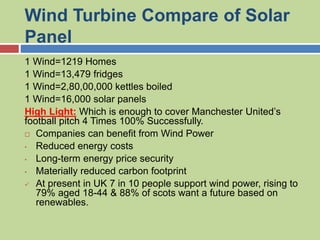
Wind turbines convert the kinetic energy of wind into mechanical or electrical energy. They consist of a tower, nacelle, rotor blades, generator, and other components. When wind blows, the rotor blades spin a shaft connecting to a generator inside the nacelle to produce electricity. Wind turbines require a minimum wind speed of 10-15 kph to function and automatically stop at 90 kph for safety. They come in both onshore and offshore varieties, with offshore turbines able to generate more electricity due to more regular winds but being more expensive to install and maintain.