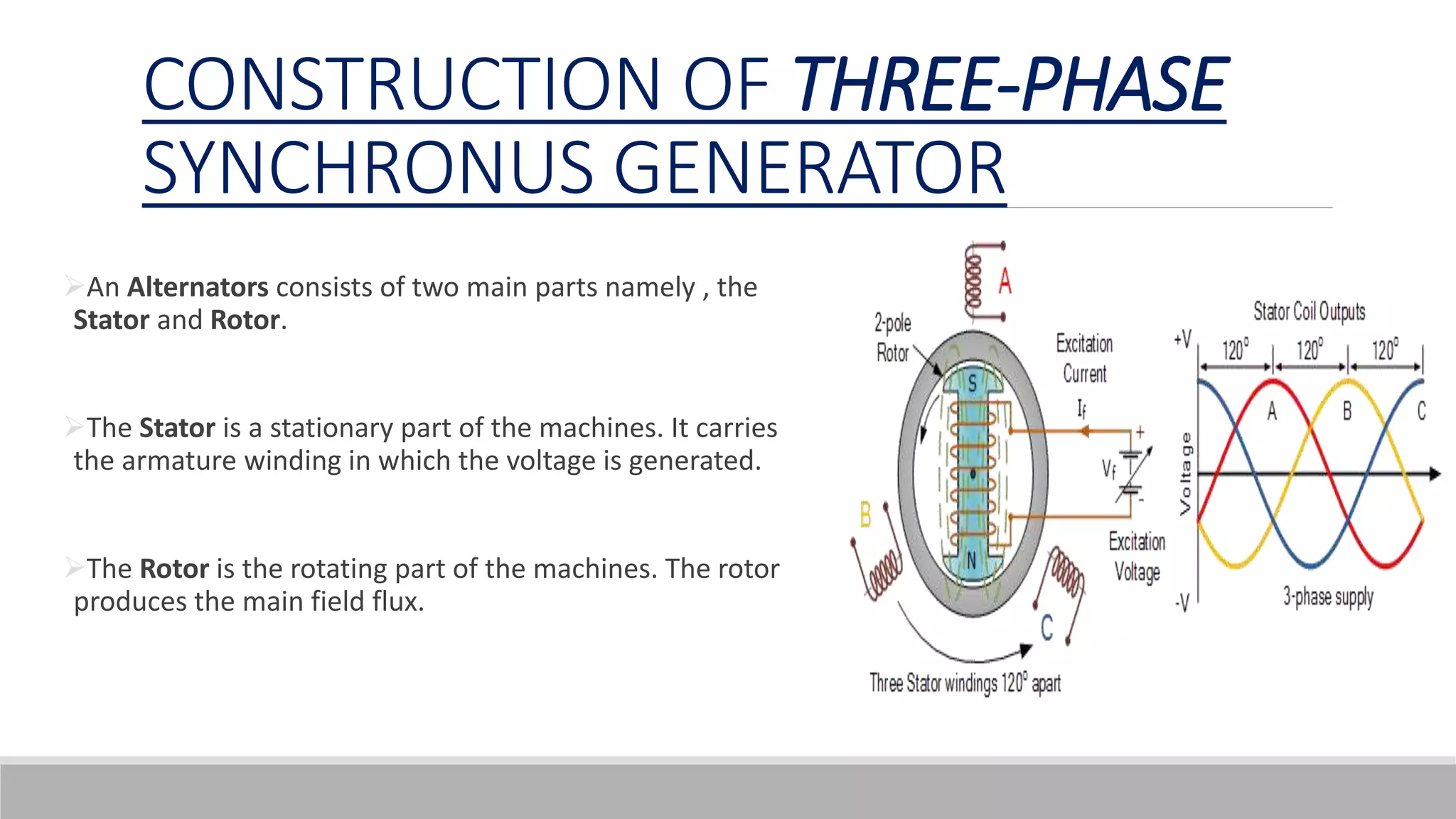
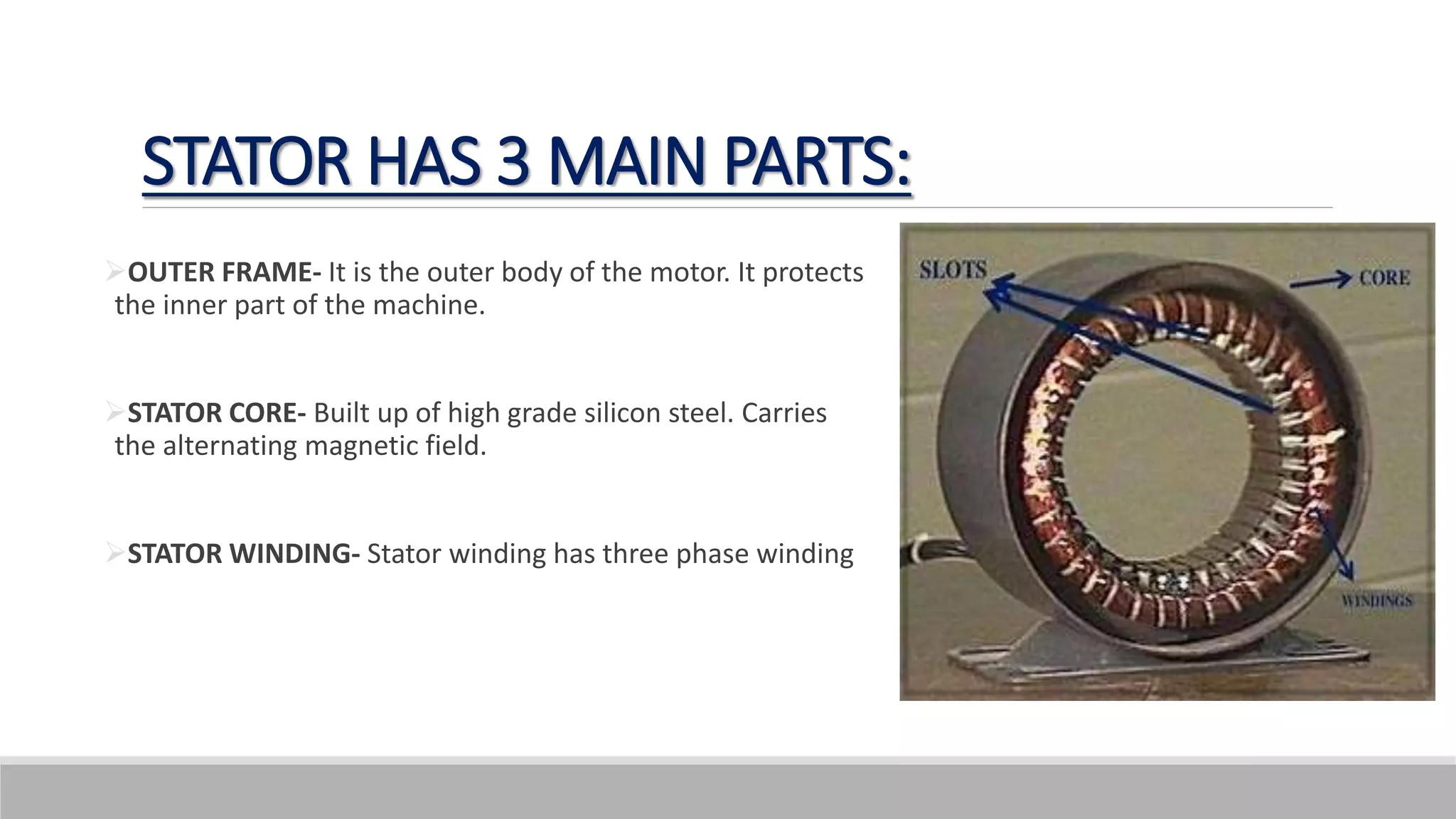
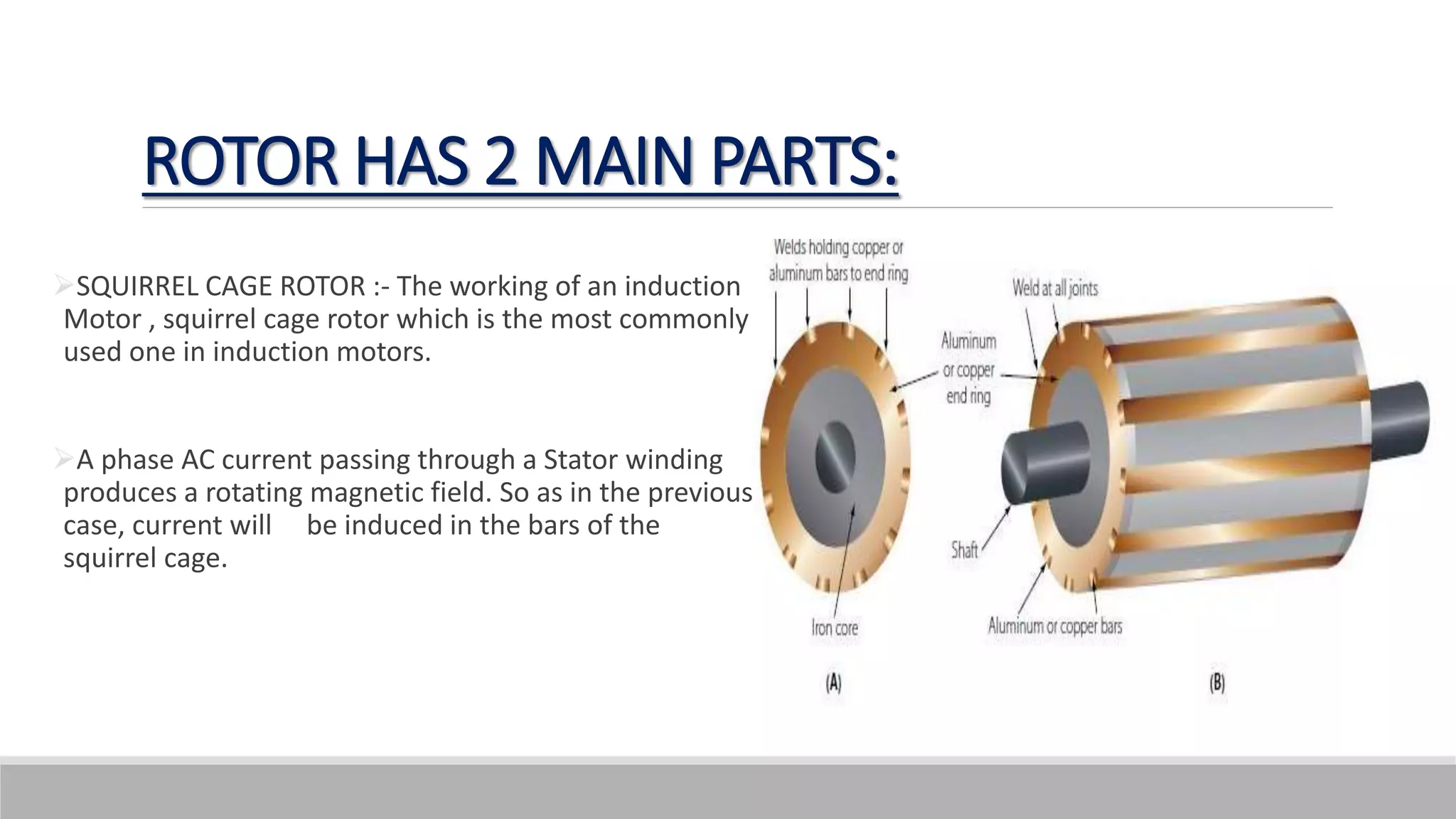
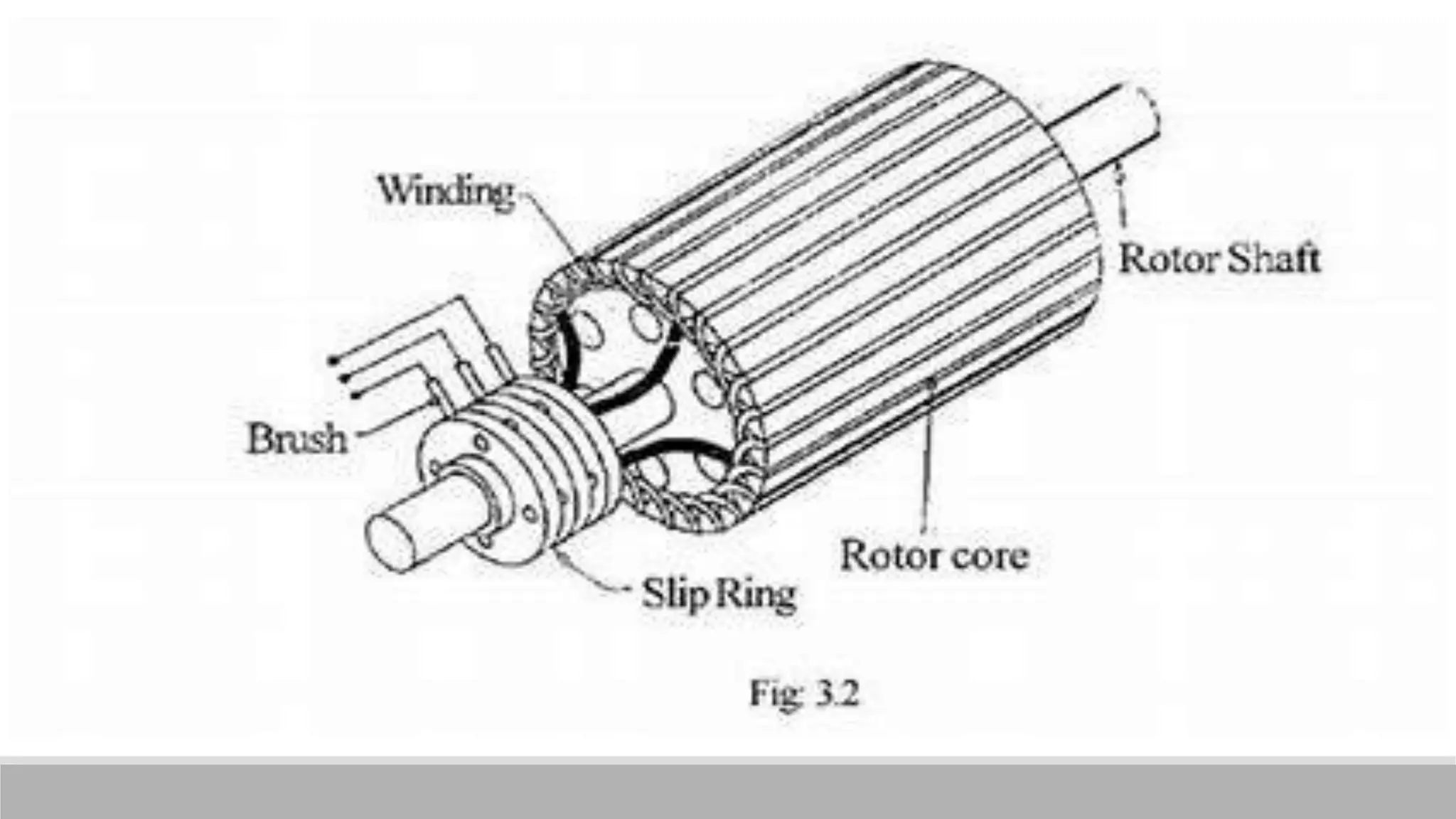
This document provides information about AC generators. It begins by defining a generator as a device that converts mechanical energy to electrical energy. It then discusses Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction, which explains how a generator works. The key components of an AC generator are described as the field, armature, and prime mover. The construction and operation of a three-phase synchronous generator is explained, including its stator, rotor, and how speed and frequency relate. Advantages of AC generators include ease of voltage transformation while disadvantages include potential hazards from heat generation.