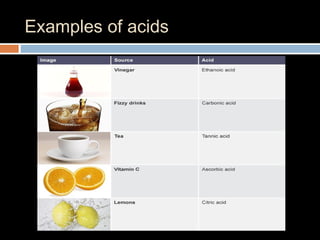
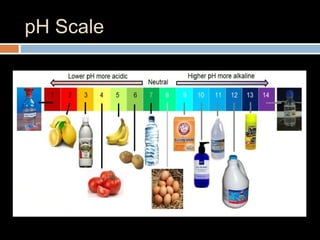
The document discusses three main categories of chemical compounds: acids, bases, and salts, detailing their properties and reactions. Acids yield hydrogen ions in water, while bases produce hydroxyl ions, with both having distinct characteristics and applications. The pH scale is introduced to measure acidity and alkalinity, with a neutral point at 7.0.






















![pH
is the negative of the logarithm of the
H3O+
ion concentration.
pH = - log [H3O+
]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidsbasesandsalts-170301091736/85/Acids-bases-and-salts-25-320.jpg)
![pOH
is the negative of the logarithm of the
OH-
ion concentration.
pOH = - log [OH-
]
pH + pOH = 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/acidsbasesandsalts-170301091736/85/Acids-bases-and-salts-26-320.jpg)
