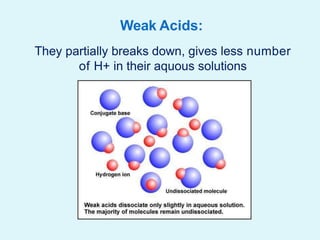
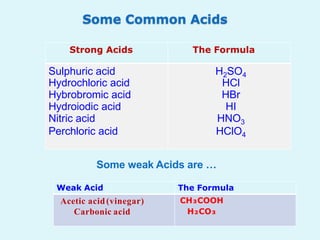
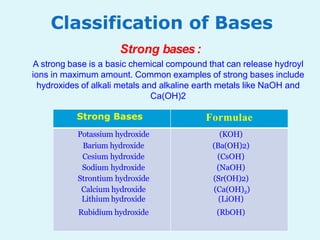
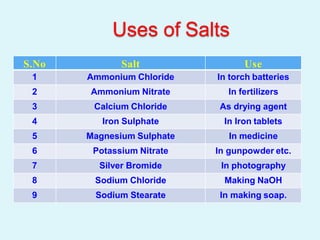
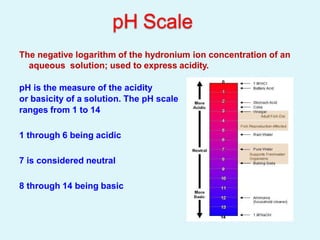
This document discusses acids, bases, and salts. It defines acids as hydrogen-containing substances that can donate protons, and bases as substances that can accept protons and produce hydroxide ions in aqueous solutions. Strong acids fully dissociate in water while weak acids only partially dissociate. Common strong acids include sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid. Common strong bases include sodium hydroxide and calcium hydroxide. Salts are formed when acid protons are replaced by metal ions. Salts have various properties and uses such as in batteries, fertilizers, and medicine. The document also explains the pH scale for measuring acidity and basicity.